Application of fluorescent carbon dots based on N-methyl o-phenylenediamine hydrochloride in lysosome target
A technology of methyl o-phenylenediamine hydrochloride and fluorescent carbon dots, which is applied in the direction of fluorescence/phosphorescence, luminescent materials, preparations for in vivo tests, etc., can solve the problems of long cultivation time, achieve high quantum yield, Good light stability and easy handling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The steps for the synthesis of carbon dots are as follows:
[0037] First, weigh 0.009 g (0.05 mmol) of N-methyl-1,2-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride solid powder, dissolve it in 10 mL of absolute ethanol, and transfer the solution to a high-pressure PTFE lined In the reaction kettle, place the reaction kettle in an oven at 180°C and reflux for 12 h, and then cool the reaction kettle to room temperature to obtain a brown-black solution. Then the crude product was purified by silica gel column chromatography. Using ethyl acetate as the eluent, the solvent was removed under vacuum and further dried to finally obtain purified carbon dots.
Embodiment 2
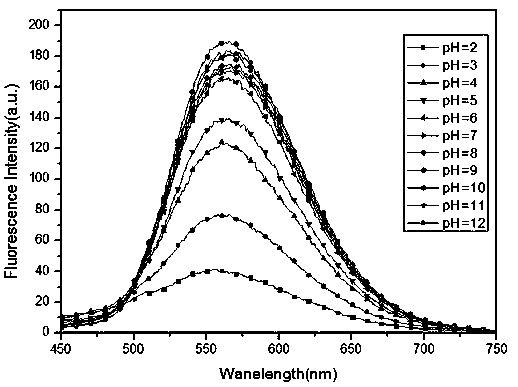
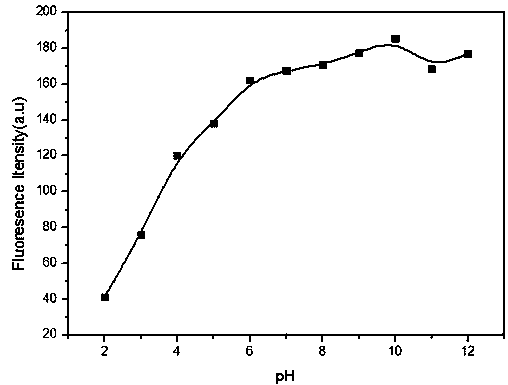
[0039] Changes in fluorescence intensity of carbon dots in different solvents
[0040] Add 2 mL of different solvents to the cuvette, add 8 µL of carbon spot storage solution, and measure the fluorescence spectrum. The experimental results show that: as shown in Table 1, Table 1 shows the physical data and fluorescence intensity changes of 40μg / mL carbon dots in different solvents under 430nm excitation. It can be seen that the fluorescence of carbon dots in aqueous solution is weak and can be ignored. Regardless, it has the potential of cell imaging without washing.
[0041] Table 1 Physical data and fluorescence intensity changes of carbon dots in different solvents
[0042]
Embodiment 3
[0044] Fast cell imaging study of carbon dots
[0045] In a 37 ℃, 95% air, 5% carbon dioxide incubator, inoculate Hela cells into a special laser confocal culture dish containing 10% fetal bovine serum for culture. After incubating for 24 hours, excitation with an excitation wavelength of 488 nm light source for confocal imaging to observe the time when the carbon dots enter the cell.
[0046] Such as image 3 As shown, the fluorescence response of cells can be observed at an excitation wavelength of 488nm; cell imaging data shows that the carbon dots can quickly enter cells and have good cell permeability.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com