Fluorescent probe for detecting viscosity, and preparation method and application thereof
A fluorescent probe and viscosity technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of few intracellular imaging, measurement of intracellular viscosity, etc., and achieve the effect of significant color change, short synthesis steps, and accurate positioning.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
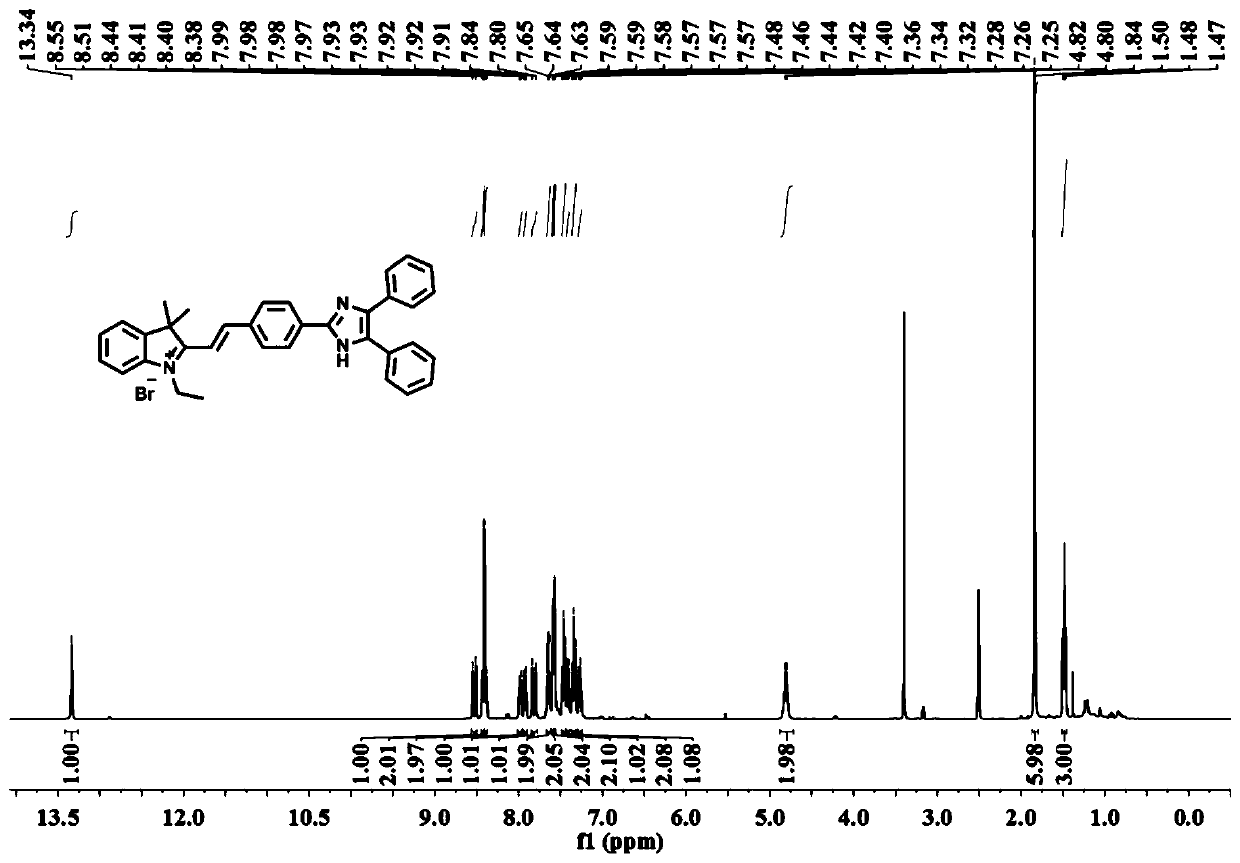
[0028] Example 1 Synthesis of Fluorescent Probes
[0029] (1) Synthesis of compound 1: 2,3,3-trimethyl-3H-indole (1 eq), bromoethane (1.5 eq) were dissolved in acetonitrile, and heated to 60 ℃ for 12 h under reflux. After the reaction was completed, the reactant was spin-dried, diethyl ether was added to the residue, suction filtration was performed with a Buchner funnel, and the obtained solid was washed with diethyl ether to obtain compound 1 with a yield of 56% as a purple-red solid. Without further purification, the next reaction can be carried out directly:
[0030] ;
