A genetically engineered bacteria producing sucrose phosphorylase
A technology of sucrose phosphorylase and genetically engineered bacteria, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, and can solve the problems of low expression level, low yield of sucrose phosphorylase, and difficulty in meeting the requirements of industrial applications.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
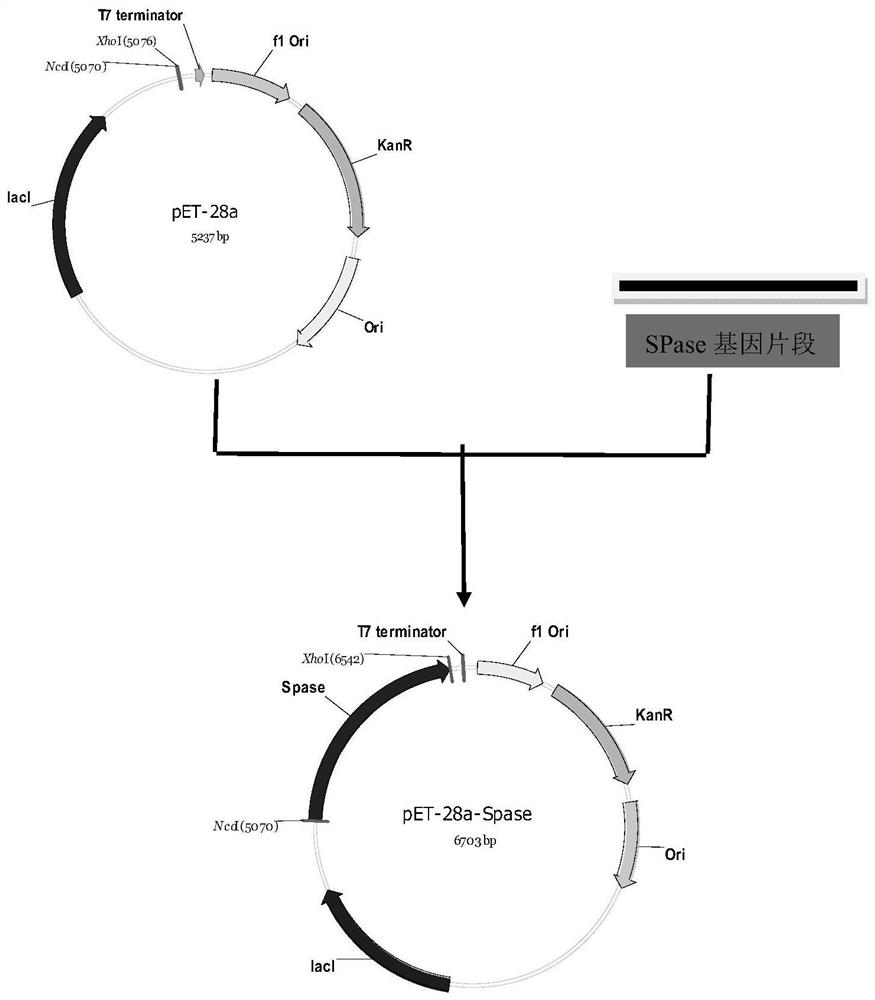
[0023] The construction of embodiment 1 Escherichia coli SPLO1 genetically engineered bacteria
[0024] 1. Primer design
[0025] According to the SPase gene sequence (GenBank Accession NO.D90314) of Leuconostoc mesenteroides ATCC12291, a pair of primers for amplifying the SPase gene