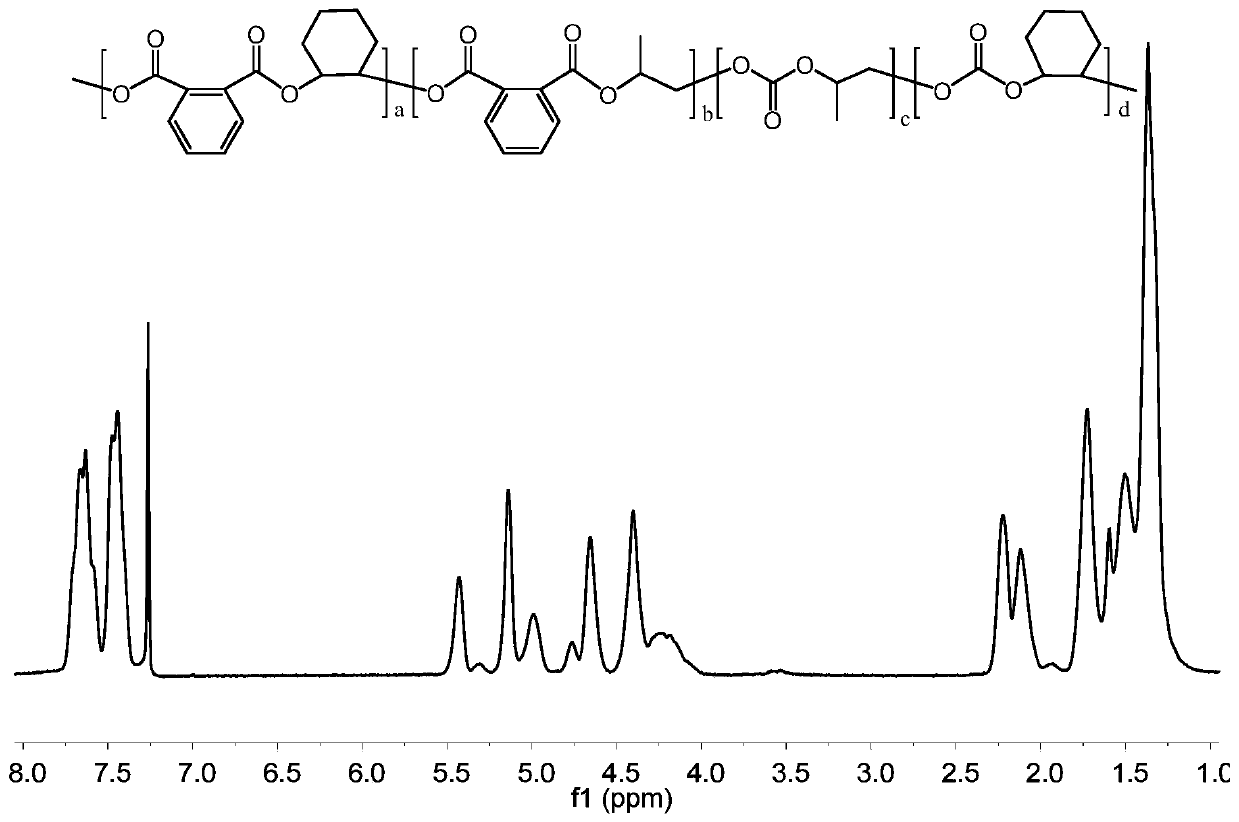
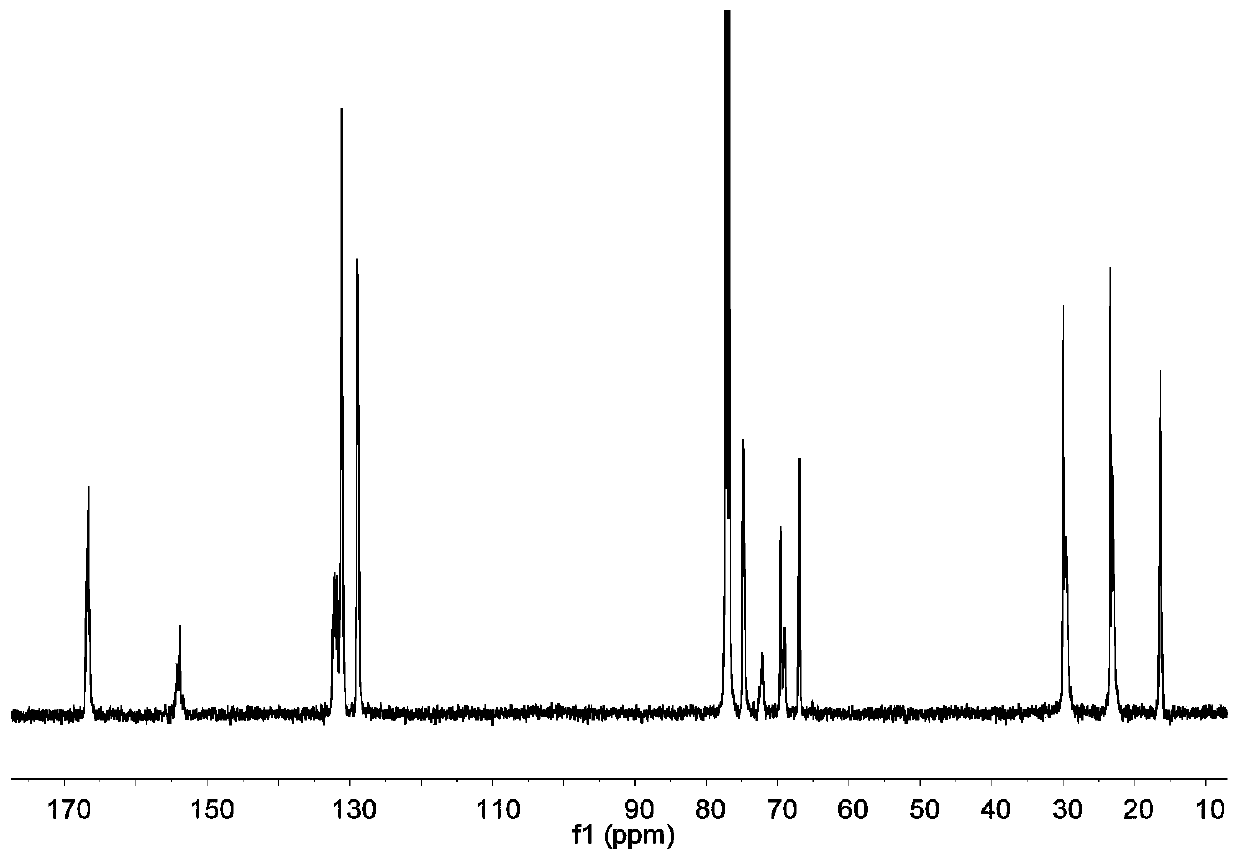
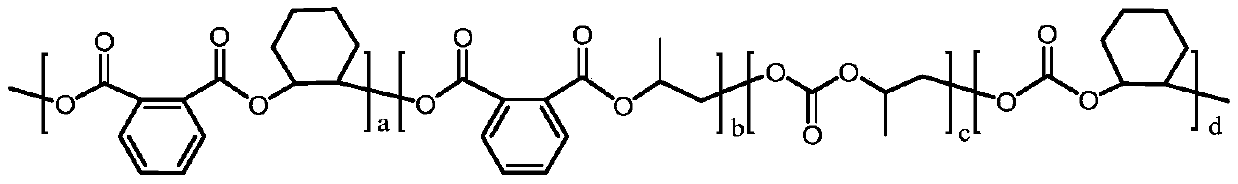
Preparation method of carbon-dioxide-based polyester-polycarbonate quadriblock copolymer
A technology of block copolymer and carbon dioxide, which is applied in the field of polymer material synthesis, can solve the problems of unfavorable cost, high price cyclohexane, control, etc., to avoid residue, good light transmittance and foaming performance, The effect of raising the glass transition temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Under anhydrous and oxygen-free conditions, mix 30mmol phthalic anhydride, 30mmol cyclohexane oxide, 30mmol propylene oxide, 0.06mmol bis(triphenylphosphine)ammonium chloride, 0.12mmol triethylboron and 15mL tetrahydrofuran Put it into a 100mL autoclave, feed 1MPa carbon dioxide, react in an oil bath at 70°C for 24h, then cool the autoclave to room temperature with cold water, and release unreacted carbon dioxide slowly. Dichloromethane was added to dissolve the product, and an appropriate amount of 1M methanolic hydrochloric acid solution was added dropwise to quench the reaction, and the polymer was precipitated from ethanol. After vacuum drying, the molecular weight, glass transition temperature, polycarbonate content and tensile strength were measured. m n = 53.2 kDa, PDI = 1.15, T g = 95.9°C, polycarbonate content = 44%, tensile strength = 53.3 MPa.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Under anhydrous and oxygen-free conditions, mix 15mmol of phthalic anhydride, 30mmol of cyclohexane oxide, 30mmol of propylene oxide, 0.06mmol of bis(triphenylphosphine)ammonium chloride, 0.12mmol of triethylboron and 15mL of tetrahydrofuran Put it into a 100mL autoclave, feed 1MPa carbon