Iron and manganese oxide-charcoal composite material and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of iron-manganese oxides and composite materials, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of poor adsorption performance, increase the contact area, enrich the morphological structure, and enhance the electrostatic adsorption effect Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
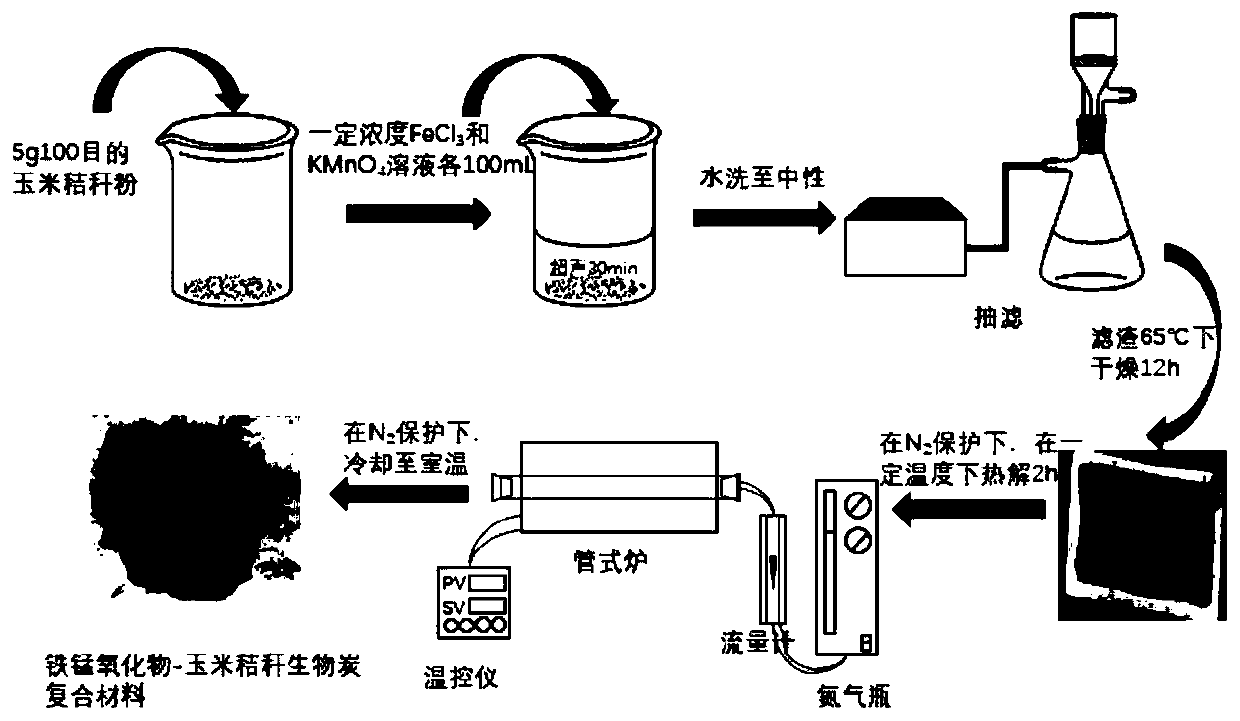
[0043] Weigh 4 parts of 5g 100-mesh corn stalk powder into a beaker, and then add modifiers (modifier 1: 100 mL of ferric chloride with a concentration of 0.15 mol / L and 100 mL of potassium permanganate with a concentration of 0.05 mol / L Modifier 2: concentration is 0.05mol / L ferric chloride 100mL and concentration is 0.05mol / L potassium permanganate 100mL; Modifier 3: concentration is 0.05mol / L ferric chloride 100mL and concentration is 0.15 mol / L potassium permanganate 100mL; modifier 4: ferric chloride 100mL with a concentration of 0.05mol / L and potassium permanganate 100mL with a concentration of 0.25mol / L), the corresponding iron, manganese and corn stalk powder theory The mass ratio is 3:1:18, 1:1:18, 1:3:18, 1:5:18. Soak for 12-14 hours after ultrasonic mixing, then wash the soaked mixture until neutral and dry at 60-70°C for 12 hours to obtain the first product 1, the first product 2, the first product 3, and the first product 4 in sequence.
[0044] The first product...
