Method for manufacturing soft algae specimen
A specimen making and software technology, applied in the direction of botany equipment and methods, application, plant preservation, etc., can solve the problems of not showing algae shape well, manual unfolding effect is not good, pressed specimens are easy to oxidize, etc., to achieve hardness Large size, good preservation, fast setting time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The making of embodiment 1 feather algae specimen
[0028] 1) Extraction of feather algae in natural state
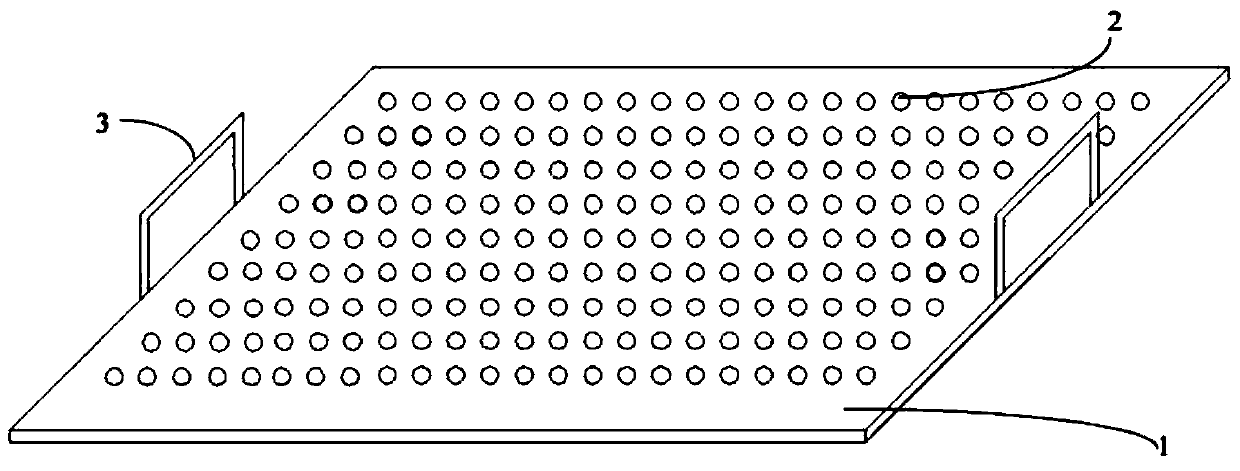
[0029] The algae extension plate ( figure 1 ) in an algae incubator filled with seawater, move the algae to the expansion board underwater, adjust the angle to expand the algae, and lift the expansion board from the water to the on the water. The algae on the expansion board are flat and complete, close to the state of the algae under natural water.
[0030] 2) Drying of feather algae
[0031] SiO 2 Spread the dry powder to a thickness of 2cm at the bottom of the drying chamber, place the expansion board attached to the molluscs in it, and then slowly spread the dry powder on the algae to a thickness of about 4cm, then buckle the lid of the drying chamber and place it for 10 minutes to Dry algae. After drying is complete, the algae are removed from the expansion plate for subsequent steps.
[0032] 3) Glue immobilization of feather algae
[0033] Choose a...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2, the making of laver specimen
[0038] 1) Extraction of Porphyra zebra in its natural state
[0039] Place the algae expansion board in the algae incubator filled with seawater, move the algae to the expansion board underwater, adjust the angle to expand the algae, and slowly lift the expansion board from the Lift underwater to the surface. The algae on the expansion board are flat and complete, close to the state of the algae under natural water.
[0040] 2) Drying of Porphyra zebra
[0041] SiO 2 Spread the dry powder to a thickness of 2cm at the bottom of the drying chamber, place the expansion board attached to the molluscs in it, and then slowly spread the dry powder on the algae to a thickness of about 4cm, then buckle the lid of the drying chamber and place it for 8 minutes to Dried nori.
[0042] 3) Glue fixation of Porphyra zebra
[0043] Choose a mold with a suitable size, and mix the glue A (epoxy resin) and glue B (polyetheramine D-230) of...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3 Duckweed specimen making
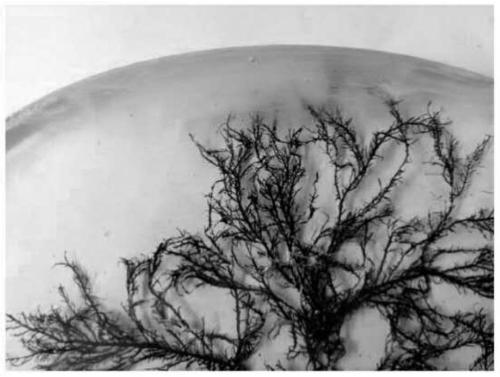
[0048] The main branches of duckweed algae are not soft, but there are many branches, and the leaflets are more dense. This method can also better preserve the shape of the algae.
[0049] 1) Extraction of Duckweed in its natural state
[0050] Place the algae expansion board in the algae incubator filled with seawater, move the algae to the expansion board underwater, adjust the angle to expand the algae, and slowly lift the expansion board from the Lift underwater to the surface. The algae on the expansion board are flat and complete, close to the state of the algae under natural water.
[0051] 2) Drying of Duckweed
[0052] SiO 2 Spread the dry powder to a thickness of 2cm at the bottom of the drying chamber, place the expansion board attached to the molluscs in it, and then slowly spread the dry powder on the algae to a thickness of about 4cm, then buckle the lid of the drying chamber and place it for 8 minutes to Duckwe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com