Distance measuring method of significant target in binocular image
A technology in distance measurement and image, applied in the field of image processing, which can solve problems such as slow processing speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
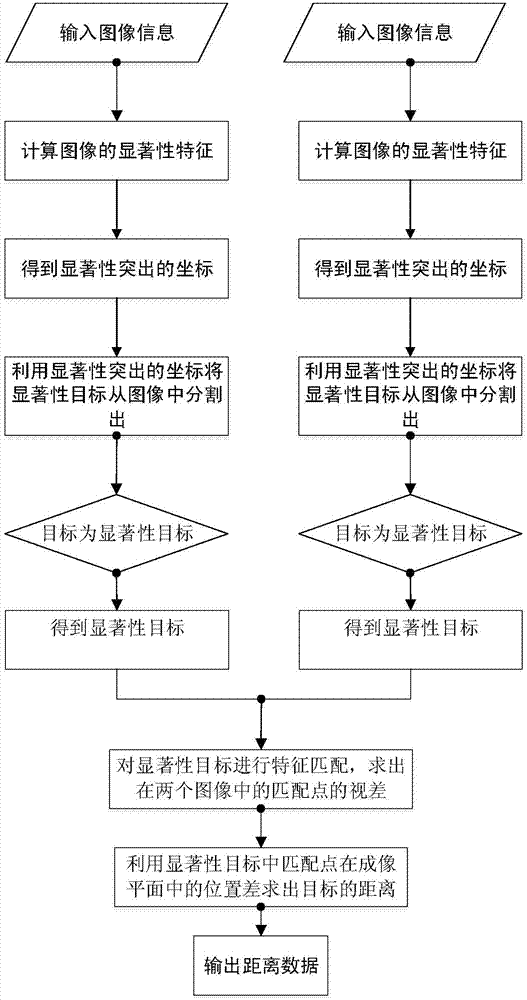
[0096] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 5 To illustrate this embodiment, the method described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0097] Step 1. Use the visual saliency model to extract the saliency features of the binocular image, and mark the seed points and background points, specifically including:
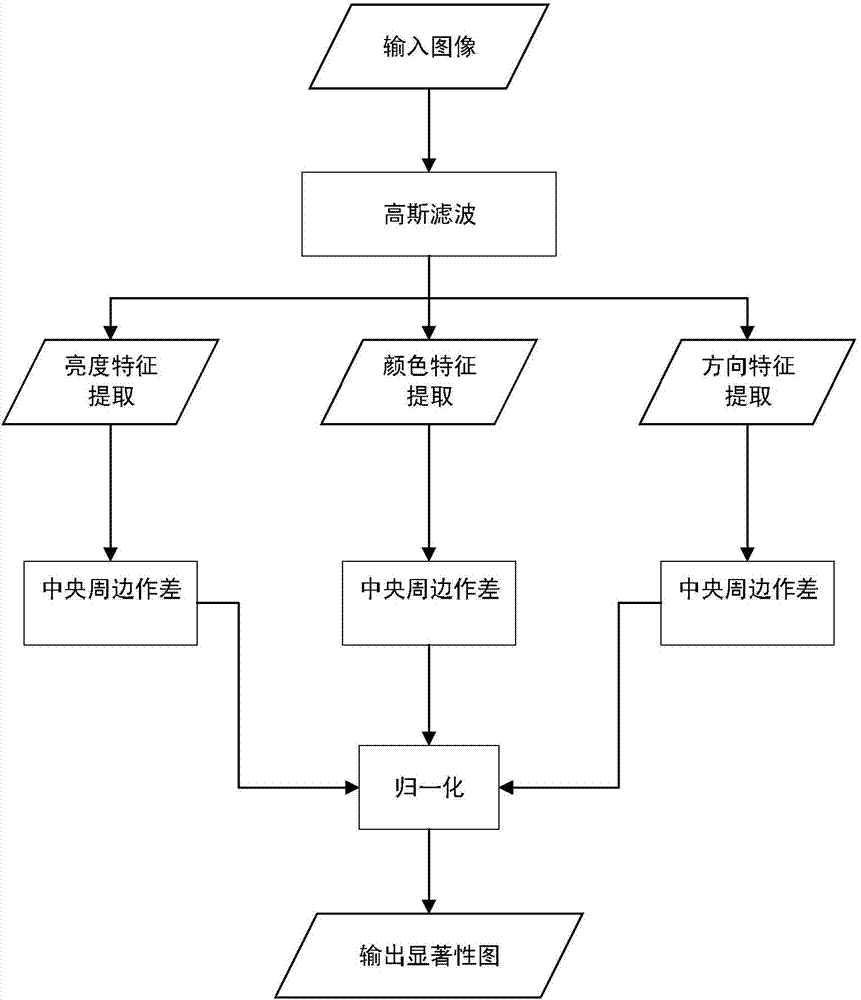
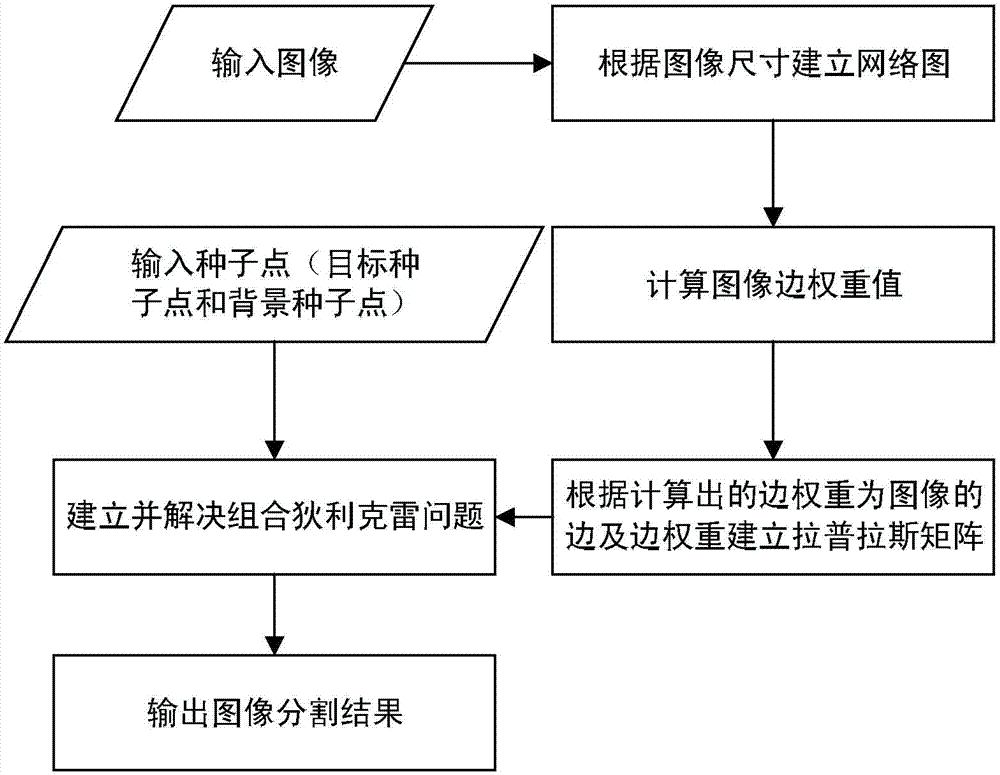
[0098] The visual saliency model is used to extract the saliency of the binocular image, and the three salient features of brightness, color, and direction of each pixel of the binocular image are calculated respectively, and the three salient features are normalized to obtain the weighted saliency of the image picture. Each pixel on the saliency map represents the saliency of the corresponding position in the image. Find the point with the largest pixel value in the picture, that is, the point with the strongest significance, and mark it as a seed point; gradually expand the range around the seed point to find th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0184] Specific embodiment two: the present embodiment is described below in conjunction with the figure, and the difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment one is: the specific process of performing edge detection on the image described in step one by one is:
