Functional food for intervening chronic alcohol-induced small intestine injury and application of functional food
A technology for functional food and small intestine injury, applied in the direction of function, application, food composition, etc. of food ingredients, and can solve problems affecting promotion and application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Effects of oligochitosan on small intestinal villi, crypts and muscular layer of rats after chronic alcohol drinking
[0039] After feeding the rats with alcohol and chitosan oligosaccharides for 6 weeks, their small intestines were taken, and pathological tissue sections were made for HE staining. Refer to figure 1 It can be seen that after intragastric administration of chitosan oligosaccharides of the present invention, the problems of alcohol-induced shortening of small intestinal villi, shedding of tips, inconspicuous shape, increased depth of crypts and decreased thickness of muscular layer can be improved.
Embodiment 2
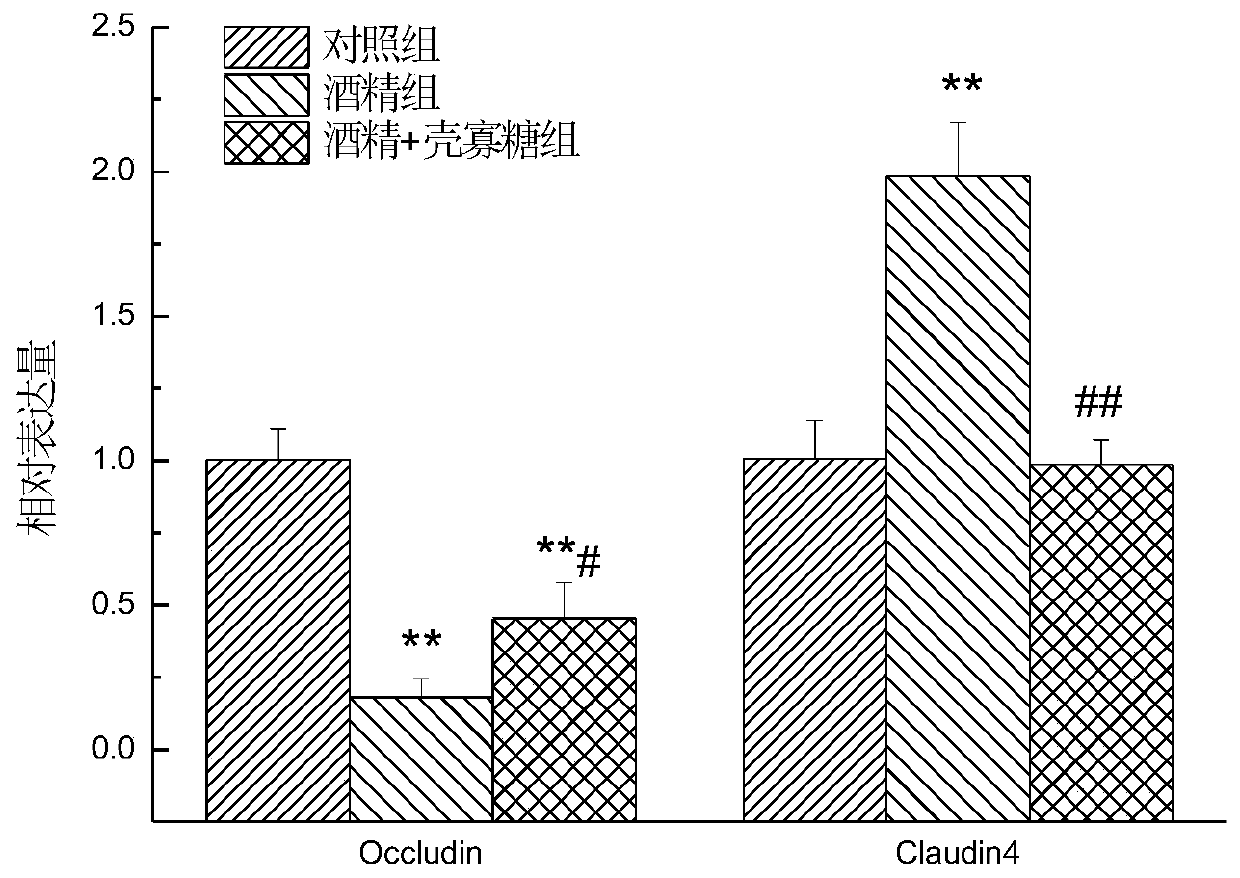
[0040] Example 2: Effect of oligochitosan on gene expression of small intestinal tight junction protein in rats after chronic drinking
[0041] Adjacent epithelial cells are connected by a junction complex composed of a variety of proteins and molecules. From the top to the basement membrane, there are tight junctions (TJ), adherens junctions, desmosome junctions, and gap junctions, etc., which together strengthen the intercellular space. Connecting function, forming the function of transmitting information