Nucleic acid composition and test kit for blood screening
A technology for nucleic acid composition and blood screening, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing the risk of missed detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The blood screening nucleic acid composition provided in this embodiment includes:
[0041] The first primer set is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and the nucleic acid sequence of the first probe is shown in SEQ ID NO.3; wherein, the 5' end of the first probe is labeled with a fluorescent reporter Group FAM, the 3' end is labeled with a fluorescent quencher group BHQ1;
[0042] The second primer set is shown in SEQ ID NO.4 and SEQ ID NO.5, and the nucleic acid sequence of the second probe is shown in SEQ ID NO.6; wherein, the 5' end of the second probe is labeled with a fluorescent reporter Group FAM, the 3' end is labeled with a fluorescent quencher group BHQ1;
[0043] The third primer set is shown in SEQ ID NO.7 and SEQ ID NO.8, and the nucleic acid sequence of the third probe is shown in SEQ ID NO.9; wherein, the 5' end of the third probe is labeled with a fluorescent reporter Group CY5, the 3' end is labeled with a fluorescent quencher group BHQ1;
[0044...
experiment example 1
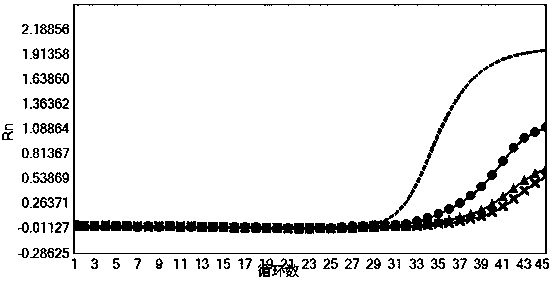
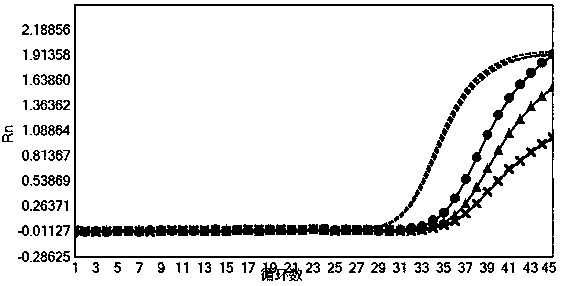
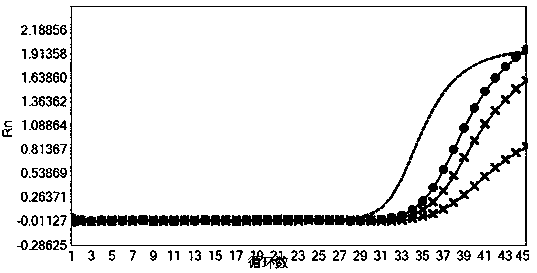
[0075] Verify the sensitivity of the nucleic acid composition of Example 1
[0076] The detection method is as follows:
[0077] HCV national reference product (340016-201701), HBV national reference product (300022-201601), HIV-1 WHO standard product (16 / 194), HIV-2 WHO standard product (16 / 296) and SARS-Cov-2 containing The positive plasmid of the ORF1ab gene fragment (SEQID NO.23) (its backbone is the pUC57 vector, see the vector map Figure 9 ) was diluted to the concentration in Table 5 for nucleic acid extraction (for the extraction method, refer to the extraction method of the nucleic acid sample to be tested in Example 1. In this experimental example, the ORF1ab plasmid of SARS-Cov-2 was extracted, mainly to simulate SARS-Cov-2 After the sample is extracted by the extraction method used in the present invention, the sensitivity of detection with the kit of the present invention), each concentration is 3 tubes, and 10 μL of internal control RNA pseudovirus (containing ...
experiment example 2
[0087] Verify the specificity of the nucleic acid composition of Example 1
[0088] Detection of human cytomegalovirus, hepatitis A virus, syphilis, herpes simplex virus type 1, herpes simplex virus type 2, Candida albicans, respiratory syncytial virus type A, respiratory virus type B, influenza A virus H1N1, influenza A Virus H3N2, influenza A virus H1N1 (2009), influenza B virus Yamagata and influenza B virus Victoria virus, and cultures of Staphylococcus aureus to verify whether there is cross-reaction with the nucleic acid composition of the example.
[0089] The specimens or cultures of the above 8 kinds of viruses and reference substances (HBV / HCV / HIV-1 positive control, HIV-2 positive control, SARS-Cov-2 positive control contain plasmids containing ORF1ab) according to Example 1 The extraction method was used for extraction, and 10 μL of internal control RNA pseudovirus was added to each tube, the extraction volume was 0.5 mL, and the elution volume was 60 μL. After ext...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com