Hemoglobin oxygen carrier based on double chemical modification as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of hemoglobin and chemical modification, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of ineffective expansion of blood volume and low colloid osmotic pressure, and achieve the effects of enhancing oxygen carrying/releasing activity, reducing affinity and improving tetramer stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Separation and purification of adult hemoglobin (HbA):
[0064] Centrifuge adult whole blood and discard the supernatant. Suspend with PBS buffer (pH=7.4), centrifuge and discard the supernatant. Repeat washing twice. Red blood cells were lysed with 3 volumes of water. Centrifuge the erythrocyte lysate, take the supernatant, and filter it with a 0.22 μm filter membrane. The filtrate was separated and purified by Q Sepharose Fast Flow anion exchange chromatography medium, and the elution peak corresponding to adult hemoglobin (HbA) was collected, concentrated, dialyzed into PBS buffer (pH=7.4), and stored at -80°C for future use.
Embodiment 2
[0066] Preparation of glyoxylated hemoglobin:
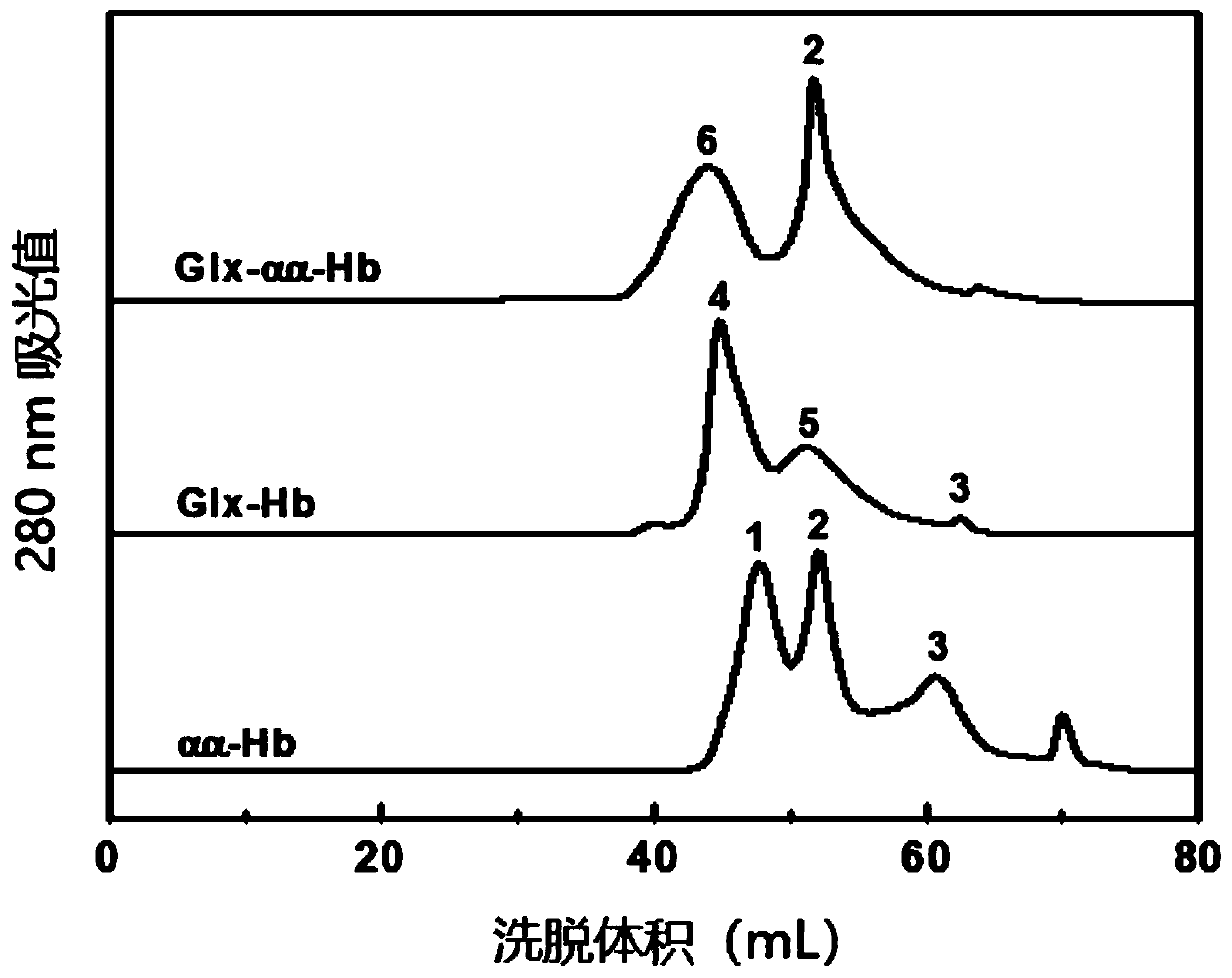
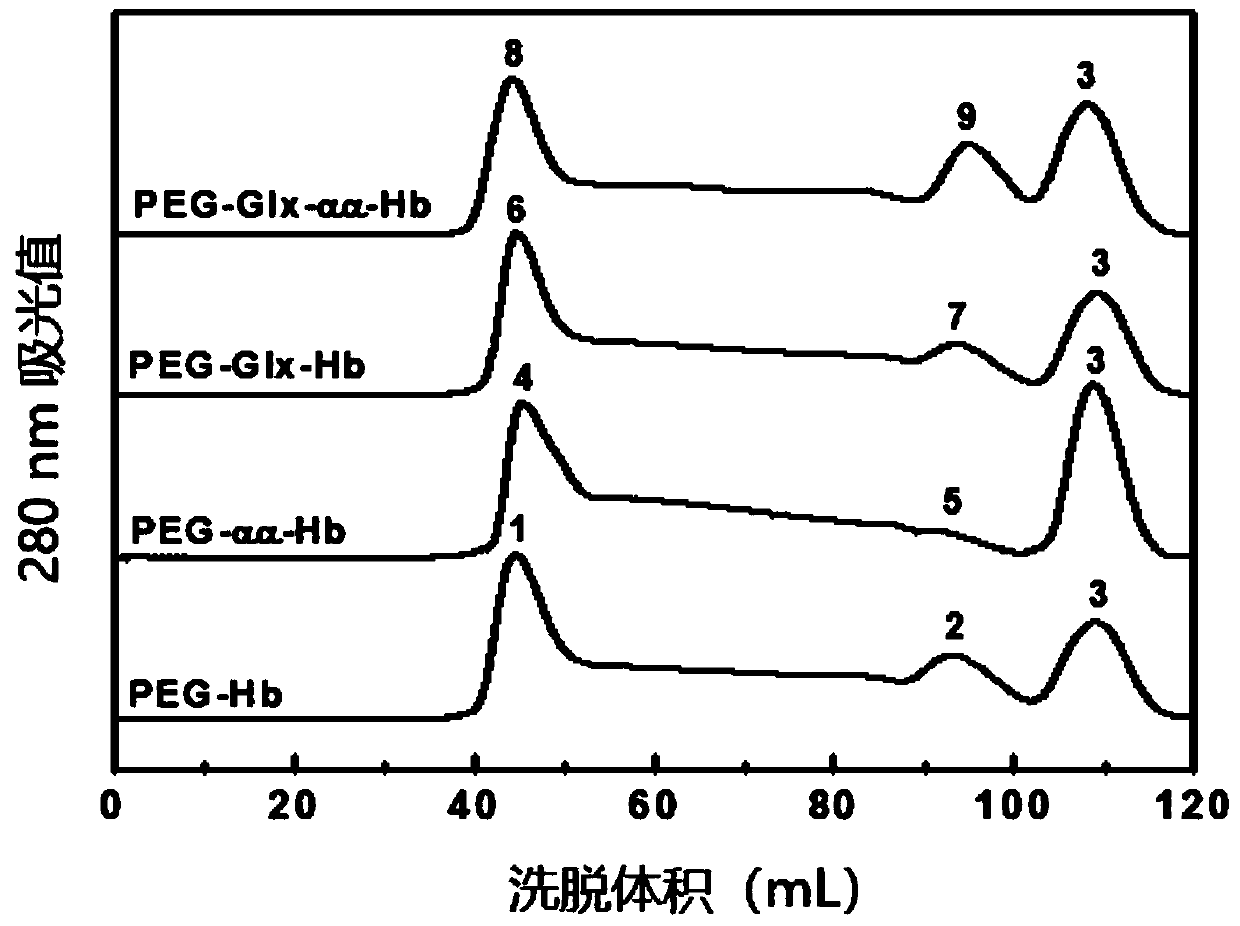
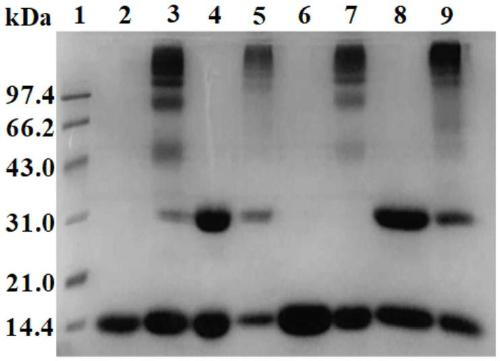
[0067] Glyoxylic acid covalently modifies the N-terminal Val-1(α) of HbA, thereby introducing a carboxymethyl group, which will destroy the salt bridge that participates in the formation of the stable R-state structure and reduce the stability of the relaxed state (R-state) of HbA , so that the HbA quaternary structure shifts from the R state to the tense state (T state), reducing the affinity of HbA for oxygen.