Embodiment 2
[0046] In this example, the iron-manganese oxide-biochar composite materials 1-4 prepared in Example 1 are used to treat Cr(VI)-containing wastewater, including the following steps:
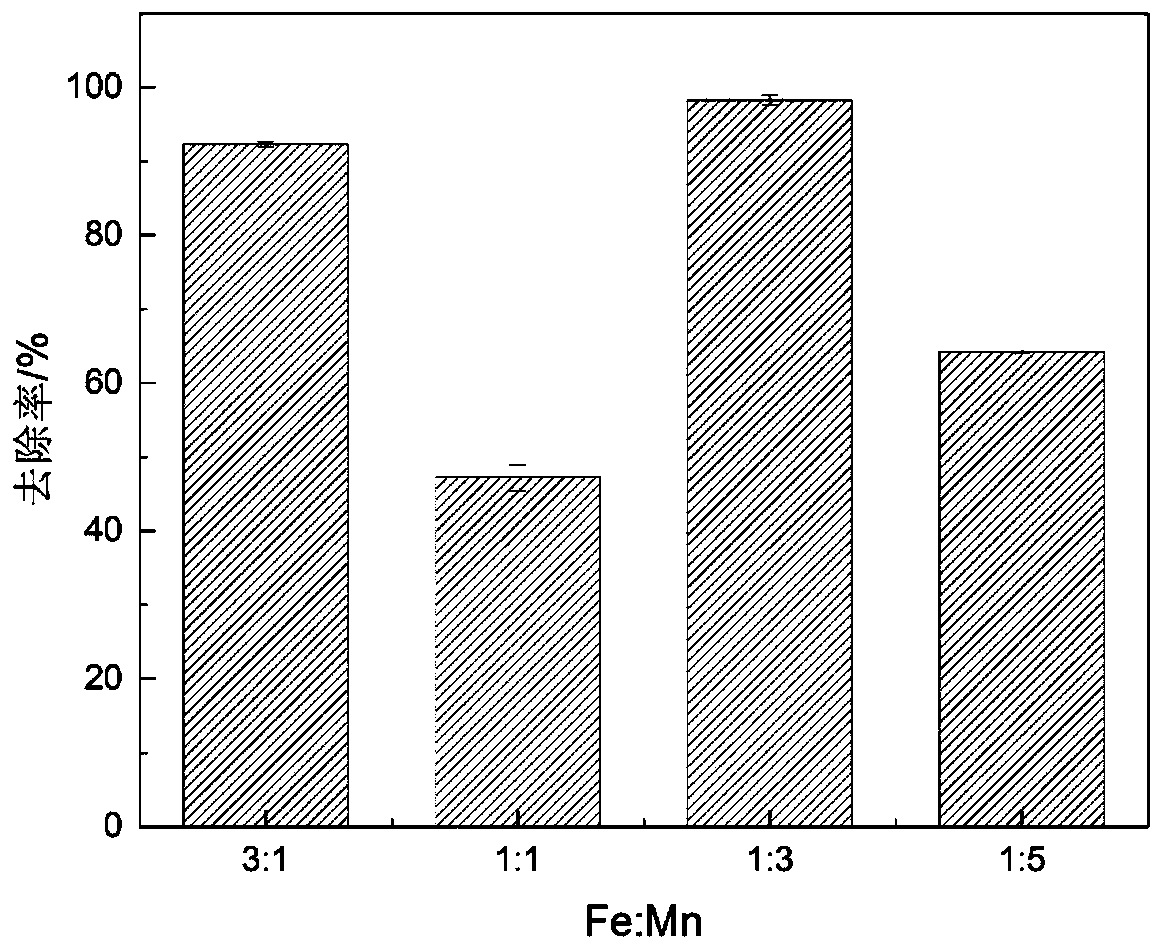
[0047] Prepare a 100mg / L Cr(VI) solution, adjust the pH to 2 with 1mol / L NaOH and HCl, and measure 4 parts of 50ml of the above 100mg / L Cr(VI) solution with a volumetric flask. The above iron-manganese oxide-biochar composite materials 1-4 were added respectively, and the dosage of the iron-manganese oxide-biochar composite material was 2 g / L. They were placed in constant temperature shaking at 30°C. The speed of the constant temperature oscillator is 120r / min, and the oscillation time is 24h. After the reaction, the supernatant solution was taken, and the remaining Cr(Ⅵ) content in the wastewater was measured by ultraviolet spectrophotometry, and the removal rate was calculated.
[0048] Such as figure 2 It can be seen that the removal rate of Cr(Ⅵ) by iron-manganese oxide-biochar composite ...
