A kind of rhodosporidium toruloides rna polymerase type III promoter and application thereof
A technology of promoter and polymerase, applied in the field of genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Example 1: Extraction of Rhodosporidium toruloides CGMCC 2.1389 genomic DNA
[0068] R. toruloides CGMCC 2.1389 (purchased from China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, CGMCC) was inoculated into 10 mL of YEPD liquid medium (glucose 20.0 g / L) from a slant. , yeast extract 10.0g / L, peptone 20.0g / L, pH 6.0), incubate at 30°C for 24h on a shaker, and then transfer the bacterial liquid to 100mL YEPD liquid medium at a volume ratio of 1:50. , cultured at 30°C in a shaker for 24h to reach the logarithmic growth phase. The extraction of Rhodosporidium toruloides genomic DNA was performed according to the method in the literature (Lin XP, et al. FEMS Yeast Res 2014, 14:547–555.). RNA was subjected to 1.5% (mass / volume concentration, 1.5g / 100ml) agarose gel electrophoresis, observed and identified using a fluorescence-ultraviolet analyzer, and a clear band was seen. Use NanoDrop to measure the quality and concentration of genomic DNA, the measured concentration...
Embodiment 2
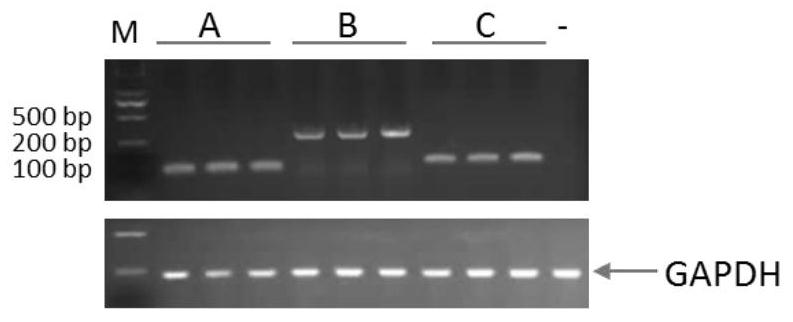
[0069] Embodiment 2: Rhodosporidium toruloides CGMCC 2.1389 suspected promoter sequence amplification
[0070] Using Rhodosporidium toruloides CGMCC 2.1389 genomic DNA as a template, six suspected promoter sequences were amplified and named as a, b, c, d, e, and f respectively. First, perform PCR amplification of fragment a: 10.0 μL of 5×PCR buffer, 1.0 μL of dNTPs (10 mM), 1.0 μL of upstream primer (a-F: 5’-TGGAGTTCGACGTTCTCCTCGC-3’ 50 mmol / L), 1.0 μL of downstream primer (a-R: 5 '- TGTGACTGATCTGGTGTTGTT-3'50mmol / L) 1.0μL, PrimeSTAR DNA polymerase (Dalian TakaRa) 0.5μL, 1.0μL genomic DNA as template, ddH 2 O supplemented to 50 μL, incubated at 94 °C for 3 min, then incubated at 98 °C for 10 s, 62 °C for 10 s, 72 °C for 1 min, 35 cycles, 72 °C for 10 min, and 4 °C to complete the reaction. The amplification of the b, c, d, e, and f fragments is the same as the amplification of the a fragment, and the primers used are b-F: 5'-GGCGGGATGACCCAGCGCTTTCA-3' / b-R: 5'-CAAGACCGAAGTCGCT...
Embodiment 3
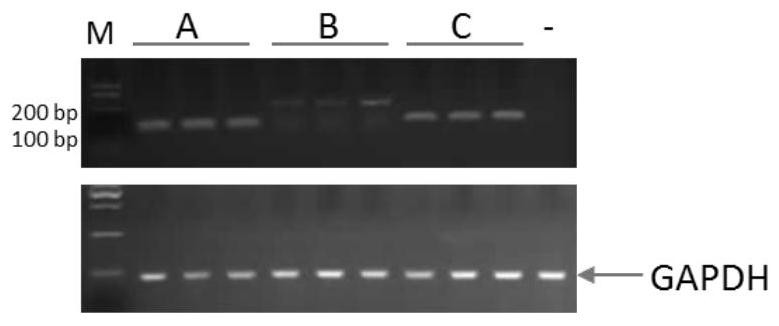
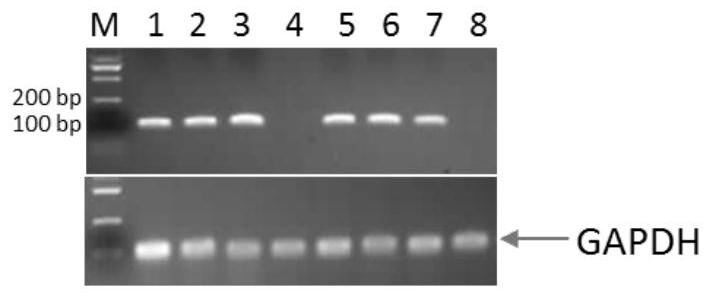
[0071] Example 3: Amplification of Rhodosporidium toruloides CGMCC 2.1389 non-coding RNA nucleotide sequence
[0072] Using the genome DNA of Rhodosporidium toruloides CGMCC 2.1389 as the template, two DNA sequences of miRNA and small nuclear RNA with different lengths were amplified, which were named A (59bp) and B (267bp). Since the siRNA fragment was small (35bp), it was directly synthesized by primers and named D. First, perform PCR amplification of fragment A: 5× PCR buffer 10.0 μL, dNTPs (10 mM) 1.0 μL, upstream primer (A-F: 5’-AAGCGCAACTACATCCTCG-3’ 50 mmol / L) 1.0 μL, downstream primer (A-R: 5 '-CTCGTAGTCGATGATGATGCCGT-3'50mmol / L) 1.0μL, PrimeSTAR DNA polymerase (Dalian TakaRa) 0.5μL, 1.0μL genomic DNA as template, ddH2O supplemented to 50μL, incubated at 94°C for 3min, then incubated at 98°C for 10s, 62 °C for 10 s, 72 °C for 1 min, 35 cycles, 72 °C for 10 min, and 4 °C to complete the reaction. The amplification of the B fragment is the same as the amplification of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com