[0185] Step 111, using 2D Gaussian filter template to perform convolution operation on the binocular image to eliminate the noise interference of the image;
[0186] Step 112, using the difference of the first-order partial derivatives in the horizontal and vertical directions to calculate the gradient magnitude and gradient direction of the pixel on the filtered binocular image I(x, y) respectively, where the partial derivatives in the x direction and y direction The derivatives dx and dy are respectively:
[0187] dx=[I(x+1,y)-I(x-1,y)] / 2 (21)
[0188] dy=[I(x,y+1)-I(x,y-1)] / 2 (22)
[0189] Then the gradient magnitude is:
[0190] D'=(dx 2 +dy 2 ) 1 / 2 (twenty three)
[0191] The gradient d...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0195] Specific embodiment three: The following describes this embodiment in conjunction with the figures. The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that: the use of the visual saliency model to extract the salient features of the binocular image described in step 12 generates a salient feature. The specific process of the characteristic map is as follows:
[0196] Step 121, after binocular image edge detection, superimpose the original image and the edge image:
[0197] I 1 (σ)=0.7I(σ)+0.3C(σ) (25)
[0198] Among them, I(σ) is the original image of the input binocular image, C(σ) is the edge image, I 1 (σ) is the image after superposition processing;
[0199] Step 122: Use the Gaussian difference function to calculate the nine-layer Gaussian pyramid of the superimposed image, wherein the 0th layer is the input superimposed image, and the 1st to 8th layers are respectively formed by using Gaussian filtering and downsampling on the previous...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com