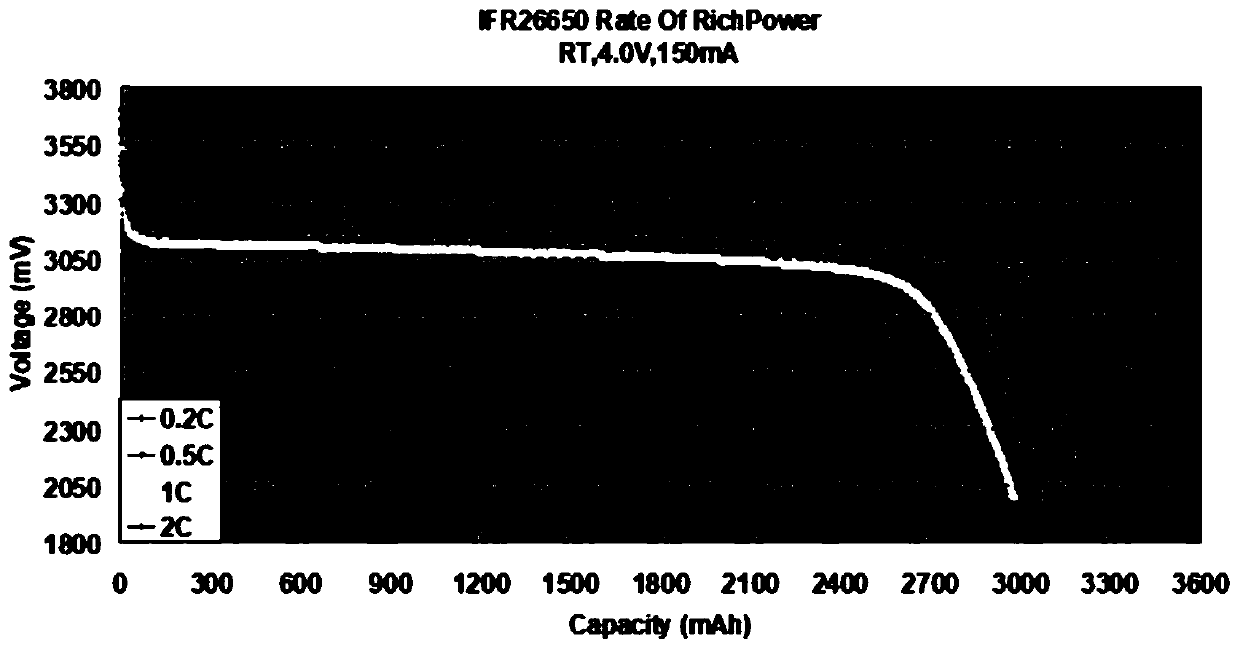
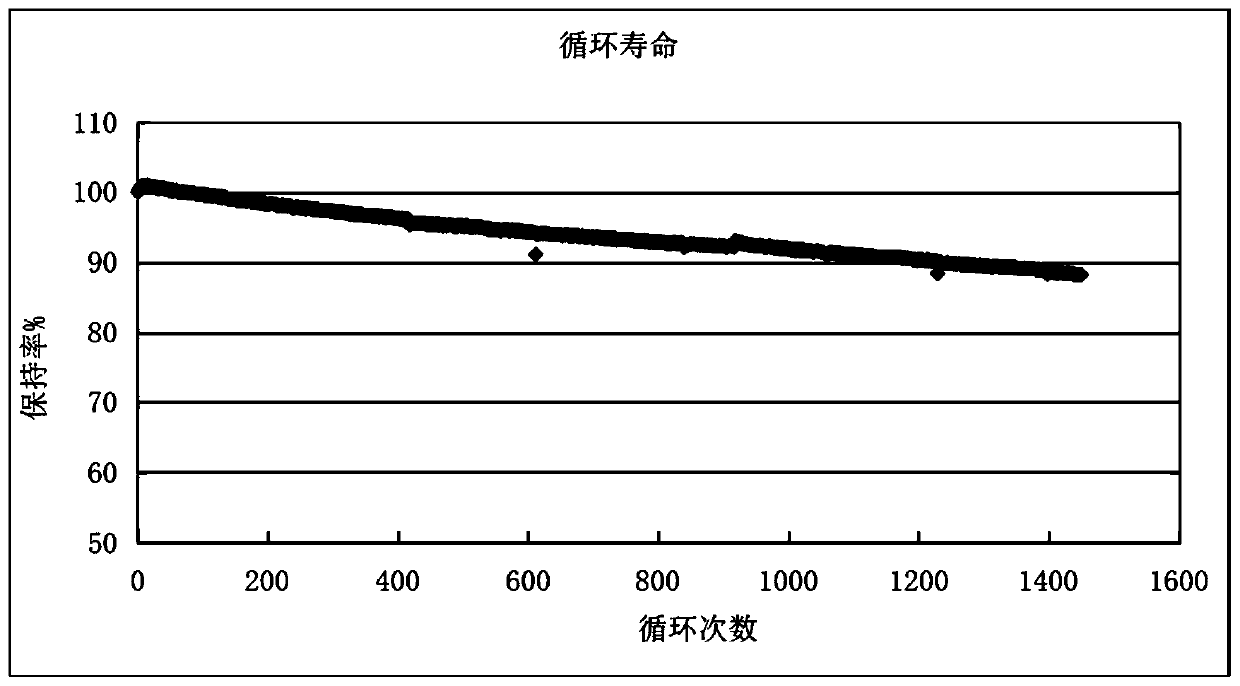
Recycling method of lithium iron phosphate waste battery
A lithium iron phosphate battery, lithium iron phosphate technology, used in battery recycling, waste collector recycling, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of electrolyte volatility and toxicity to people and the environment, and achieve comprehensive utilization and cleaning. Production, improve production efficiency, and facilitate the effect of exhaust gas treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] (1) Take 100 discarded lithium iron phosphate batteries, put them into a box-type atmosphere resistance furnace, close the inlet, feed nitrogen, and the gas flow rate is 10m 3 / h, after 60 minutes, the temperature was raised to 300°C for high-temperature calcination, and after 6 hours of heat preservation, the temperature was naturally lowered, and the waste lithium iron phosphate battery slag was taken out after the furnace temperature dropped to 60°C;
[0027] (2) The residue in the above step 1 is separated from the shell and the powder by crushing and screening, and the shell is removed to obtain lithium iron phosphate coarse powder;
[0028] (3) The lithium iron phosphate coarse powder in step 2 is separated by an air flow separation device to obtain carbon powder and lithium iron phosphate fine powder; the iron content in the lithium iron phosphate fine powder is determined by analysis 28.5%, phosphorus content 19.7%, and lithium content 3.9%, carbon content 5.8%;...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Take 100 discarded lithium iron phosphate batteries, put them into a box-type atmosphere resistance furnace, close the inlet, feed nitrogen, and the gas flow rate is 15m 3 / h, after 80 minutes, the temperature was raised to 500°C for high-temperature calcination, and after 4 hours of heat preservation, the temperature was naturally lowered, and the waste lithium iron phosphate battery slag was taken out after the furnace temperature dropped to 50°C;
