A method for brazing wear-resistant alloys on shock-absorbing bosses of low-pressure rotor blades
A low-pressure rotor and wear-resistant alloy technology, applied in welding equipment, welding medium, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problem of discontinuous machining allowance of wear-resistant layer, large heat-affected zone width of boss, and low pass rate of brazing at one time and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving brazing quality, good economic benefits, improving one-time pass rate and processing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The blades of the low-pressure first-stage rotor are made by forging and machining. There are basin-facing shock-absorbing bosses and back-facing shock-absorbing bosses on the blade body. The blade material is TC4 titanium alloy.
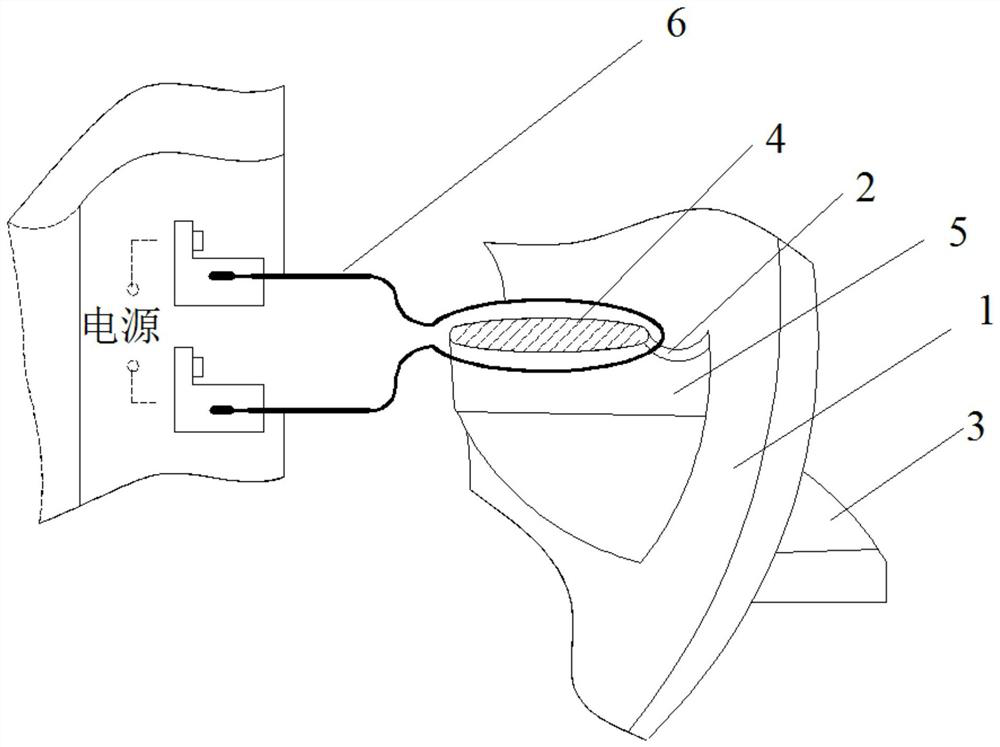
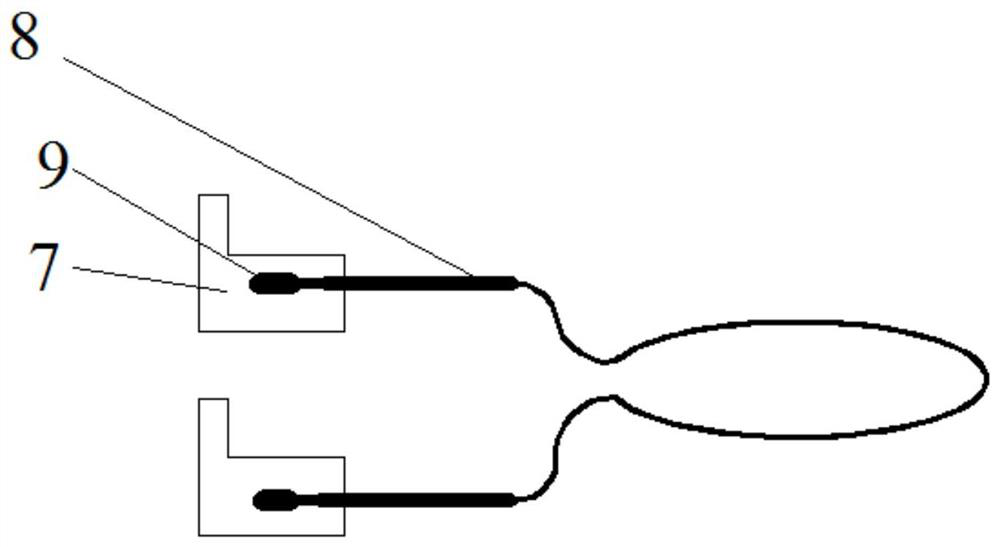
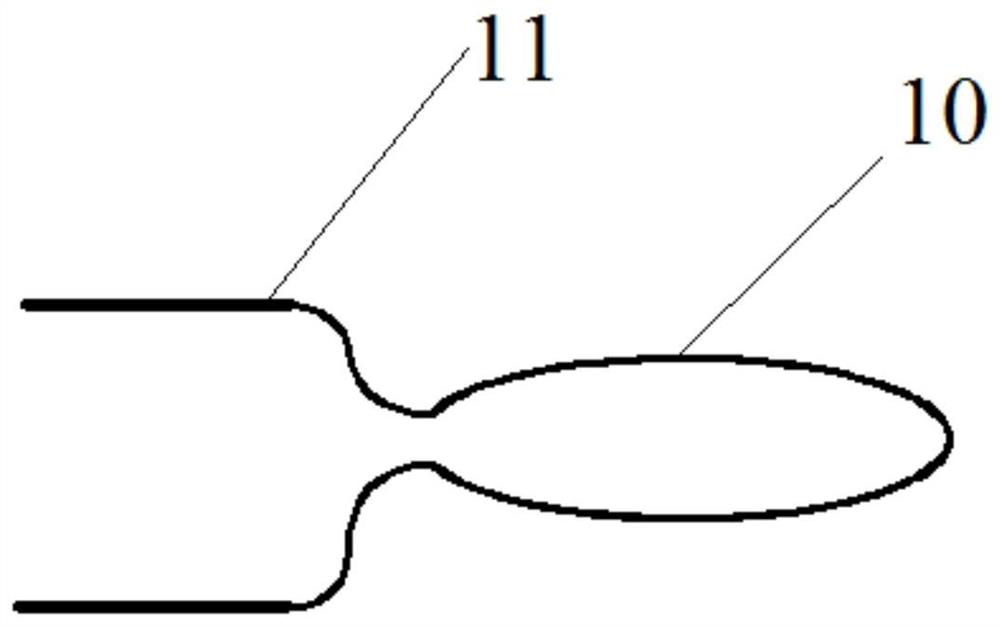
[0031] A method for brazing wear-resistant alloys on shock-absorbing bosses of low-pressure rotor blades, such as Figure 1 to Figure 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0032] Step 1, cleaning before welding
[0033] Use a micro-grinder equipped with a hard alloy grinding wheel to clean the burrs around the basin of the low-pressure first-stage rotor blade facing the shock-absorbing boss and facing away from the shock-absorbing boss, and do not damage the substrate during grinding; clean the low-pressure first-stage rotor with acetone after grinding The basin of the blade faces the shock-absorbing boss, faces away from the shock-absorbing boss and its adjacent surfaces to remove oil and other impurities;
[0034] Step 2, Powder Mixin...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The blades of the low-pressure secondary rotor are made by forging and machining. There are basin-facing shock-absorbing bosses and back-facing shock-absorbing bosses on the blade body. The blade material is TC6 titanium alloy.
[0050] A method for brazing a wear-resistant alloy on a shock-absorbing boss of a low-pressure rotor blade, comprising the following steps:
[0051] Step 1, cleaning before welding
[0052] Use a micro-grinder equipped with a carbide grinding wheel to clean the burrs around the basin of the low-pressure secondary rotor blade facing the shock-absorbing boss and facing away from the shock-absorbing boss, and do not damage the substrate during grinding; clean the low-pressure secondary rotor with acetone after grinding The basin of the blade faces the shock-absorbing boss, faces away from the shock-absorbing boss and its adjacent surfaces to remove oil and other impurities;
[0053] Step 2, Powder Mixing Preparation
[0054] Put the Ti-Ni-Cu-Zr ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com