Method for regulating and controlling expansion coefficient of light compact near-zero expansion metal matrix composite material
A composite material, near-zero expansion technology, applied in the field of lightweight near-zero-expansion composite materials, can solve the problems of inability to change the temperature range of low thermal expansion coefficient, easy aging, material brittleness, etc., and achieve the effect of good mechanical properties and electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
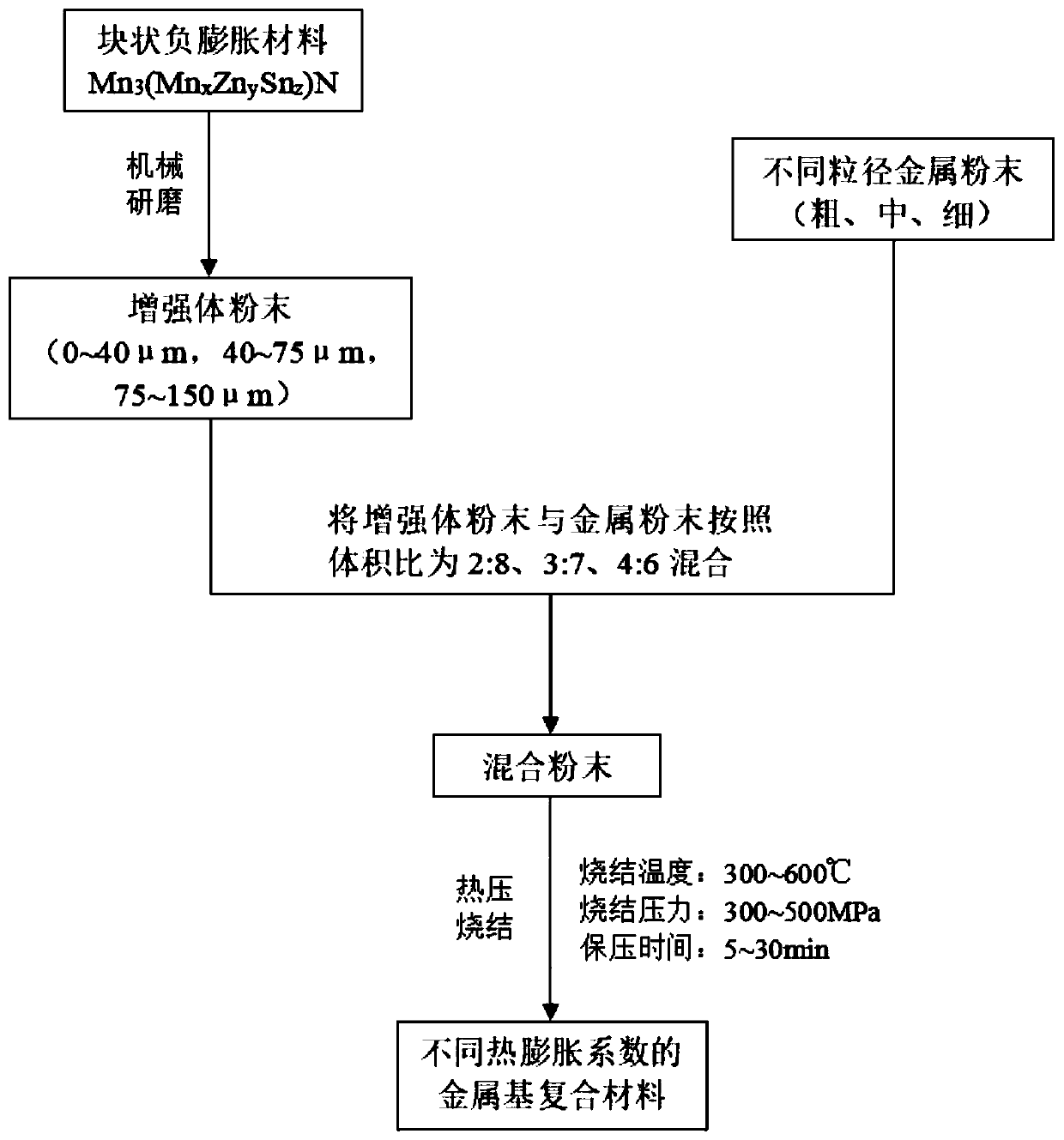
[0031] refer to figure 1 As shown, it is a flow chart of a method for regulating the expansion coefficient of a light-weight dense near-zero-expansion metal matrix composite material according to an embodiment of the present invention. The figure includes the following steps:
[0032] Negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 ) Preparation of N powder: the bulk negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N is ground with a vacuum ball mill, and sieved to obtain a powder of 75-150 μm, and set aside.
[0033] Then the prepared negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N powder and pure aluminum powder with a purity of 99.95% and a particle size of 25 μm are mixed according to the volume ratio of 2:8, 3:7, and 4:6 respectively. The mixing time is 30 hours, and the mixing speed is 150r / min. The first composite material mixed powder, the second composite material mixed powder and the third composite material mixed powder are respec...