[0068] Deoxygenated HbA was prepared by continuously bubbling nitrogen gas into the 0.5 mM HbA solution. Then 1.0 mM glyoxylic acid and 10 mM sodium cyanoborohydride (NaCNBH 3 ) solution, so that the mol ratio of HbA, glyoxylic acid and sodium cyanoborohydride is 1:2:20. Continuing to feed nitrogen, the reaction was carried out at 4° C. for 3.5 h under anaerobic conditions to obtain glyoxylic acid-modified HbA (expressed as Glx-Hb). Finally, 20 mM glycine solution was added to terminate the reaction, and unreacted gl...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Preparation of DBBF intramolecularly cross-linked hemoglobin:
[0071] When bis(3,5-dibromosalicylic acid) fumarate (DBBF) modified deoxy HbA, an intramolecular cross-linking reaction occurred between two Lys-99(α).
[0072] Deoxygenated HbA was prepared by continuously bubbling nitrogen gas into the 0.5 mM HbA solution. Subsequently, an equal volume of 4 mM inositol hexaphosphate (IHP) solution was added, nitrogen gas was continuously introduced, and the reaction was carried out at 25° C. for 3 h under anaerobic conditions. Subsequently, 0.5 mM DBBF solution was added so that the molar ratio of HbA to DBBF was 1:1, and reacted at 25° C. for 4 h to obtain intramolecularly cross-linked HbA (expressed as αα-Hb) of DBBF. Finally, 20 mM glycine solution was added to terminate the cross-linking reaction, and unreacted DBBF and glycine were removed by dialysis. The schematic diagram of its preparation is as Figure 13 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Protein concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com