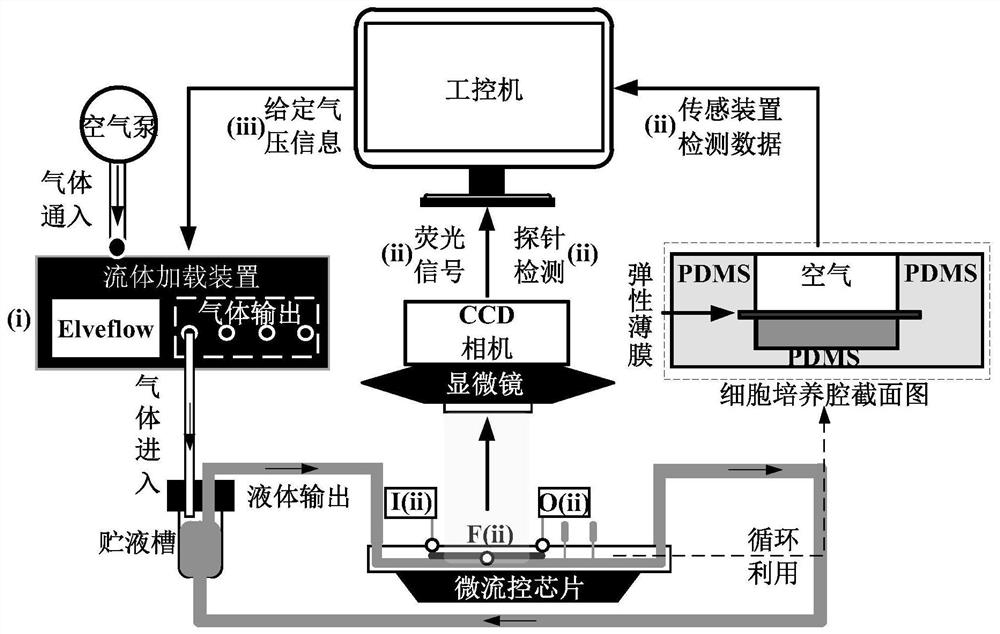
A microfluidic chip-scale extracorporeal circulation system for mechanobiology research of vascular endothelial cells
A microfluidic chip and circulatory system technology, applied in biological testing, laboratory containers, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of failure to realize closed-loop control of pressure or flow signal, and failure to realize endothelial cell mechanobiology Quantitative monitoring and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
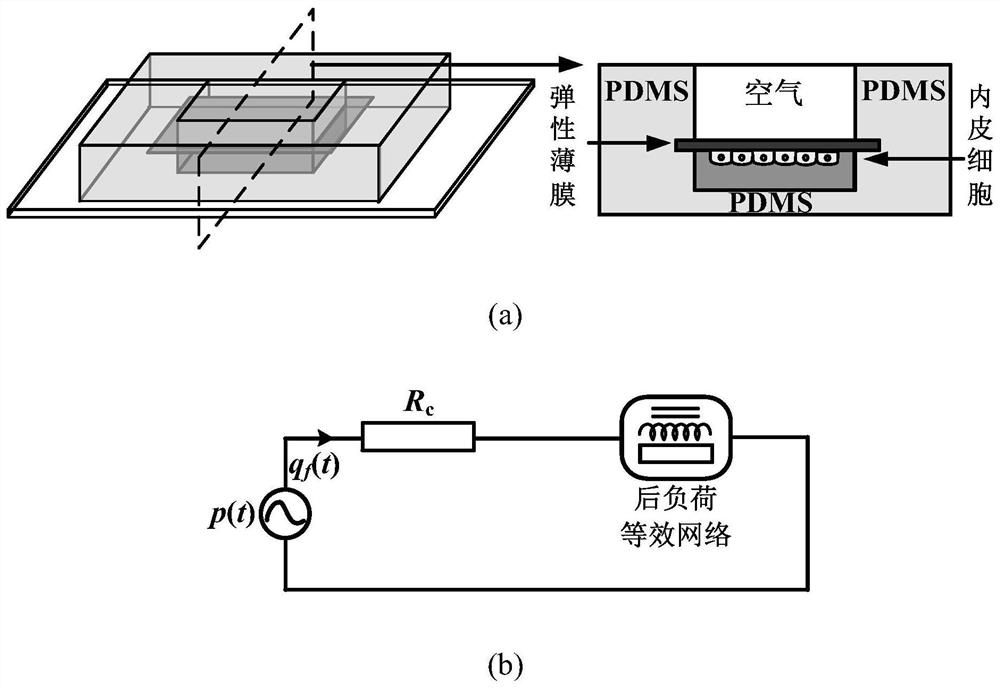
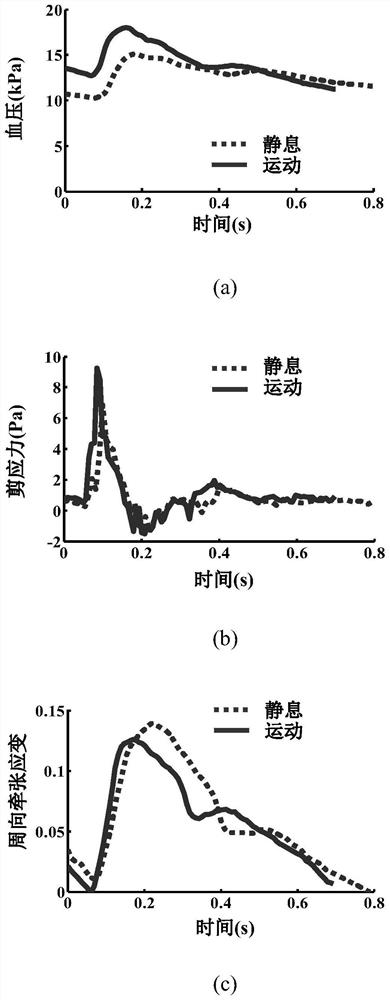
[0050] (1) Design the cell culture chamber height H c , width W c and length L c They are 0.5mm, 10mm and 15mm respectively, and the viscosity η of the cell culture medium is usually 0.001Pa·s. The blood pressure of common carotid artery before and after exercise intervention p(t)( image 3 (a)) and the wall shear stress τ w (t) Waveform ( image 3Substituting (b)) in formula (2a) to calculate the input flow waveform q(t) of the "sandwich" cell culture chamber, substituting into formula (2b), we can know that max(Δp(t) / p(t))=0.04n )(like Figure 4 shown by the solid line);
[0051] (2) For the common carotid artery system, it can be constructed as Figure 5 In the five-component lumped parameter model shown in (a), the cell culture chamber R c The afterload input impedance of Expressed as:
[0052]
[0053] where R c , R f1 , R f2 Simulate the flow resistance of the target artery segment and the total flow resistance of the vascular bed downstream of the target...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com