Embodiment 3
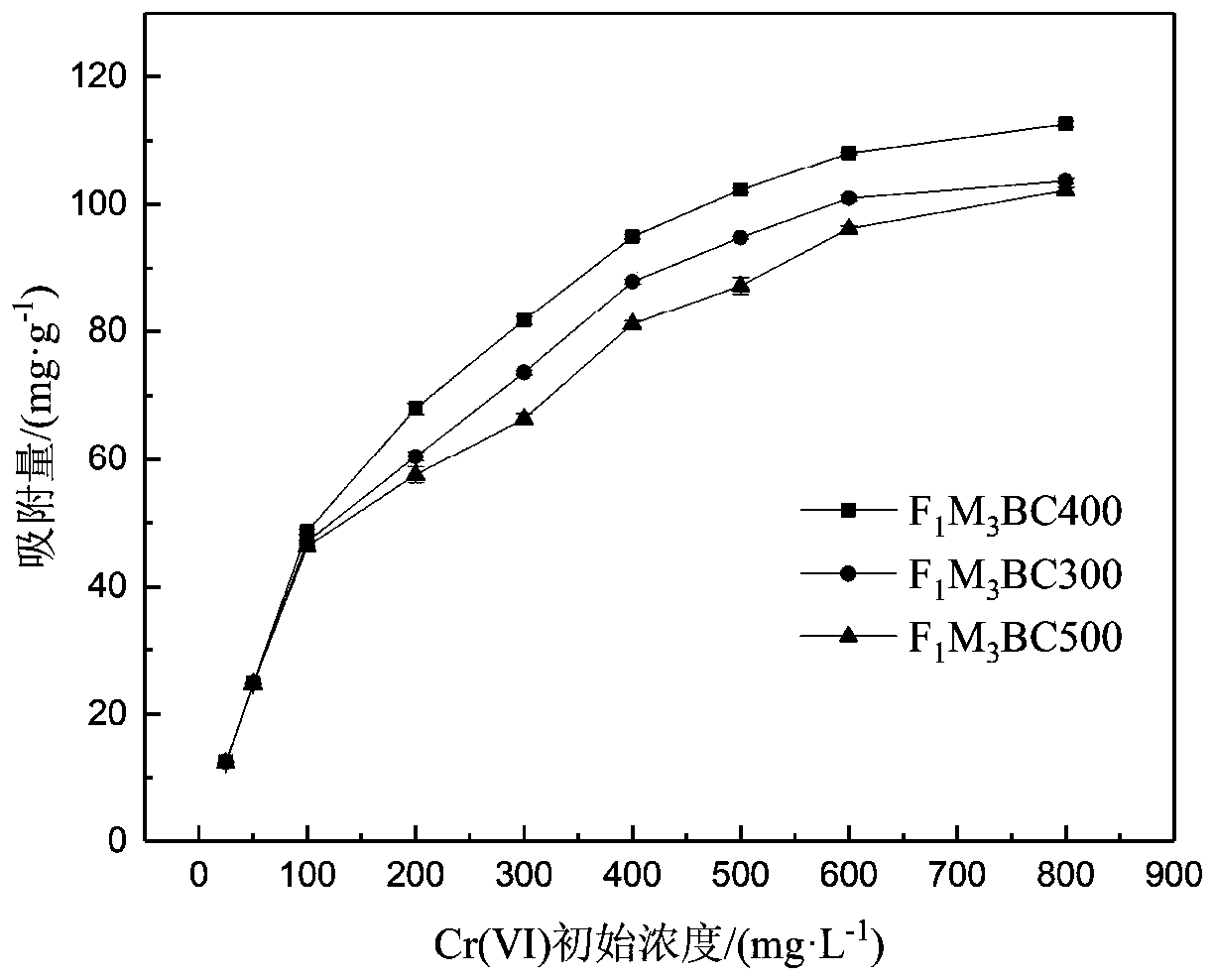
[0050] In this embodiment, the first product 3 prepared in Example 1 is put into a tube furnace, and the temperature is 80-160 cm 3 Nitrogen was introduced at a rate of 5-8 °C / min, and the temperature was increased from room temperature to 300 °C, 400 °C, and 500 °C at a rate of 5-8 °C / min, and pyrolyzed at this temperature for 2 hours, and then cooled to room temperature to obtain 3 different The iron-manganese oxide-biochar composites prepared at the pyrolysis temperature were labeled as F1M3BC300, F1M3BC400, and F1M3BC500, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com