[0031] (2) Synthesis of Compound 2: Dibenzoyl (1 eq) and ammonium acetate (8 eq) were added to acetic acid, terephthalaldehyde (1 eq) was added under nitrogen protection, and reacted at 110 °C for 12 h. TCL tracking monitors the response. After the reaction was completed, the reactant was cooled to room temperature, poured into ice water to precipitate a solid, suction filtered with a Buchner funnel, ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Responses of fluorescent probes to solutions of different viscosities
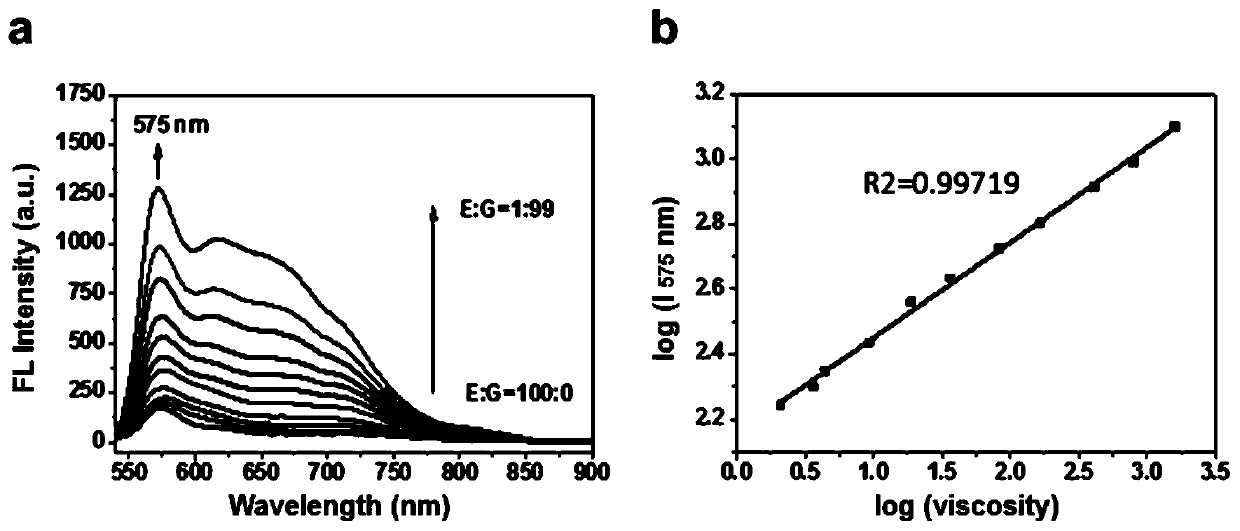
[0037] The fluorescent probe RM-V prepared in Example 1 was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to prepare a 1.0 mM probe stock solution. The solution system used is a mixed solvent of ethanol and glycerol. Use ethanol and glycerol to make different ratios (10:90; 20:80; 30:70; 40:60; 50:50; 60:40; 70:30; 80:20; 90:10; 95:5 ) viscosity test solution. Take 2 mL series of viscosity test solutions, add 20 μL probe mother solution to each, the final concentration of the probe in the test system is 10.0 μM, use 530 nm for excitation, and its fluorescence ratio at 575 nm (I / I 0 ) shows a good linear relationship with the logarithm of the solution viscosity. Such as