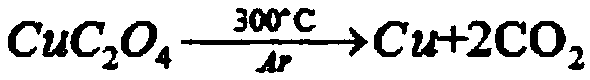Method for leaching copper from acid pickling copper slag for zinc hydrometallurgy
A hydrometallurgical zinc smelting and pickling technology, applied in the field of copper leaching, can solve the problems of high cost, difficulty in leaching copper, long process flow, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, small usage, and realizing recycling.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] The pickling copper slag in this embodiment is the copper cadmium slag produced in the purification process of the hydro-zinc smelting leaching solution after pickling to remove zinc and cadmium, and the copper content is 20%.
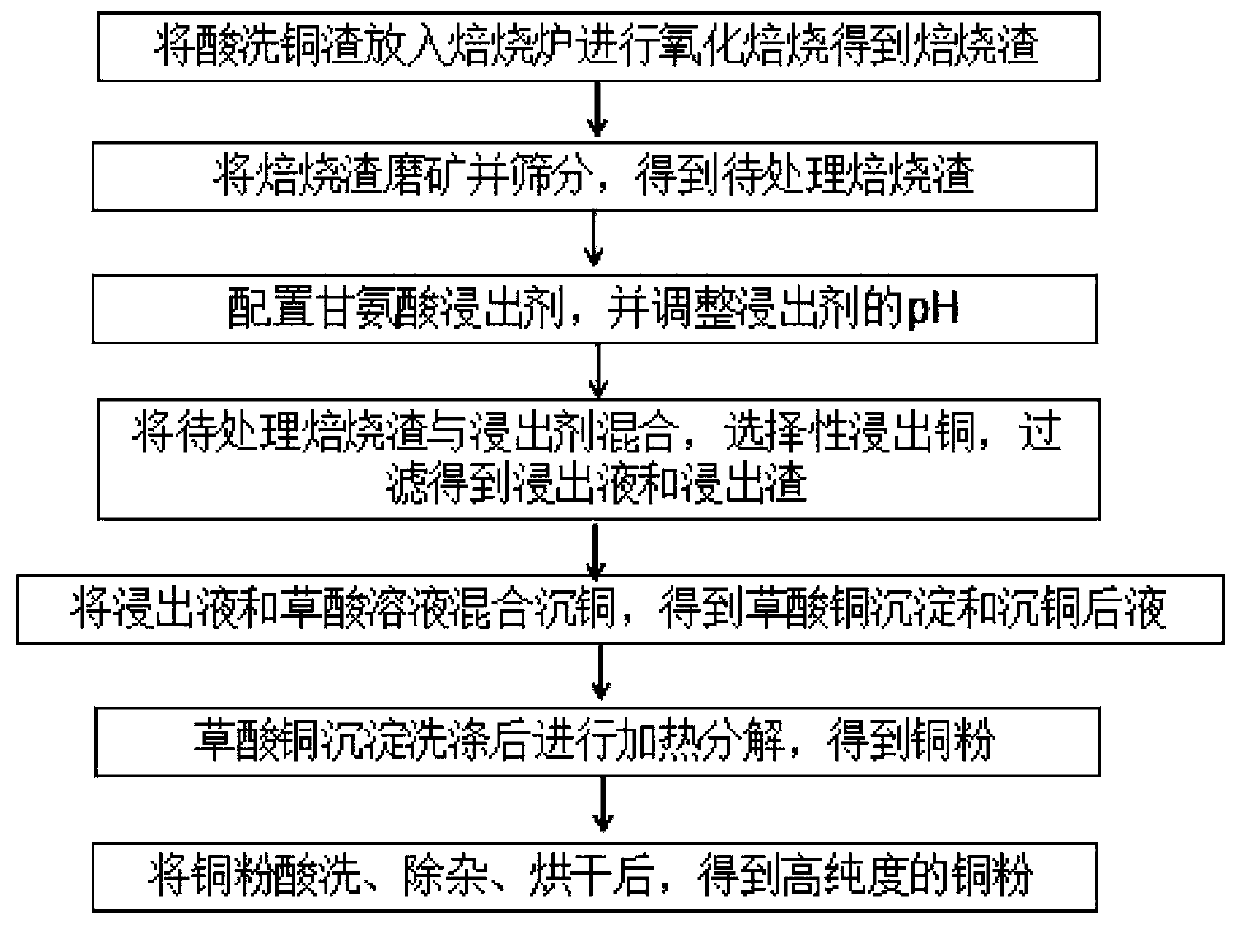
[0072] This embodiment provides a method for leaching copper from pickling copper slag of hydro-zinc smelting, including the following steps:
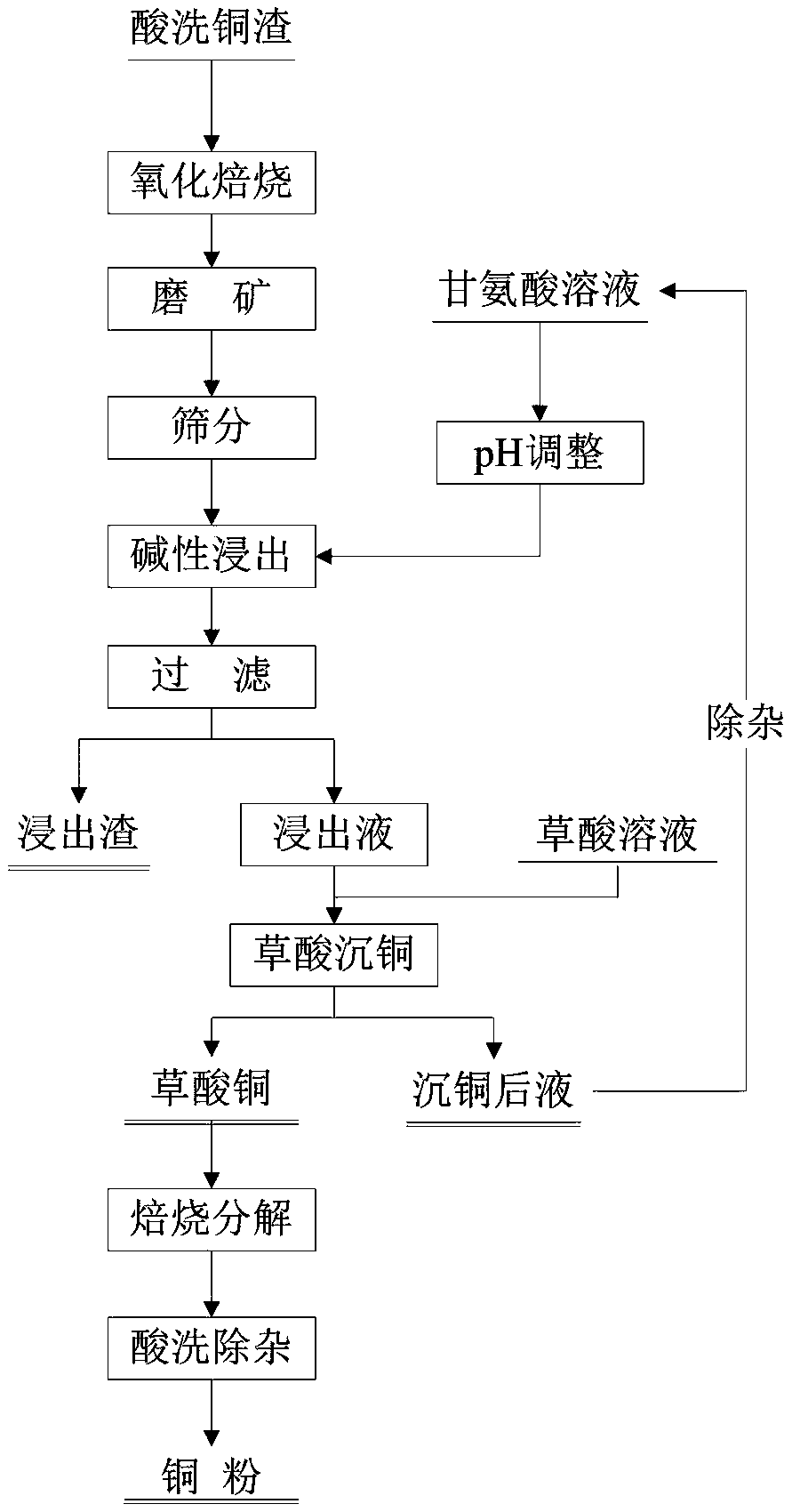
[0073] (1) Oxidation roasting: Put the pickled copper slag into a high-temperature roasting furnace and roast it at 400°C for 30 minutes to oxidize the elemental copper in the pickled copper slag, and the copper oxidation rate is more than 80%;
[0074] (2) Grinding: crushing, grinding, and sieving the roasted pickled copper slag to a particle size of less than 0.074mm, which accounts for more than 90% of the mass to obtain the roasting slag to be processed;
[0075] (3) Alkaline leaching: configure the concentration of glycine leaching agent to be 50g / L, and adjust the pH of the leaching agent solution to 10 wit...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The copper content in the pickling copper slag in this embodiment is 25%.
[0081] This embodiment provides a method for leaching copper from pickling copper slag of hydro-zinc smelting, including the following steps:
