Analysis method for detecting microorganisms by using metagenome or metatranscriptome
A macrotranscriptome and metagenome technology, which is applied in the field of analysis of microorganisms using metagenome or macrotranscriptome, can solve the problems of speeding up the analysis speed, poor specificity, and many false positives in the test results, so as to reduce the search speed and avoid redundant The effect of searching and ensuring integrity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] Embodiment 1 A kind of microbial detection and identification analysis method based on metagenomic sequencing
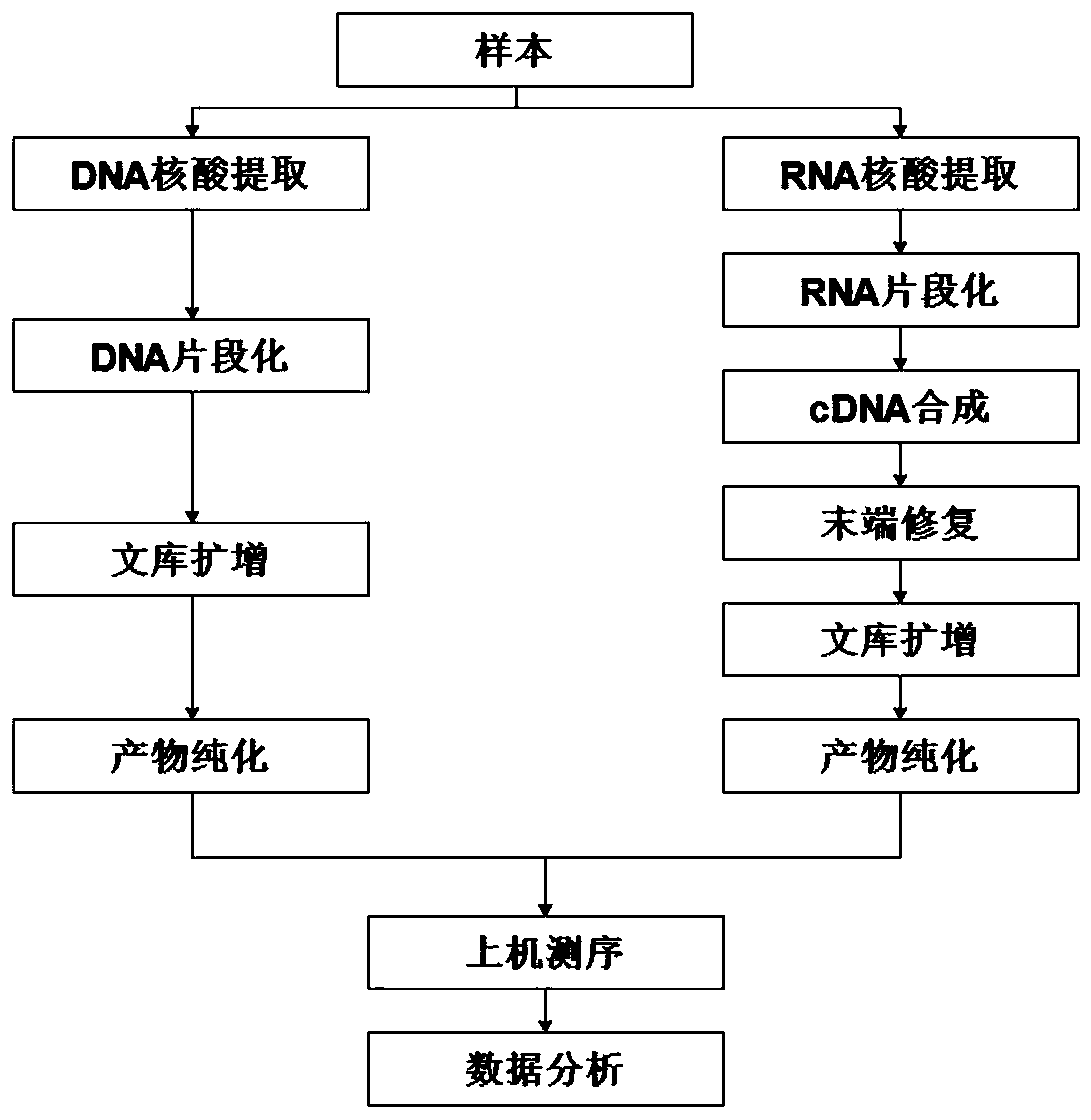
[0098] 1. Obtain nucleic acid from the sample
[0099] Process such as figure 1 As shown, standard specimens were collected, and RNA extraction and DNA extraction were performed respectively according to requirements (when it is expected to detect that DNA is a sample of genetic material, extract DNA; when it is expected to detect that RNA is a sample of genetic material, extract RNA). DNA nucleic acid was extracted using QIAamp cador Pathogen Mini Kit (54104, giagen), and RNA nucleic acid was extracted using miRNeasy Serum / Plasma Kit (217184, giagen). After the nucleic acid is extracted, the quality of the nucleic acid will be tested. If the quality of the nucleic acid does not meet the quality control standards (Table 1), the nucleic acid needs to be re-extracted.
[0100] After the nucleic acid is extracted from the sample, the DNA is fragmented using ult...
Embodiment 2
[0131] Embodiment 2 A kind of microbial detection and identification analysis method based on metagenomic sequencing
[0132] 1. Experimental method
[0133] 1. Sample preparation
[0134] Mixed sample Mix1 is configured. Mix1 is cultivated, concentration determined, mixed and identified. The titer added to the sample is 3.2×10 8 TCID 50 / mL of human parainfluenza virus 2, 3.2×10 7 TCID 50 / mL of human parainfluenza virus 1, 6.3×10 5 TCID 50 / mL of human respiratory syncytial virus type B, 3.2×10 8 TCID 50 / mL of human respiratory syncytial virus type A mixed. Mix1 spiked with human interference: HeLa cells at a concentration of 2.5×10 5 pieces / ml.
[0135] Mix1 reference substance was diluted according to the concentration gradient (stock solution, 1:10 1 Dilution, 1:10 2 Dilution, 1:10 3 Dilution) to test 4 samples (named Mix1-0, Mix1-1, Mix1-2 and Mix1-3), and the amount of sequencing data is 13.6M reads. Then, carry out data volume gradient analysis with stoc...
Embodiment 3
[0154] Embodiment 3 method scope of application detection
[0155] 1. Experimental method
[0156] 1. Sample preparation
[0157] Four types of standard substances are used to detect the detection rate of the present invention to medium and low concentration target microorganisms. The four types of standard products are divided into: RNA virus standard products, DNA virus standard products, bacterial standard products, and fungal standard products.
[0158] RNA virus standard in 2.5×10 5 / mL Hela cells as matrix, add 3.2×10 2 TCID 50 Respiratory syncytial virus B / L, 3.2×10 3 TCID 50 Parainfluenza virus type 1 (PIV1) per L, 3.2×10 3 TCID 50 / L parainfluenza virus type 2 (PIV2) three kinds of RNA viruses to make RNA virus standard.
[0159] DNA virus standard in 2.5×10 5 / mL Hela as matrix, add 3.8×10 3 TCID 50 / L adenovirus C.
[0160] Bacterial standards are 2.5×10 5 / mL Hela cells as matrix, add 4.9×10 3 CFU / mL of Enterococcus faecium, 7.8×10 3 Escherichia col...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com