[0033] (2) The residue in the above step 1 is separated from the shell and the powder by crushing and screening, and the shell is removed to obtain lithium iron phosphate coarse powder;
[0034] (3) The lithium iron phosphate coarse powder in step 2 is separated by an air flow separation device to obtain carbon powder and lithium iron phosphate fine powder; the iron content in the lithium iron phosphate fine powder is determined by analysis 28.5%, phosphorus content 19.7%, and lithium content 3.9%, carbon content 5.8%;...
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) Take 200 discarded lithium iron phosphate batteries, put them into a box-type atmosphere resistance furnace, close the inlet, feed nitrogen, and the gas flow rate is 25m 3 / h, after 90 minutes, the temperature was raised to 650°C for high-temperature calcination, and after 0.5 hours of heat preservation, the temperature was naturally lowered, and the waste lithium iron phosphate battery slag was taken out after the furnace temperature dropped to 40°C;
[0039] (2) The residue in the above step 1 is separated from the shell and the powder by crushing and screening, and the shell is removed to obtain lithium iron phosphate coarse powder;
[0040] (3) The lithium iron phosphate coarse powder in step 2 is separated by an air flow separation device to obtain carbon powder and lithium iron phosphate fine powder; by analyzing and determining iron content in lithium iron phosphate fine powder 28.5%, phosphorus content 20%, and lithium content 4%, carbon content 6%;
[0041...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com