Long-chain non-coding RNA for screening hepatopulmonary syndrome and application of long-chain non-coding RNA
A long-chain non-coding, pulmonary syndrome technology, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as lack of coding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Example 1. Screening of highly expressed lncRNA in liver of HPS model rats using gene chip method
[0018] 1. Establishment of a rat model of hepatopulmonary syndrome by ligation of the common bile duct
[0019] The HPS rat model was established by common bile duct ligation (CBDL), 30 rats in the sham group and 30 in the operation group. SD male adult rats, weighing 200-220 g, were used to establish an animal model of HPS by common bile duct ligation (common bile duct ligation, CBDL). Rats in the control group were only subjected to laparotomy without ligation of the common bile duct.
[0020] Blood gas analysis was used to judge the expansion of pulmonary microvessels: after weighing the rats, they were anesthetized with 5% chloral hydrate at 7 mL / g; the abdominal cavity was quickly opened to expose the abdominal aorta, and blood was drawn with a blood gas needle. Immediately after the completion, the blood gas analyzer ABL 800 (Radiometer Copenhagen) was used for an...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2. Identification, naming and expression analysis of lncRNA numbered MRAK138283
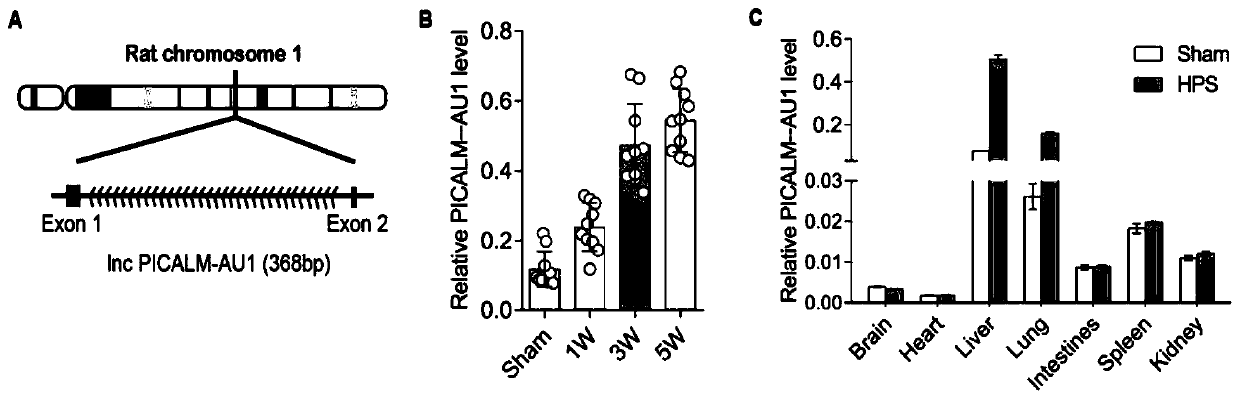
[0024] The analysis found that the molecule has the number ENSRNOG00000062120 on the ensenble website. Located on the first chromosome of the rat, it consists of 2 exons and 1 intron. Since the lncRNA is upstream of the antisense strand of the gene picalm, it was named PICALM-AU1 according to the lncRNA naming rules. The structure of PICALM-AU1 is as figure 2 As shown in A, its full-length nucleic acid sequence contains 368 bases, and its sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. qRT-PCR showed that the lncRNA was mainly expressed in the liver, and the expression was significantly up-regulated in the liver of HPS model rats ( figure 2 , B), the content of HPS blood exosomes was significantly more than that of the control group ( figure 2 , C).
[0025] Rat / PICALM-AU1 detection conditions: Primers: PICALM-AU1-F: 5'-gctgcacccctctttcacc-3' (SEQ ID NO.2); PICALM-AU1-R: 5'-tcaaccccagg...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Example 3, PICALM-AU1 is used for clinical screening of HPS patients
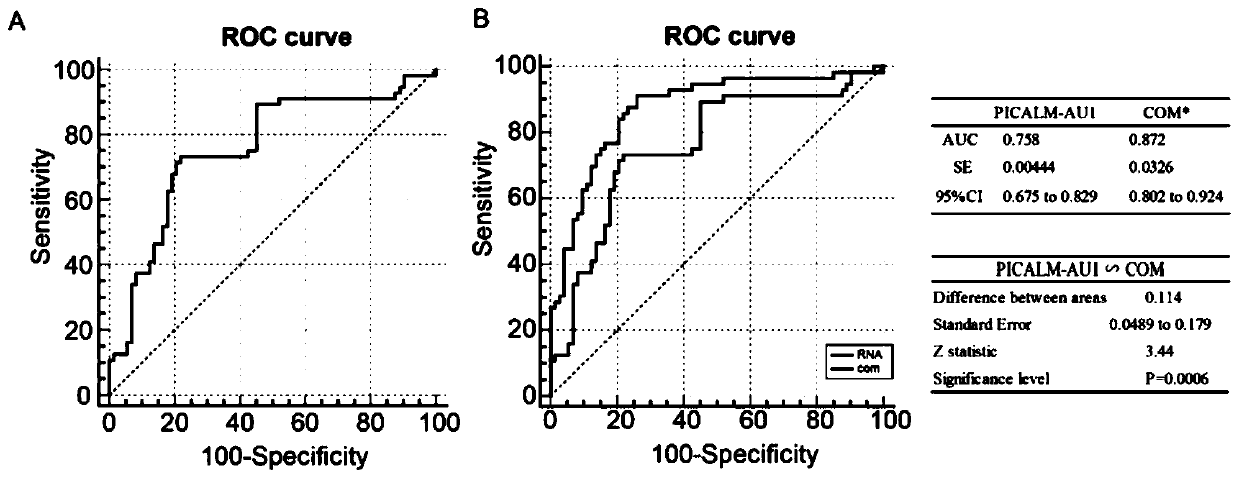
[0027] Collect clinical samples (normal liver cirrhosis patients are the control group, and liver cirrhosis-induced HPS patients are the experimental group), and analyze the patient-related indicators and PICALM-AU1 in blood exosomes to find out whether there is a certain relationship with the detection of HPS. Using ROC curve analysis to use PICALM-AU1 alone as an HPS screening index, it was found that the AUC was 0.758, which had a relatively good detection rate ( image 3 , A); PICALM-AU1 was combined with spider angioma+cholic acid content as the HPS screening index, and the results showed that the AUC was 0.872, which had a more efficient HSP detection rate ( image 3 , B).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com