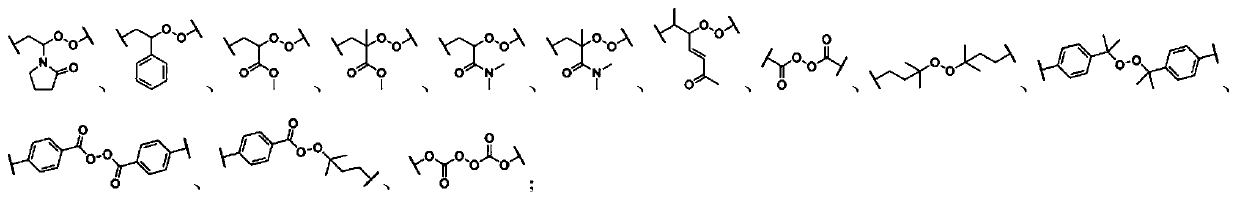
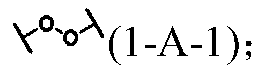Force-induced response dynamic polymer and application thereof
A polymer and polymer chain technology, applied in the field of force-responsive dynamic polymers, can solve the problems of single response effect, weak dynamic and self-healing ability, and difficulty in reflecting the control ability of the acting force.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[2098] In the preparation process of dynamic polymer foam materials, three methods of mechanical foaming, physical foaming and chemical foaming are mainly used to foam dynamic polymers.
[2099] Among them, the mechanical foaming method is to introduce a large amount of air or other gases into the emulsion, suspension or solution of the polymer with the help of strong stirring during the preparation of the dynamic polymer to make it a uniform foam, and then through physical Or chemical changes make it shape and become a foam material. In order to shorten the molding cycle, air can be introduced and emulsifiers or surfactants can be added.
[2100] Wherein, the physical foaming method is to use physical principles to realize the foaming of the polymer during the preparation of the dynamic polymer, which includes but not limited to the following methods: (1) inert gas foaming method, that is, after adding Press the inert gas into the molten polymer or pasty material under press...
Embodiment 1
[2133]
[2134] Weigh 20g of compound 2 into a 100ml round-bottomed flask, add 50mL of ethanol and 50mL of deionized water as a mixed solvent, and stir well; then add 16.2g of compound 3, set up a reflux device, and stir in an oil bath at 80°C for 12 hours; the reaction is complete Afterwards, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and the obtained product was recrystallized in a mixed solvent of acetonitrile:water=7:3, filtered, and dried to obtain the spiropyrandiol compound (a).
[2135] Add 20g of hydroxyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane and 2g of boric acid into a three-necked flask, raise the temperature to 80°C, add a small amount of triethylamine, and carry out polymerization reaction for 3 hours under stirring to form the first network.
[2136] Take 8g of hexamethylene diisocyanate and add it to another three-necked flask, vacuum dehydrate it at 120°C for 2 hours, add 12ml of DMF to dissolve and dilute after cooling down to 45°C, protect with argon, and the...
Embodiment 2
[2138]
[2139] Dissolve 8g of 4-hydroxybenzophenone in 20ml of DMF solvent, heat to 90°C, slowly add 7.5g of 2-bromoethanol dropwise using a dropping funnel, and then add 11g of anhydrous potassium carbonate as a catalyst, under argon atmosphere The reaction was stirred for 24h. After the reaction, the product was cooled and filtered to remove the solid catalyst, precipitated with deionized water, vacuum filtered and freeze-dried to obtain 4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)benzophenone. Get 4.8g prepared 4-(2-hydroxyethoxyl) benzophenone and dissolve in 20ml DMF solvent, then add 30ml isopropanol, drop two drops of acetic acid, after mixing uniformly, utilize 350nm ultraviolet light to irradiate 4 -6d, pour deionized water to obtain the crude product, and then use 1:1 petroleum ether-ethyl acetate as eluent to purify by silica gel column chromatography to obtain the hydroxyl compound (a).
[2140] Using equimolar amounts of 2-aminoethylaminoboronic acid and dopamine as raw materials and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Stretching rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com