High-ionic-conductivity composite solid electrolyte and preparation method thereof
A solid electrolyte and ionic conductivity technology, which is applied in the manufacture of solid electrolytes, composite electrolytes, electrolyte batteries, etc., can solve the problem of work efficiency and cost that cannot meet the needs of large-scale production, poor crystallinity of LLZO ceramic phase, and low conductivity of the composite system and other problems, to achieve the effects of large-scale promotion and application, improvement of ionic conductivity, and good crystallinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] A method for preparing a composite solid electrolyte with high ionic conductivity, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0030] Step 1. Preparation of LLZO ceramic powder by solid phase sintering method: after mixing lithium hydroxide, lanthanum oxide and zirconia by ball milling, calcining at 900°C for 12 hours; then wet ball milling the calcined powder for 12 hours, the ball milling medium is ethanol, Drying to obtain LLZO ceramic powder with uniform particle size, the average particle size of the obtained powder is about 0.5 μm;
[0031] Step 2. Add 0.1 g of water-soluble isobutylene polymer with a short molecular chain of 5000 to 6000 in 10 g of deionized water as a dispersant, and stir for 10 minutes to mix evenly; Mix ball milling in a type ball mill for 60 minutes; then add 0.3 g of water-soluble isobutylene polymers with molecular chains of 45,000 to 65,000 and 0.3 g of molecular chains of 85,000 to 100,000 respectively, and obtain uniform water-based c...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A method for preparing a composite solid electrolyte with high ionic conductivity, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0040] Step 1. Add 0.4g ammonium polyacrylate in 10g deionized water as a dispersant, stir for 10min to mix evenly; then add 15g LAGP ceramic powder to it, mix and ball mill in a planetary ball mill for 60min; then add 0.8g epoxy Resin and 0.2g tetraethylenepentamine are mixed by ball milling to obtain a uniform water-based ceramic slurry;
[0041] Step 2, immerse the cellulose and polyester template into the water-based ceramic slurry obtained in step 1 to fully infiltrate, then take out the template, solidify and dry at room temperature (25°C);
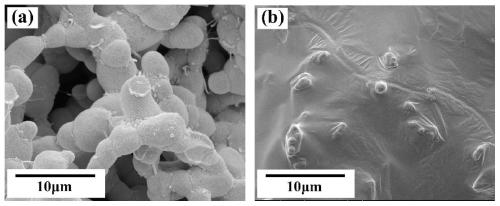
[0042] Step 3. Calcining the sample obtained in step 2 to discharge the cellulose template. The calcination temperature is 550°C for 6 hours to obtain the calcined green body; then continue to heat up to 850°C and sinter for 8 hours to obtain a three-dimensional porous ceramic with a dense skeleton...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
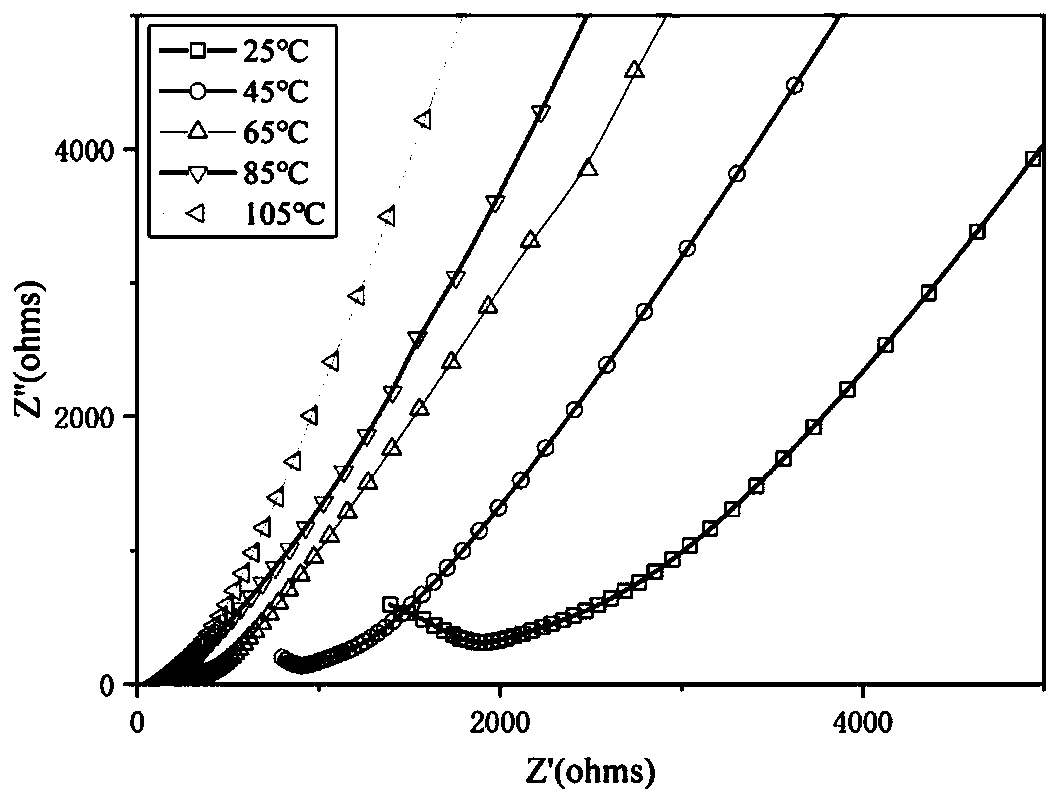
| Ionic conductivity at room temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com