figure 2 Shown, wherein, a is the change of the fluorescence spectrum of RM-V with the increase of glycerol content in the glycerol / ethanol system under the excitation of the probe at 530 nm; b is the log of the probe RM-V (...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3 Selectivity of Fluorescent Probes to Various Molecules and Ions at Different Viscosities
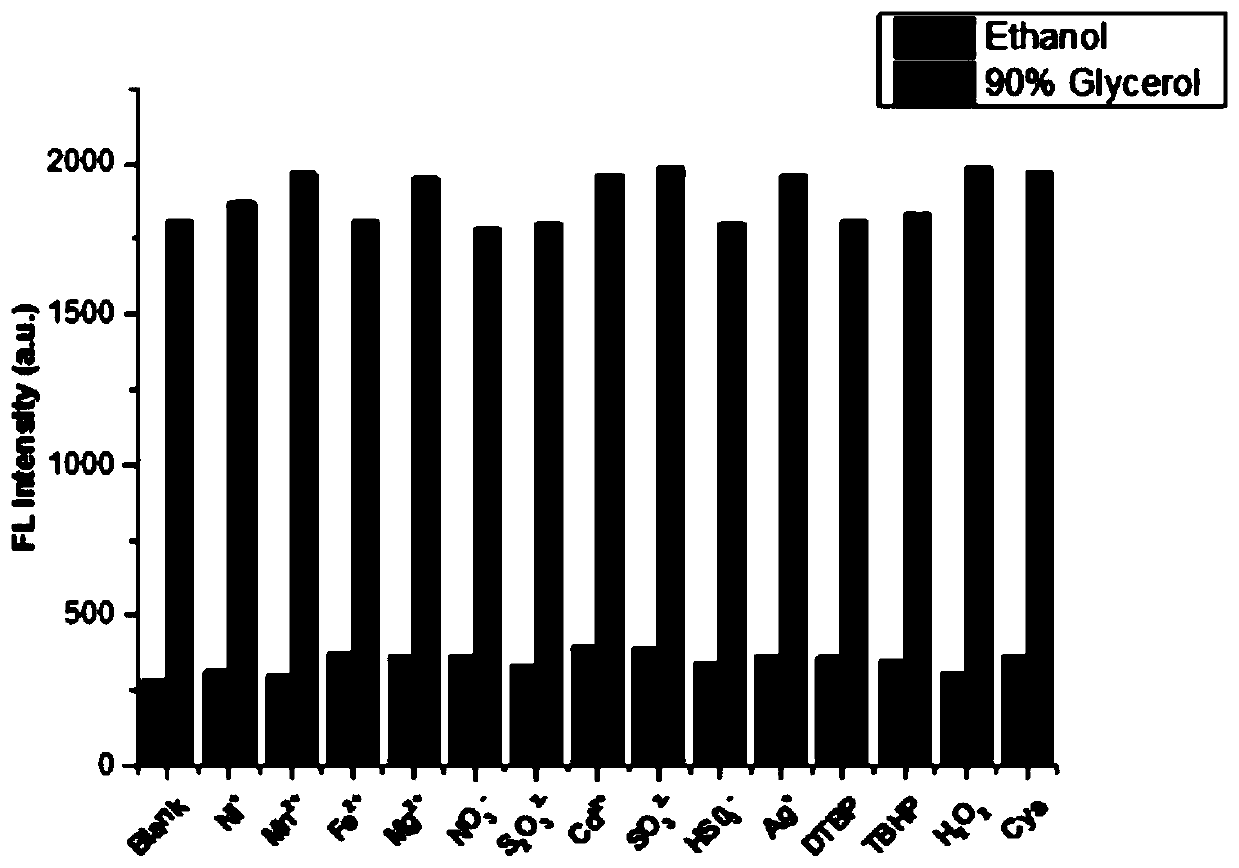
[0039] Take the probe mother liquor prepared in Example 2, and add two systems respectively, one system is pure ethanol solution, the other system is ethanol; glycerol is a mixed solution of 10:90. Ni was added to the two systems respectively + , Mn 2+ , Fe 2+ , Mg 2+ , NO 3 - , S 2 o 3 2- , Cd 2+ , SO 3 2- , HSO 3 - , Ag + , DTBP, TBHP, H 2 o 2 , Cys. Use 530 nm for excitation, detection wavelength 575nm, get the fluorescence spectrum, and process the spectrum data into a histogram, such as image 3 shown. It can be found that none of these ions or molecules can cause a significant change in the fluorescence intensity of the probe in viscous / non-viscous solutions.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com