A Lattice-Based Encryption Method
An encryption method and secret technology, which is applied in the field of information security, can solve problems such as lattice password threats, and achieve the effects of clear structure, fast encryption and decryption speed, and reduced bandwidth requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings.
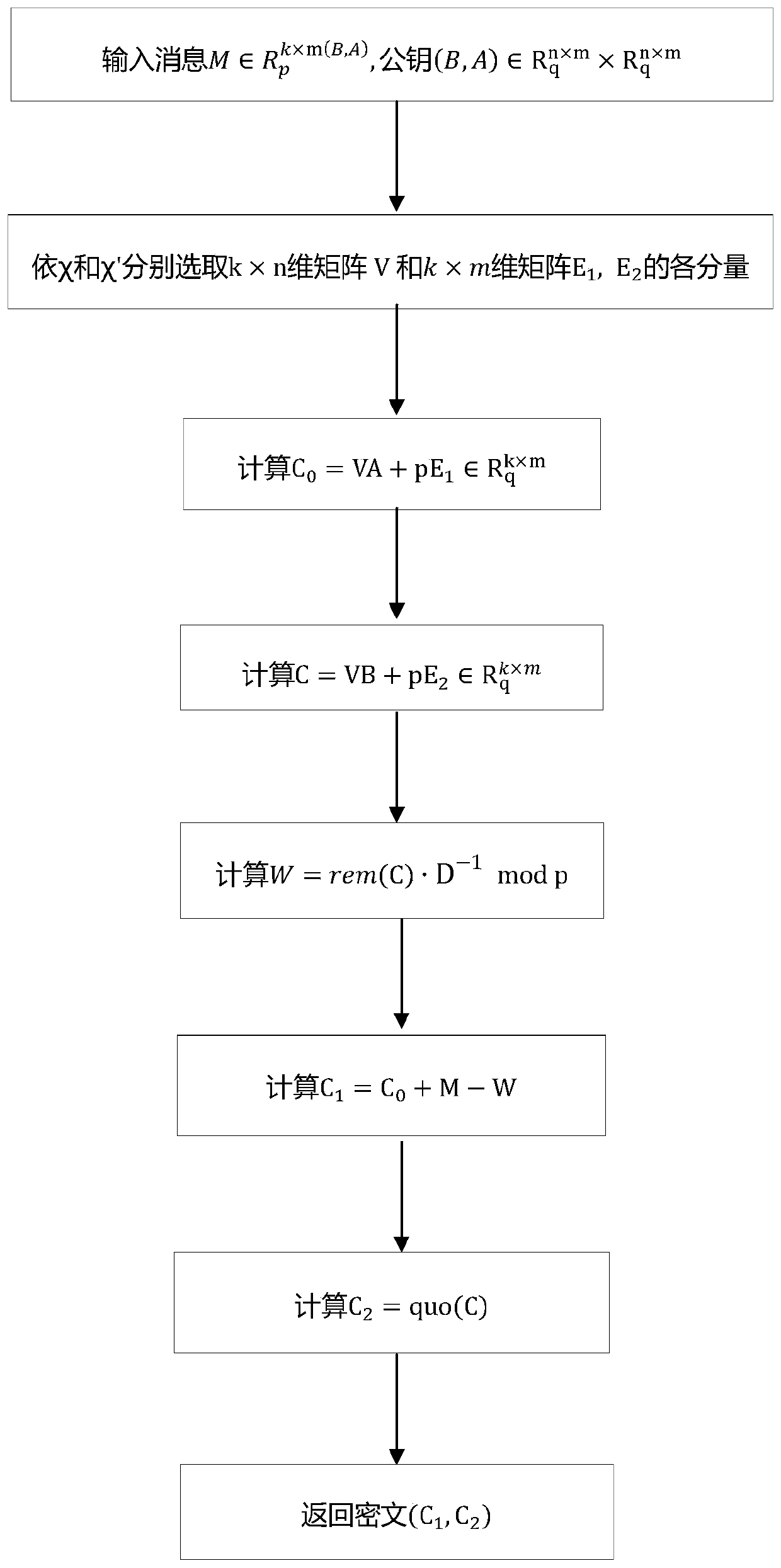
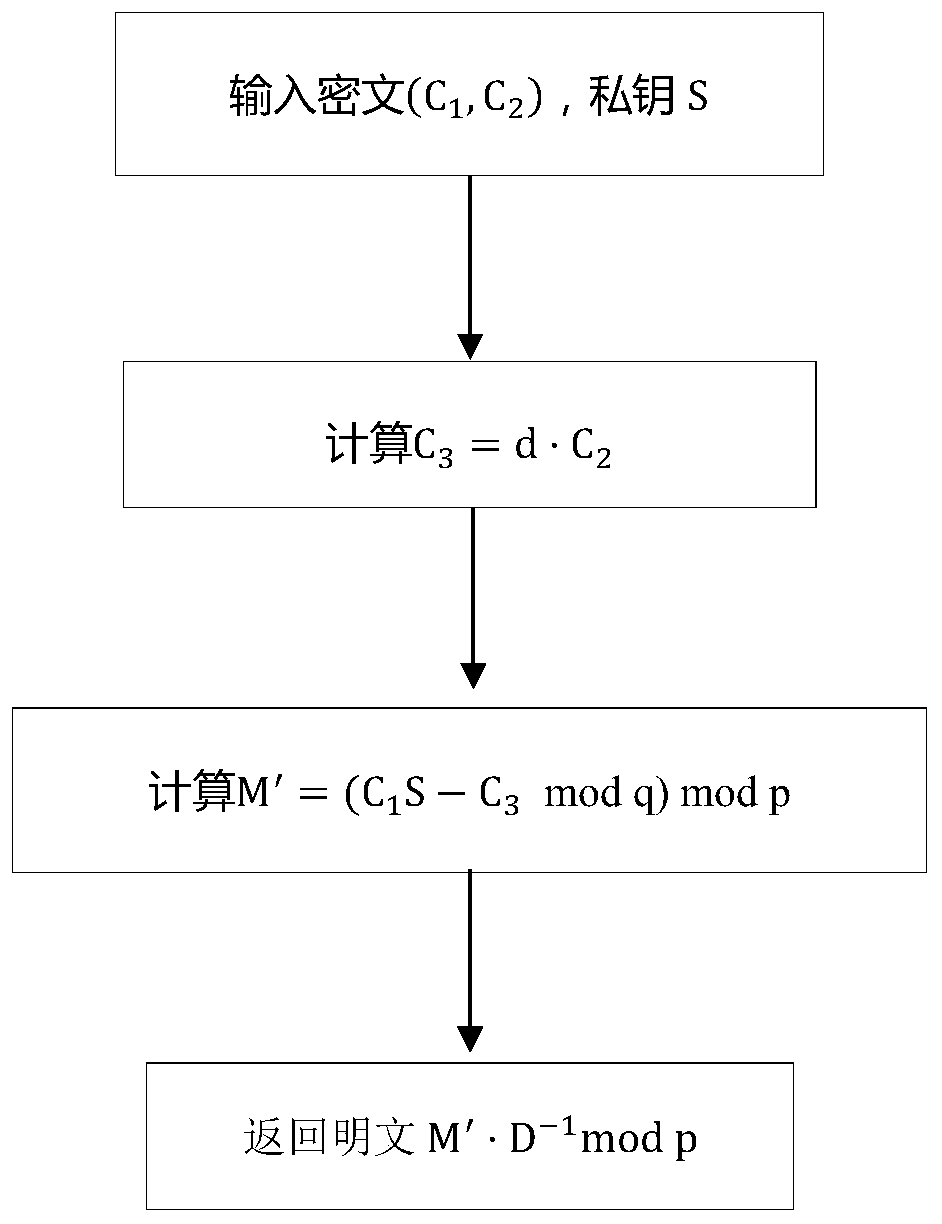