[0082] (1) Oxidation roasting: Put the pickled copper slag into a high-temperature roasting furnace and roast it at 450°C for 60 minutes to oxidize the elemental copper in the pickled copper slag, and the copper oxidation rate is over 85%;
[0083] (2) Grinding: crushing, grinding, and sieving the roasted pickled copper slag to a particle size of less than 0.074mm, which accounts for more than 90% of the mass to obtain the roasting slag to be processed;
[0084] (3) Alkaline leaching: configure the concentration of glycine leaching agent to be 100g / L, and adjust the pH of the leaching agent solution to 10.5 with sodium hydroxide solution; mix the configured glycine leaching agent with the roasting residue to be treated at a liquid-to-solid ratio of 10:1 , Heated...
Embodiment 3
[0089] The copper content in the pickling copper slag in this embodiment is 30%.
[0090] This embodiment provides a method for leaching copper from pickling copper slag of hydro-zinc smelting, including the following steps:
[0091] (1) Oxidation roasting: Put the pickled copper slag into a high-temperature roasting furnace and roast it at 500°C for 90 minutes to oxidize the elemental copper in the pickled copper slag with a copper oxidation rate of more than 90%;
[0092] (2) Grinding: crushing, grinding, and sieving the roasted pickled copper slag to a particle size of less than 0.074mm, which accounts for more than 90% of the mass to obtain the roasting slag to be processed;
[0093] (3) Alkaline leaching: configure the concentration of glycine leaching agent to be 150g / L, and adjust the pH of the leaching agent solution to 11 with sodium hydroxide solution; mix the configured glycine leaching agent with the roasting residue to be treated at a liquid-solid ratio of 15:1 , Heated t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com