were designed with DNAMAN, NcoI and XhoI restriction enzyme sites (underlined) were introduced respectively, and protective bases were added. The upstream and downstream primers are as follows:
[0026] Upstream primer: 5'-AATTACCG CCATGG ATGGAAATTCAAAACAAAGC-3'
[0027] Downstream primer: 5'-AATTACCG CTCGAG TTAGTTCTGA GTCAAATTAT C-3’
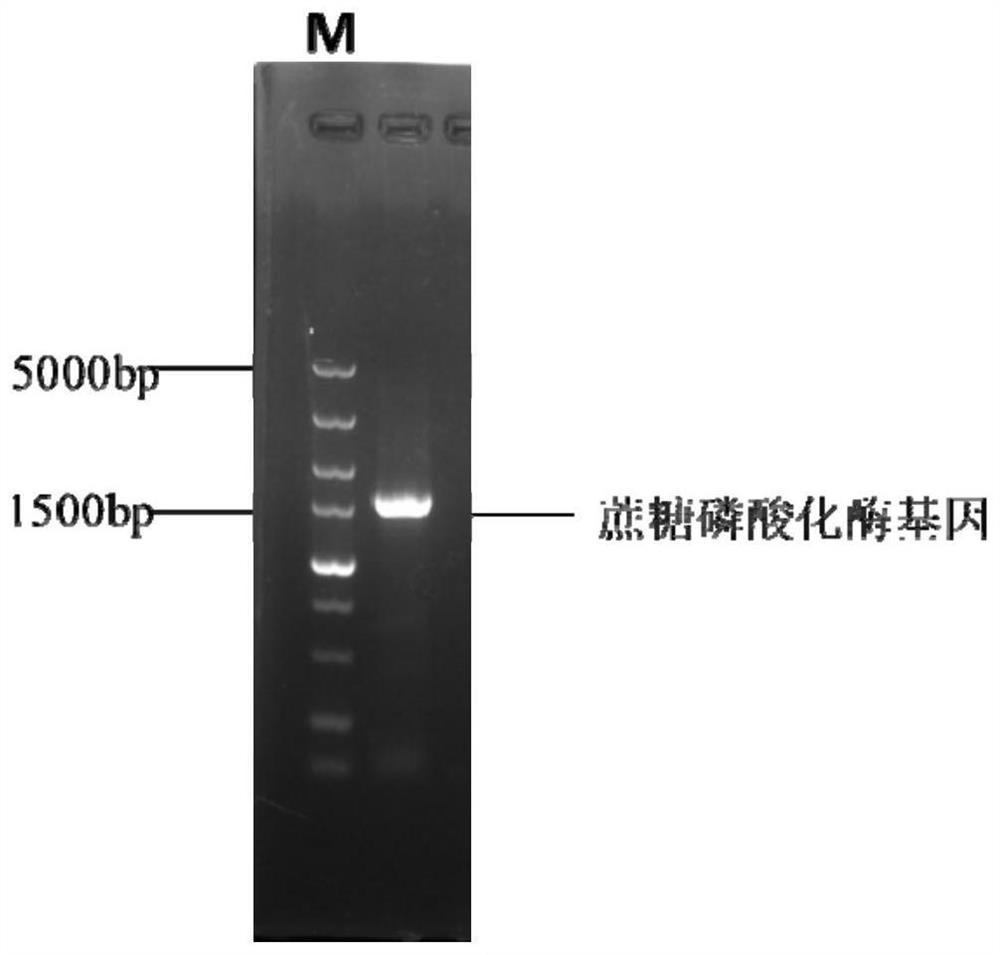
[0028] 2. PCR amplification of Leuconostoc enteromenis SPase fragment
[0029] ⑴ Leuconostoc enterolis genome DNA extraction
[0030] ① Streak and activate Leuconostoc mesenteroides ATCC 12291, inoculate a single colony in 5ml MRS medium and culture overnight at 30°C;
[0031] ②Collect 1 mL of the bacterial solution by centrifugation to collect the bacteri...
