Preparation method of zin-ion-containing tissue engineering scaffold with anti-inflammatory function
A tissue engineering scaffold, zinc ion technology, applied in the field of biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of incomparable biomechanical and physiological functions of hyaline cartilage, unsatisfactory treatment effect, unable to meet functional requirements, etc., and achieve a good internal immune environment, Good histocompatibility, good cell adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1 Preparation of simple Wharton's gum stent
[0038] (1) After taking out the umbilical cord, wash away the remaining blood in and on the surface of the umbilical vessels with normal saline, remove the outer capsule and internal blood vessels of the umbilical cord on a sterile operating table, and the separated transparent jelly-like substance is the human umbilical cord Wharton glue;
[0039](2) Repeatedly wash the Wharton gum twice with distilled water, then place the Wharton gum in the pulverizer, add triple distilled water, start the pulverization, and repeat several times until the Wharton gum is in a homogenized state;
[0040] (3) Put the Wharton gum homogenate prepared in step (2) into a refrigerator for freezing, then thaw at room temperature, and freeze and thaw repeatedly 3 to 4 times;
[0041] (4) Use gradient centrifugation to take the supernatant, add 1% TritonX-100 (polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether), 0.25% trypsin, Tris-HCl buffer in sequ...
Embodiment 2
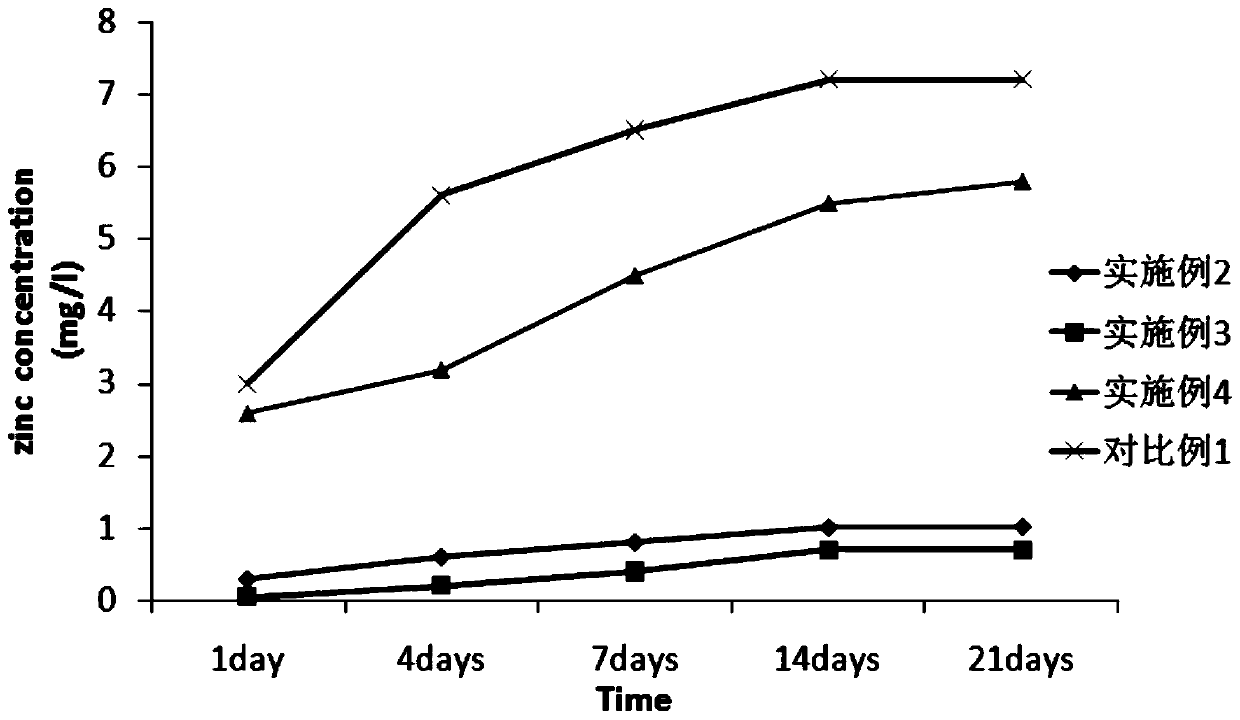
[0044] (1) Prepare a simple Wharton's gum stent according to the method described in steps (1) to (5) in Example 1;
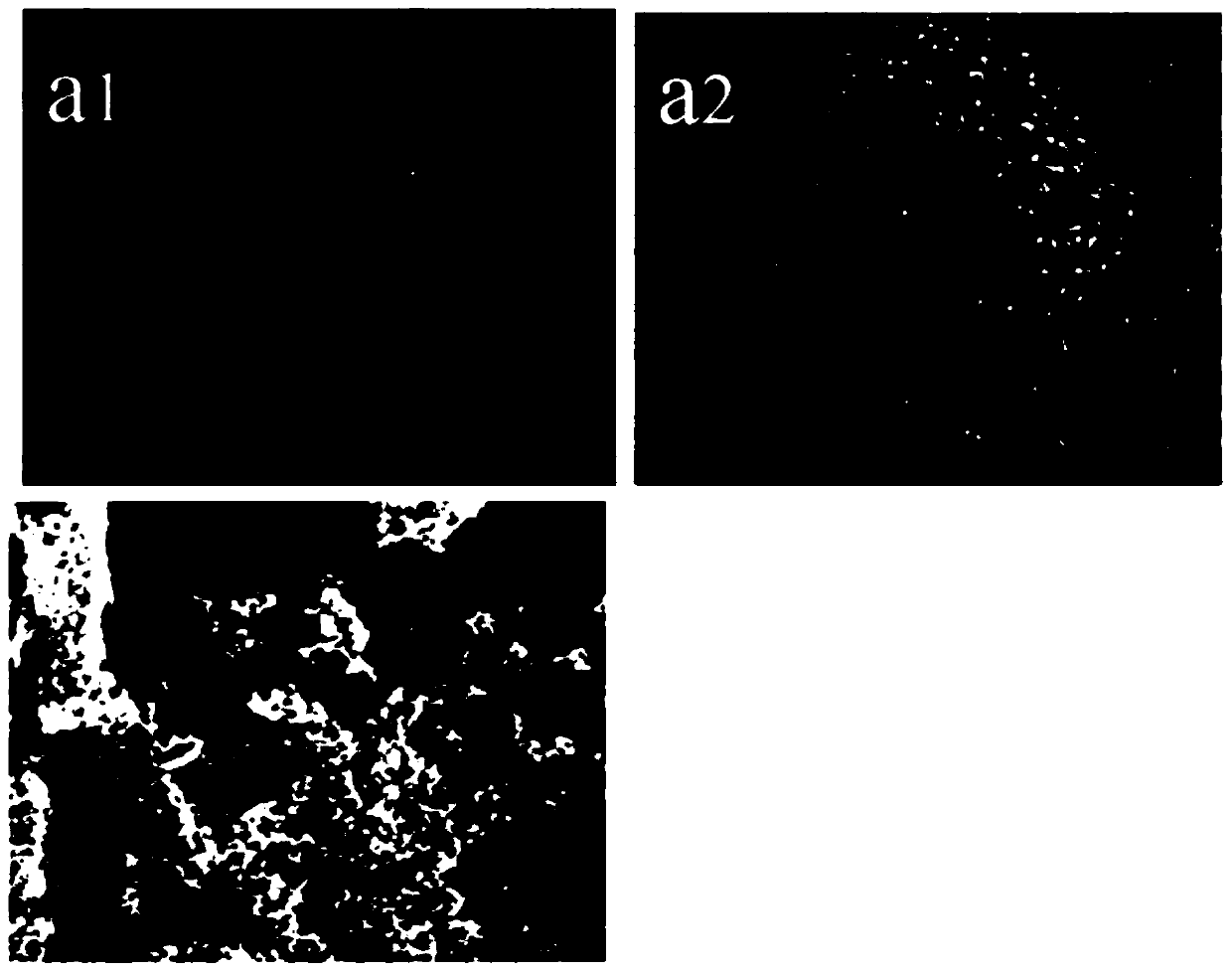
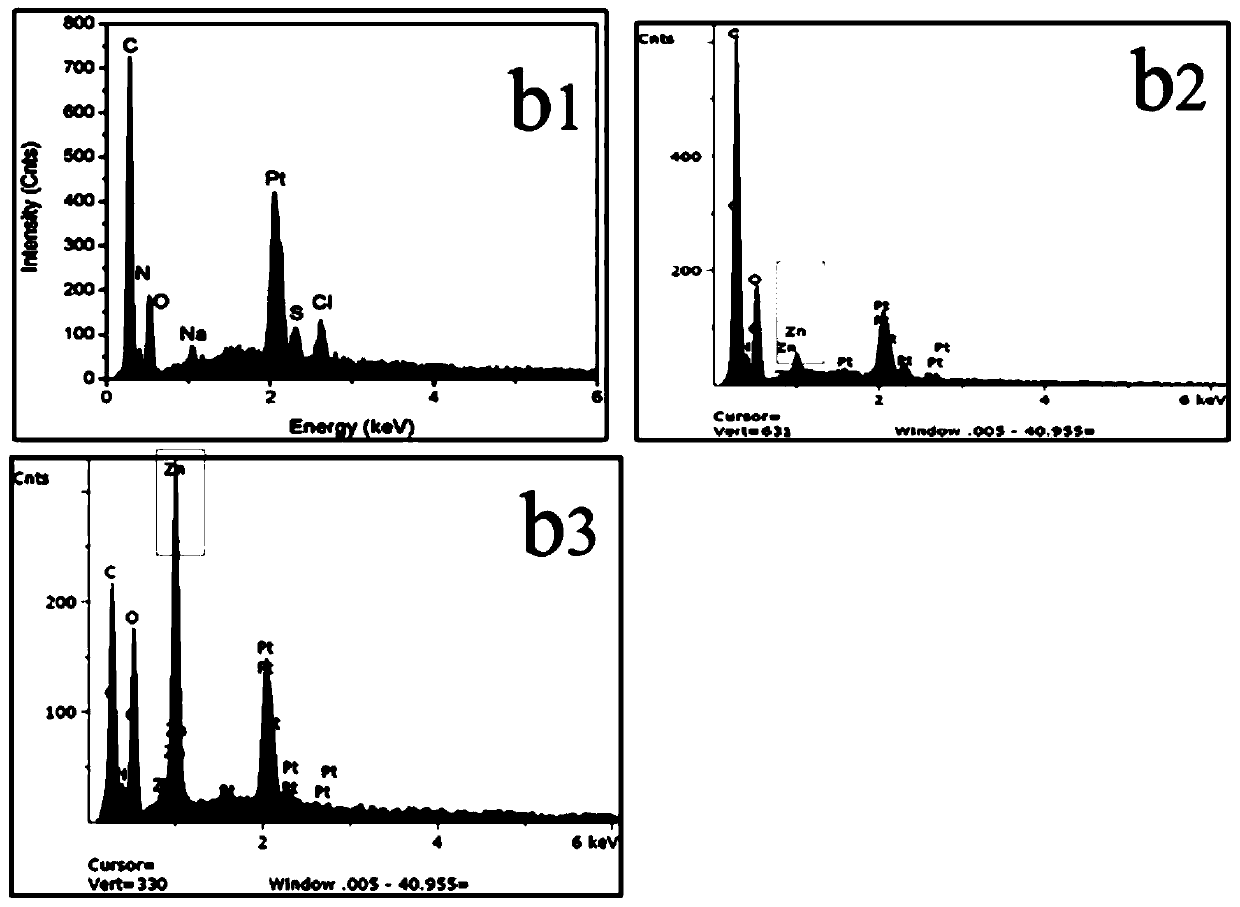
[0045] (2) Take NaCl: 120mmol / L, NaHCO respectively 3 : 2.0mmol / L, KCl: 4.0mmol / L, K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O: 3.0mmol / L, HCl: 40.0mmol / L, CaCl 2 : 3.0mmol / L, Na 2 SO 4 : 0.8mmol / L, (CH 2 OH)3CNH 2 (Tris): 40mmol / L, Zn(CH 3 COO) 2 : 10mmol / L, prepare zinc-containing simulated body fluid, and place the simple Wharton gum stent prepared in step (1) in the simulated body fluid to induce deposition for 24 hours at 37°C;
[0046] (3) Take out the Wharton gum stent soaked in step (2), place it in a 5% ammonia solution in a hydrothermal kettle, and perform a gas phase hydrothermal reaction at 50°C for 24 hours;