channel, among which TJ is the most important. During the onset of inflammatory bowel disease, a large number of inflammatory factors produced by the intestinal mucosa will damage the intestinal epithelial cells, affect the expression and distribution of TJ protein in intestinal epithelial cells, destroy the TJ structure, and cause damage to the intestinal mucosal barrier function. refer to figure 2As shown, compared with the normal group, 6 weeks of alcohol gavage signif...
Embodiment 3
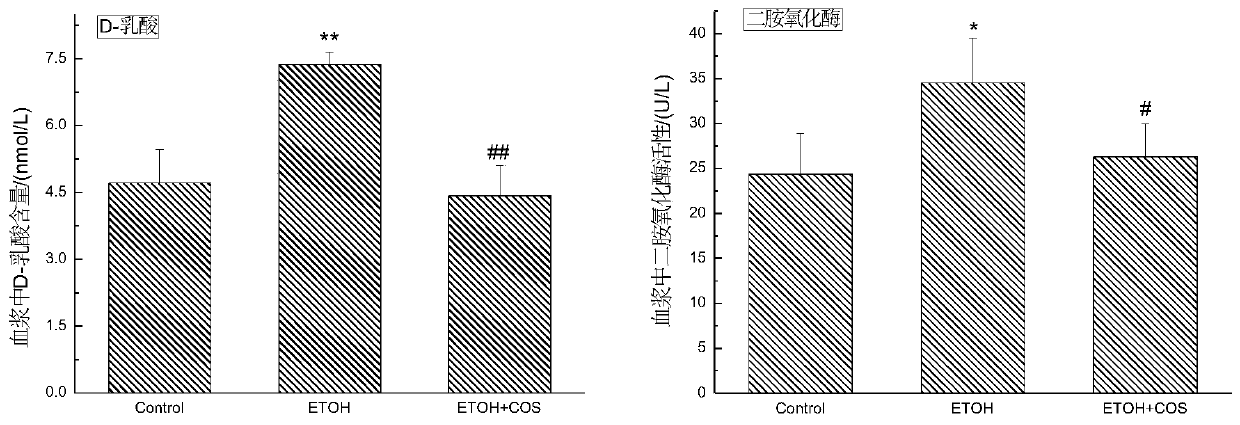
[0042] Embodiment 3: The effect of chitosan oligosaccharide on D-lactic acid and diamine oxidase in rat blood after chronic drinking
[0043] When intestinal mucosal permeability increases, large amounts of D-lactic acid (D-LA) produced by intestinal bacteria can enter the blood circulation, so it can be used as a reliable indicator of bacterial infection and increased intestinal permeability. refer to image 3 It can be seen that compared with the control group, the D-LA content in the plasma of rats fed with alcohol for 6 weeks increased significantly (P<0.01). It can be seen that alcohol damages the intestinal barrier and increases the permeability of the small intestinal mucosa, while chitosan oligosaccharide The intervention of D-LA can significantly reduce the content of D-LA in plasma (P<0.01), and restore it to a level with no significant difference from the normal group (P<0.01).
[0044] Diamine oxidase (DAO) mainly catalyzes the diamine oxidation process of histami...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com