Embodiment 2
[0038] refer to figure 1 As shown, it is a flow chart of a method for regulating the expansion coefficient of a light-weight dense near-zero-expansion metal matrix composite material according to an embodiment of the present invention. The figure includes the following steps:
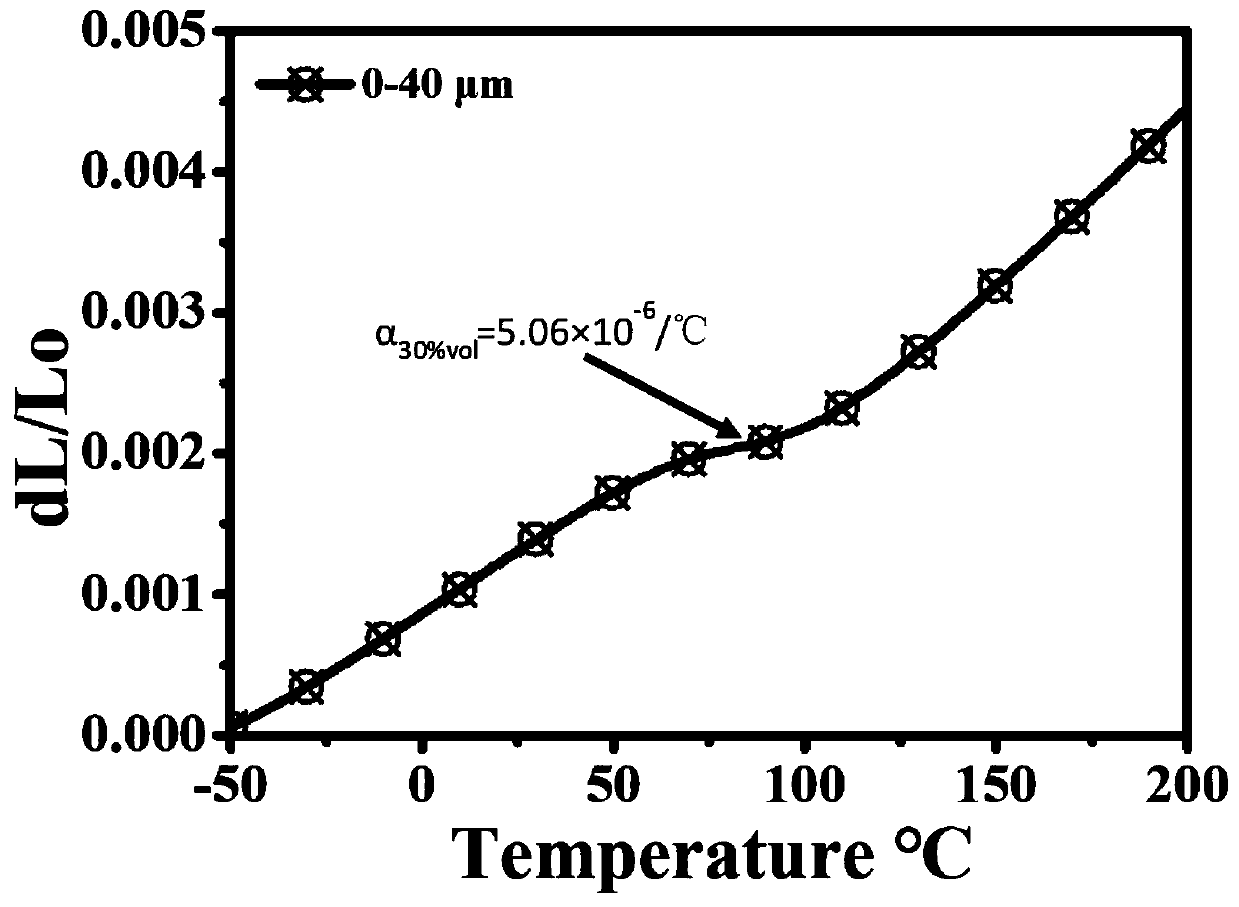
[0039] Negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 ) Preparation of N powder: the bulk negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N is ground with a vacuum ball mill, and sieved to obtain a powder of 2-40 μm, and set aside.
[0040] Then the prepared negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N powder and aluminum powder with a purity of 99.95% and a particle size of 25 μm were mixed according to a volume ratio of 3:7, the mixing time was 30 hours, and the mixing speed was 150 r / min to obtain a composite material mixing powder for later use.
[0041] Put the prepared composite material mixed powder into a vacuum hot-press sintering furnace for hot-press s...
Embodiment 3
[0044] refer to figure 1 As shown, it is a flow chart of a method for regulating the expansion coefficient of a light-weight dense near-zero-expansion metal matrix composite material according to an embodiment of the present invention. The figure includes the following steps:
[0045] Negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 ) Preparation of N powder: the bulk negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N is ground with a vacuum ball mill, and sieved to obtain a powder of 40-75 μm, and set aside.
[0046] Then the prepared negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N powder and aluminum powder with a purity of 99.95% and a particle size of 25 μm were mixed according to a volume ratio of 3:7, the mixing time was 30 hours, and the mixing speed was 150 r / min to obtain a composite material mixing powder for later use.
[0047] Put the prepared composite material mixed powder into a vacuum hot-press sintering furnace for hot-press ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com