[0047] (4) Place the Wharton gum support loaded with zinc ions prepared in step (3) in a vacuum freeze dryer, then place it in a 60°C irradiation sterilizer for irradiation disinfection, and place it at 4°C Store under airtight conditions in the refrigerato...
Embodiment 3
[0049] (1) Prepare a simple Wharton's gum stent according to the method described in steps (1) to (5) in Example 1;
[0050] (2) Take NaCl: 137.0mmol / L, NaHCO respectively 3 : 4.0mmol / L, KCl: 3.6mmol / L, K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O: 4.0mmol / L, HCl: 30.0mmol / L, CaCl 2 : 2.5mmol / L, Na 2 SO 4 : 0.2mmol / L, (CH 2 OH)3CNH 2 (Tris): 30.0mmol / L, Zn(CH 3 COO) 2 : 5.0mmol / L zinc-containing simulated body fluid was prepared, and the simple Wharton's gum stent prepared in step (1) was placed in the simulated body fluid to induce deposition at 37°C for 24 hours;
[0051] (3) Take out the Wharton gum stent soaked in step (2), place it in a hydrothermal kettle with a concentration of 5% ammonia solution, and perform a gas phase hydrothermal reaction at 70°C for 48 hours;
[0052] (4) Place the Wharton gum support loaded with zinc ions prepared in step (3) in a vacuum freeze dryer, then place it in a 60°C irradiation sterilizer for irradiation disinfection, and place it at 4°C Store under air...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com