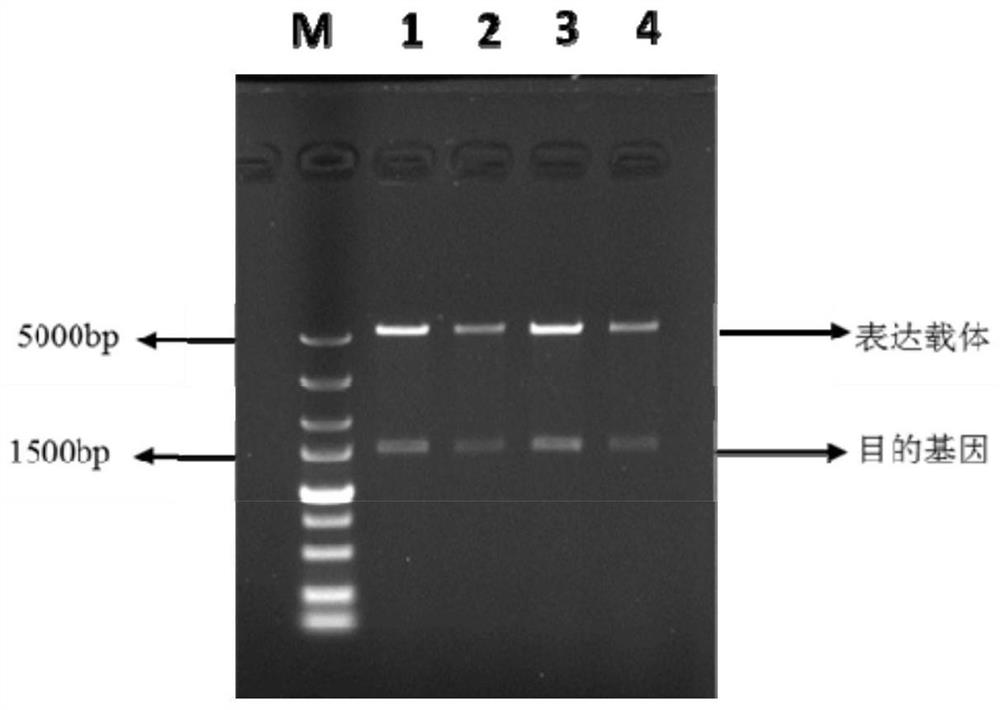
Embodiment 2
[0040] The preparation of embodiment 2 recombinant sucrose phosphorylase
[0041] Inoculate a single colony of the recombinant strain in the LB liquid medium containing Kana, cultivate overnight at 37°C, 200r / min, and insert it into the TB liquid medium containing Kana at 37°C, 200r / min Min culture to bacterial density OD 600 After reaching 0.6, add IPTG inducer and induce at 25°C, 200r / min for 24h, then collect the bacterial liquid. Centrifuge the bacterial liquid in a low-temperature refrigerated centrifuge at 7000 r / min at 4°C for 15 minutes to collect the bacterial cells. Bacteria use 50mmol / L K 2 HPO 4 / KH 2 PO 4 The bacterial cells were collected after washing twice with buffer solution (pH6.5). Add the collected wet bacteria to 50mmol / L K 2 HPO 4 / KH 2 PO 4 Buffer solution (pH 6.5) was used to prepare bacterial suspension, placed on ice and fixed, and then the bacterial cells were disrupted by ultrasonic waves. Ultrasonic breaker working time: 2s, intermitten...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The enzyme activity assay of embodiment 3 recombinant sucrose phosphorylase
[0044] In phosphate buffer, sucrose phosphorylase can catalyze sucrose and inorganic phosphoric acid to generate glucose-1-phosphate and D-fructose. The sucrose hydrolysis reaction can be carried out first, and then the content of the generated D-fructose can be detected by DNS to determine the sucrose phosphate [Choi H.C.,Seo D.H.,Jung J.H.,et al.Developmemt of new assay for sucrose phosphorylase and its application to the characterization of Bifidobacterium longumSJ32 sucrose phosphorylase[J].Food Science and Biotechnology,2011,20(2):813 .].
[0045] The enzyme activity determination method refers to [Wu Jing, Wu Dan, Zhu Jie, et al. A recombinant Bacillus subtilis expressing sucrose phosphorylase derived from L. mesenteroides. Chinese invention patent application, application number: 201710637427.6, publication number: CN107236696A]. The assay steps include: 500 μL of 5% sucrose solution, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com