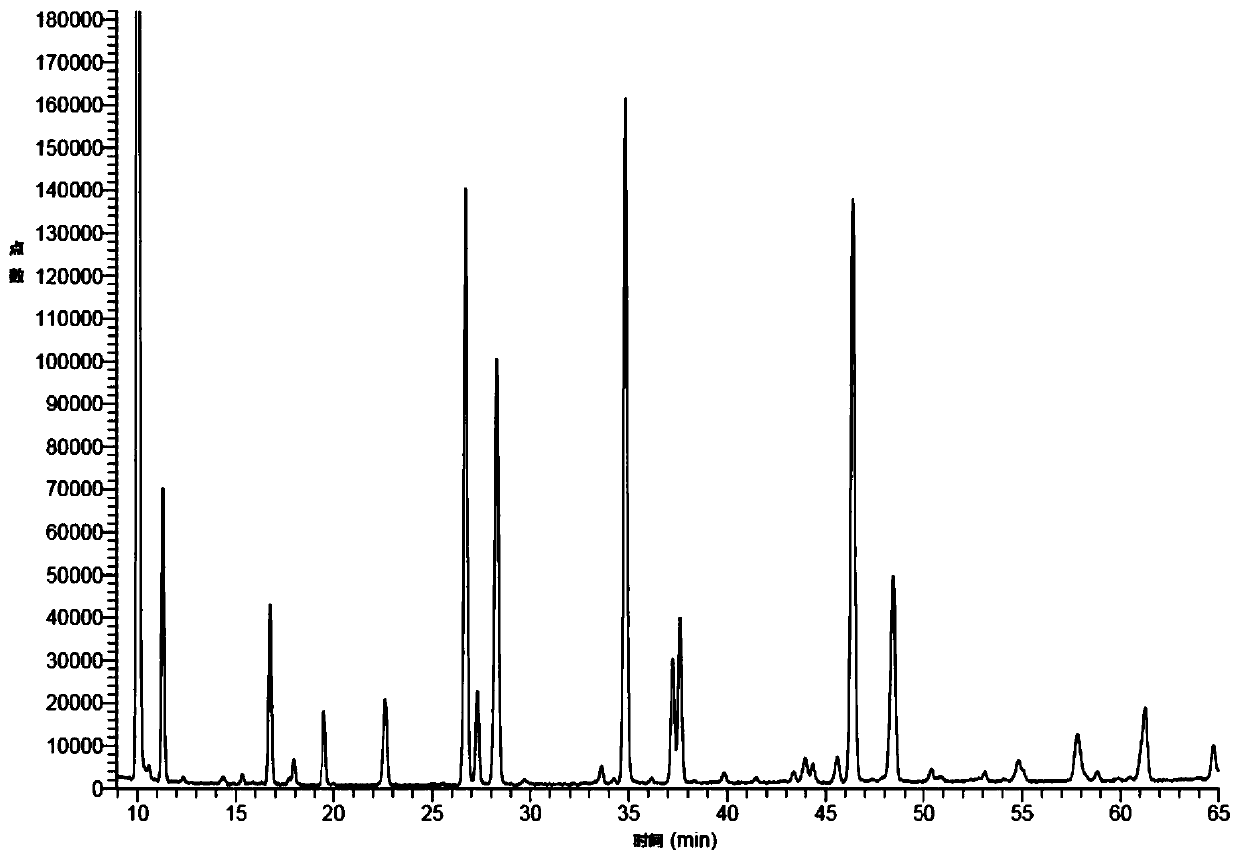
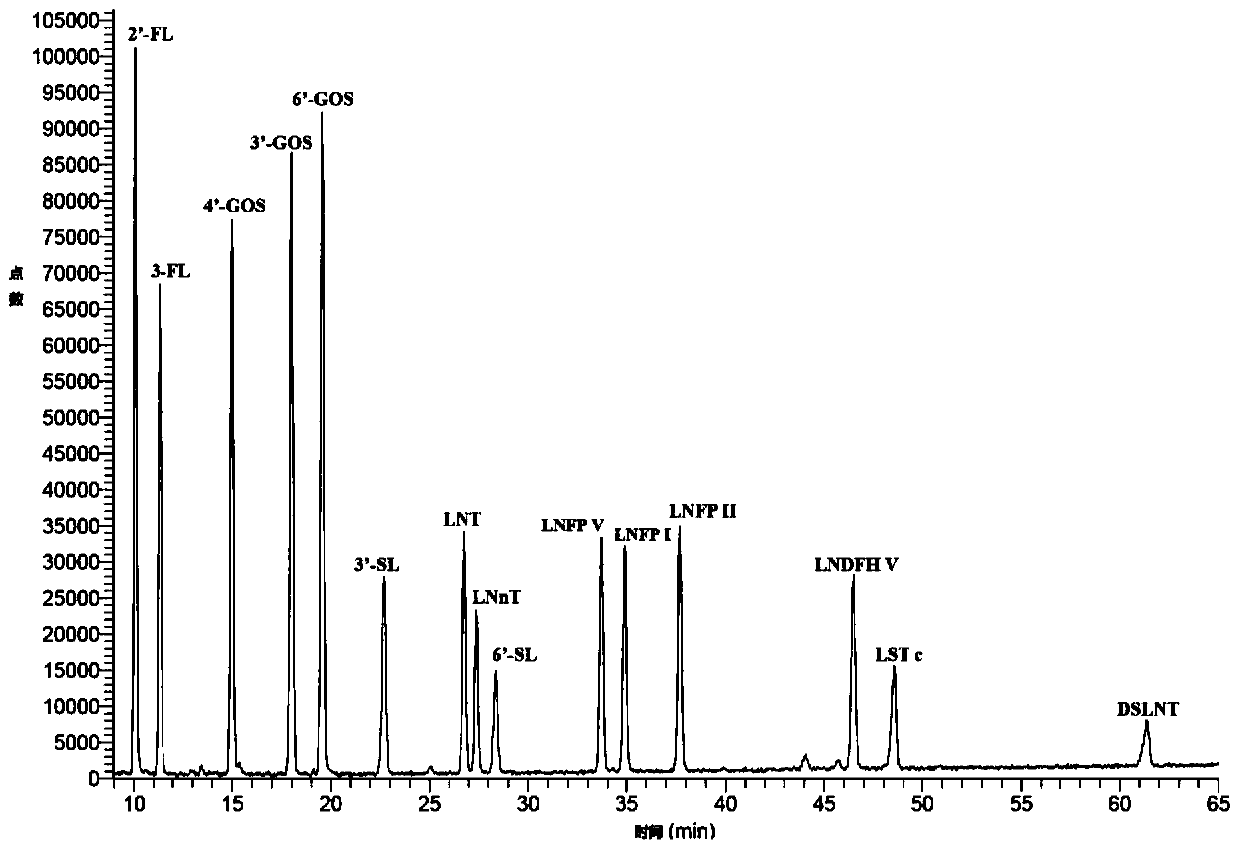
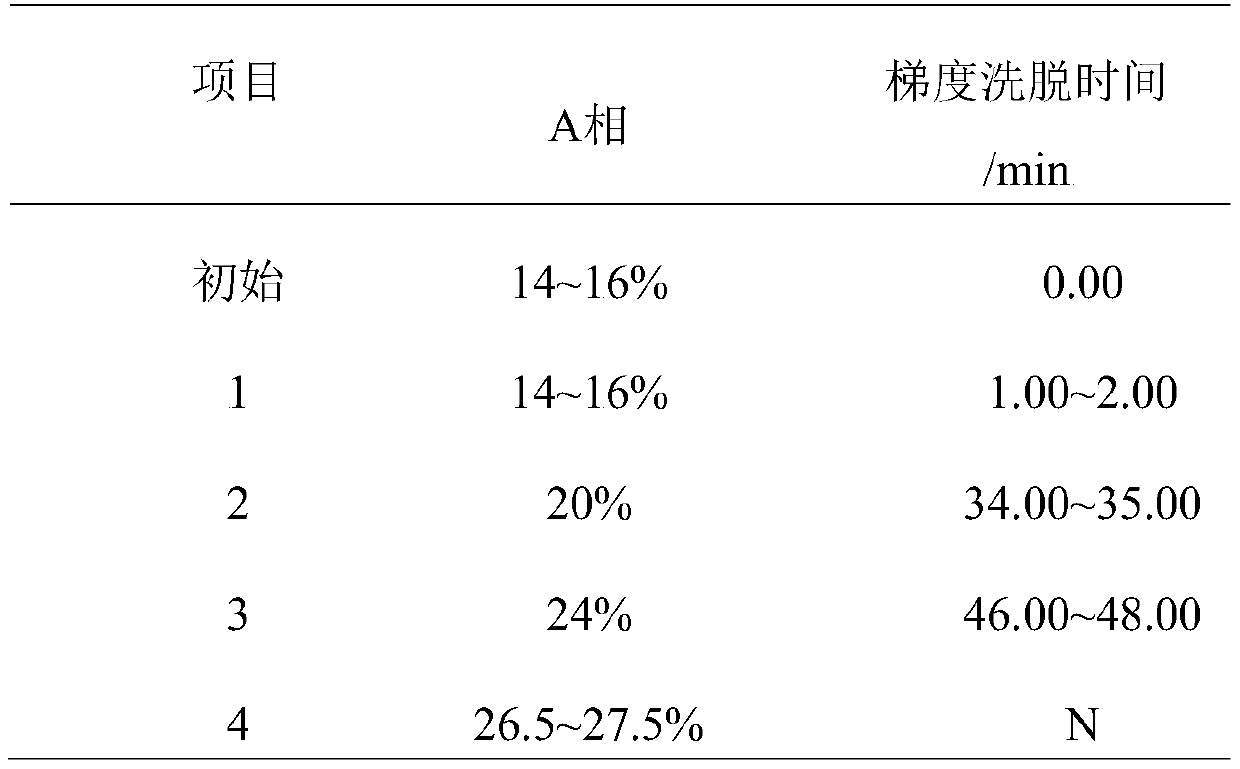
High-flux quantitative determination method for free oligosaccharide in milk
A quantitative determination and oligosaccharide technology, applied in the field of chemical analysis, can solve the problems of ion source, mass analyzer, high detection cost, high milk fat volume content that are easy to contaminate mass spectrometry, achieve stable chromatographic baseline, good separation effect, The effect of good separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0057] A high-throughput quantitative assay method for free oligosaccharides in milk, comprising the following steps:
[0058] 1) Separation of free oligosaccharides in breast milk
[0059] Thaw breast milk (colostrum) to room temperature, vortex to mix, take 10 microliters into a 2 ml centrifuge tube, add 990 microliters of ultra-pure water, vortex to mix, and follow the following two steps Either of:
[0060] The first method: transfer the solution obtained after vortex mixing to an ultrafiltration centrifuge tube (ultrafiltration membrane molecular cut-off 10kDa), centrifuge for 20min, and the obtained permeate is a free oligosaccharide sample solution;