dioxide, react in an oil bath at 70°C for 24h, then cool the autoclave to room temperature with cold water, and release unreacted carbon dioxide slowly. Dichloromethane was added to dissolve the product, and an appropriate amount of 1M methanolic hydrochloric acid solution was added dropwise to quench the reaction, and the polymer was precipitated from ethanol. After vacuum drying, the molecular weight, glass transition temperature, polycarbonate content and tensile strength were measured. m n = 58.7 kDa, PDI = 1.17, T g = 94.7°C, polycarbonate content = 70%, tensile strength = 48.0 MPa.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Under anhydrous and oxygen-free conditions, mix 45mmol of phthalic anhydride, 30mmol of cyclohexane oxide, 30mmol of propylene oxide, 0.06mmol of bis(triphenylphosphine)ammonium chloride, 0.12mmol of triethylboron and 15mL of tetrahydrofuran Put it into a 100mL autoclave, feed 1MPa carbon dioxide, react in an oil bath at 70°C for 24h, then cool the autoclave to room temperature with cold water, and release unreacted carbon dioxide slowly. Dichloromethane was added to dissolve the product, and an appropriate amount of 1M methanolic hydrochloric acid solution was added dropwise to quench the reaction, and the polymer was precipitated from ethanol. After vacuum drying, the molecular weight, glass transition temperature, polycarbonate content and tensile strength were measured. m n = 52.1 kDa, PDI = 1.16, T g = 101.5°C, polycarbonate content = 11%, tensile strength = 54.8 MPa.
[0027] From the above results, it can be seen that the polyester-polycarbonate tetrablock copo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tg | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tg | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com