[0047] First generate public parameters: select positive integers p, q, m, n, k, and d, where 1 q =Z q [x] / F(x), R p =Z p [x] / F(x); select ring R q Discrete Gaussian distribution on χ, χ′; choose Any invertible matrix D in, such as the identity matrix, and record it in The inverse in is D -1 :
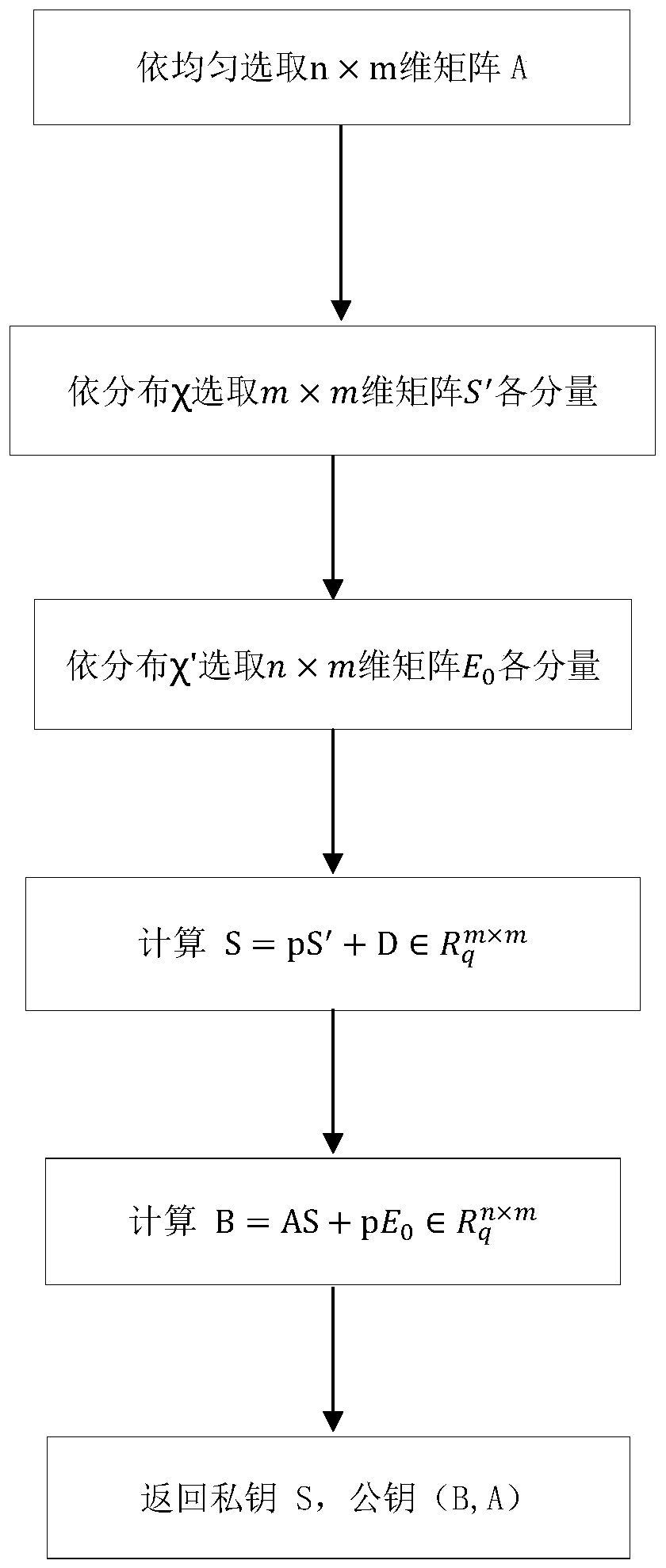
[0048] Such as figure 1 The steps of the key generation method include:
[0049] Step 1: Generate an n×m dimensional matrix A, where the components of A are in the polynomial ring R q Select evenly on top.
[0050] Step 2: Generate m×m dimension R q S′ on the square matrix, the components of the square matrix follow the ring R q The distribution on χ is extracted.
[0051] Step 3: Generate n×m dimension R q Phalanx E 0 , The components of the square matrix follow the ring R q The distribution on χ′ is extracted.
[0052] Step 4: Calculation
[0053] Step 5: Calculation
[0054] Step 6: Re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com