[0061] The second method: transfer the solution obtained after vortexing to a centrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 8000 g for 10 min at 4° C., and the lower layer is the free oligosaccharide sample solution.
[0062] 2) 2-AB fluorescently labeled oligosaccharides (derivatized)
[0063] Take 100 microliters of the free oli...
experiment example 2
[0075] A high-throughput quantitative assay method for free oligosaccharides in milk, comprising the following steps:
[0076] 1) Separation of free oligosaccharides in breast milk
[0077] Thaw breast milk (colostrum) to room temperature, vortex to mix, take 50 microliters into a 2 ml centrifuge tube, add 950 microliters of ultra-pure water, vortex to mix, and follow the following two steps Either of:
[0078] The first method: the solution obtained after vortex mixing is transferred to an ultrafiltration centrifuge tube (ultrafiltration membrane molecular cut-off 10kDa), centrifuged for 25min, and the obtained permeate is a free oligosaccharide sample solution;
[0079] The second method: transfer the solution obtained after vortexing to a centrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 10000 g for 10 min at 4° C., and the lower layer is the free oligosaccharide sample solution.
[0080] 2) 2-AB fluorescently labeled oligosaccharides (derivatized)
[0081]Take 100 microliters of the f...
experiment example 3
[0094] A high-throughput quantitative assay method for free oligosaccharides in milk, comprising the following steps:
[0095] 1) Separation of free oligosaccharides in breast milk
[0096] Thaw the breast milk (colostrum) to room temperature, vortex to mix, take 100 microliters into a 2 ml centrifuge tube, add 900 microliters of ultra-pure water, vortex to mix, and follow the following two steps Either of:
[0097] The first method: the solution obtained after vortex mixing is transferred to an ultrafiltration centrifuge tube (ultrafiltration membrane molecular cut-off 10kDa), centrifuged for 30min, and the obtained permeate is a free oligosaccharide sample solution;
[0098] The second method: transfer the solution obtained after vortexing to a centrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 6000 g for 10 min at 4° C., and the lower layer is the free oligosaccharide sample solution.
[0099] 2) 2-AB fluorescently labeled oligosaccharides (derivatized)
[0100] Take 100 microliters of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com