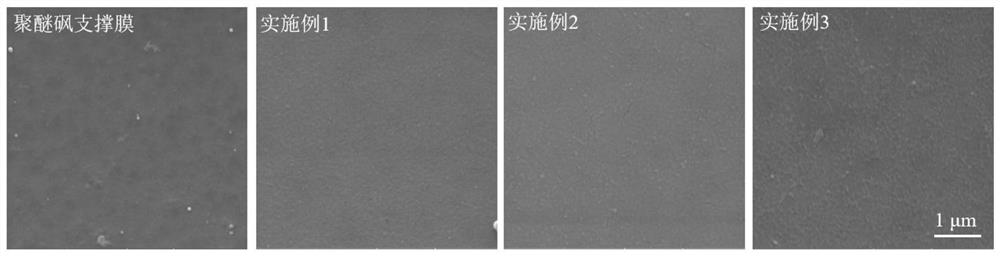
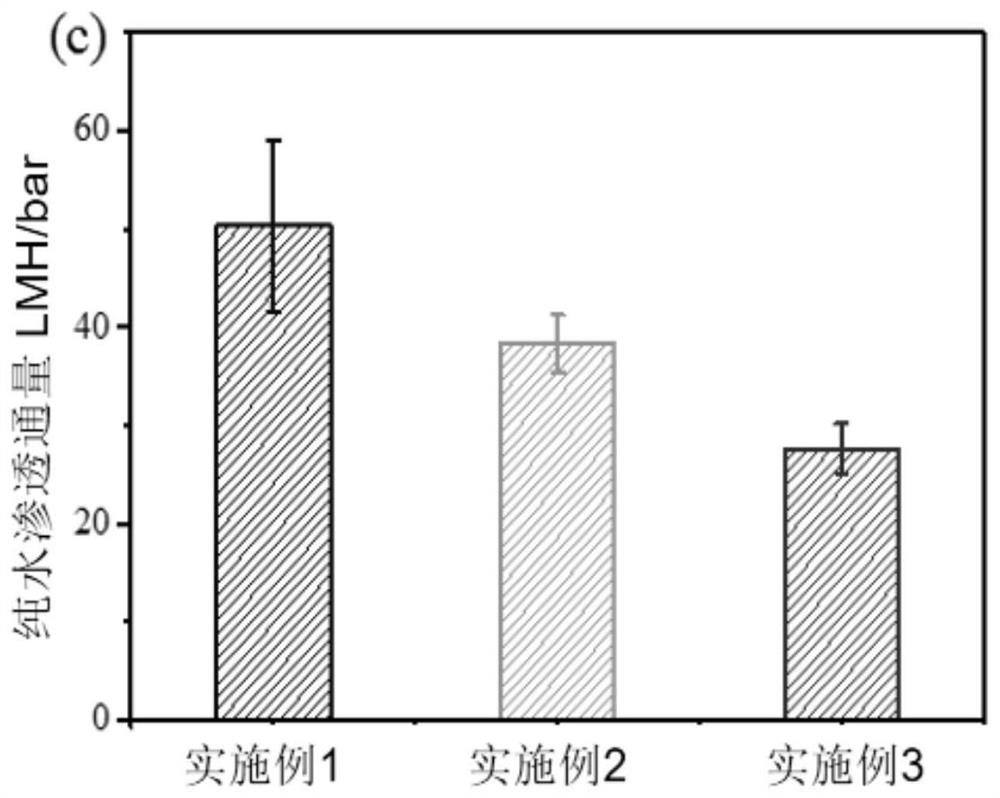
A kind of loose nanofiltration membrane based on branched polyethyleneimine, its preparation and application
A technology of branched polyethyleneimine and polyethyleneimine, which is applied in the field of membrane separation, can solve the problems of poor stability and low separation selectivity, and achieve the effects of good stability, high selectivity and high water flux
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0039] The present invention also provides the preparation method of described loose nanofiltration membrane, comprises the steps:
[0040] Soak the polymer support layer in the aqueous solution of polyethyleneimine, the aqueous solution of polyethyleneimine derivatives and the aqueous solution of crosslinking agent respectively, the soaking order is adjustable, and only soak in one of the solutions at a time; through soaking, the polymer Two or three of the ethyleneimine, the polyethyleneimine derivative and the crosslinking agent contact and interact on the surface of the polymer support layer at the same time; by this method, the polyethyleneimine and the polyethyleneimine derivative When in contact, assembly occurs once through electrostatic interaction, polyethyleneimine and polyethyleneimine derivatives are chemically crosslinked once with a crosslinking agent, and a polyelectrolyte active layer is formed on the surface of the polymer support layer, which is taken out aft...
Embodiment 1
[0064] R in the polyethyleneimine derivative of the composite membrane of embodiment 1 1 for R 2 is H atom, n=4, the molecular weight of polyethyleneimine is 70000Da, the crosslinking agent is glutaraldehyde, and the polymer support layer is a polyethersulfone microfiltration membrane; the preparation process of the composite membrane includes the following steps:
[0065] (1) Soak the polyethersulfone support layer in an aqueous solution of 2% polyethyleneimine derivatives by mass fraction for 30 minutes, then take it out and rinse it with deionized water;
[0066] (2) immersing the above-mentioned polymer support layer in an aqueous solution containing a mass fraction of 3% glutaraldehyde cross-linking agent for 15 minutes of chemical cross-linking;
[0067] (3) Then the polymer support layer is transferred to an aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 3% polyethyleneimine and soaked for 30 minutes, then taken out and rinsed with deionized water;
[0068] (4) Finally, i...
Embodiment 2
[0070] R in the polyethyleneimine derivative of the composite membrane of embodiment 2 1 for R 2 is H atom, n=20, molecular weight of polyethyleneimine is 70000Da, crosslinking agent is glutaraldehyde, polymer support layer is polyethersulfone microfiltration membrane; the preparation steps of this composite membrane are exactly the same as that of Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com