Rare earth-iron-nitrogen system magnetic powder and method for producing same
A manufacturing method and rare earth technology, applied in metal processing equipment, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of main phase magnetization decrease, saturation magnetization decrease, magnetization decrease, etc. thermal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
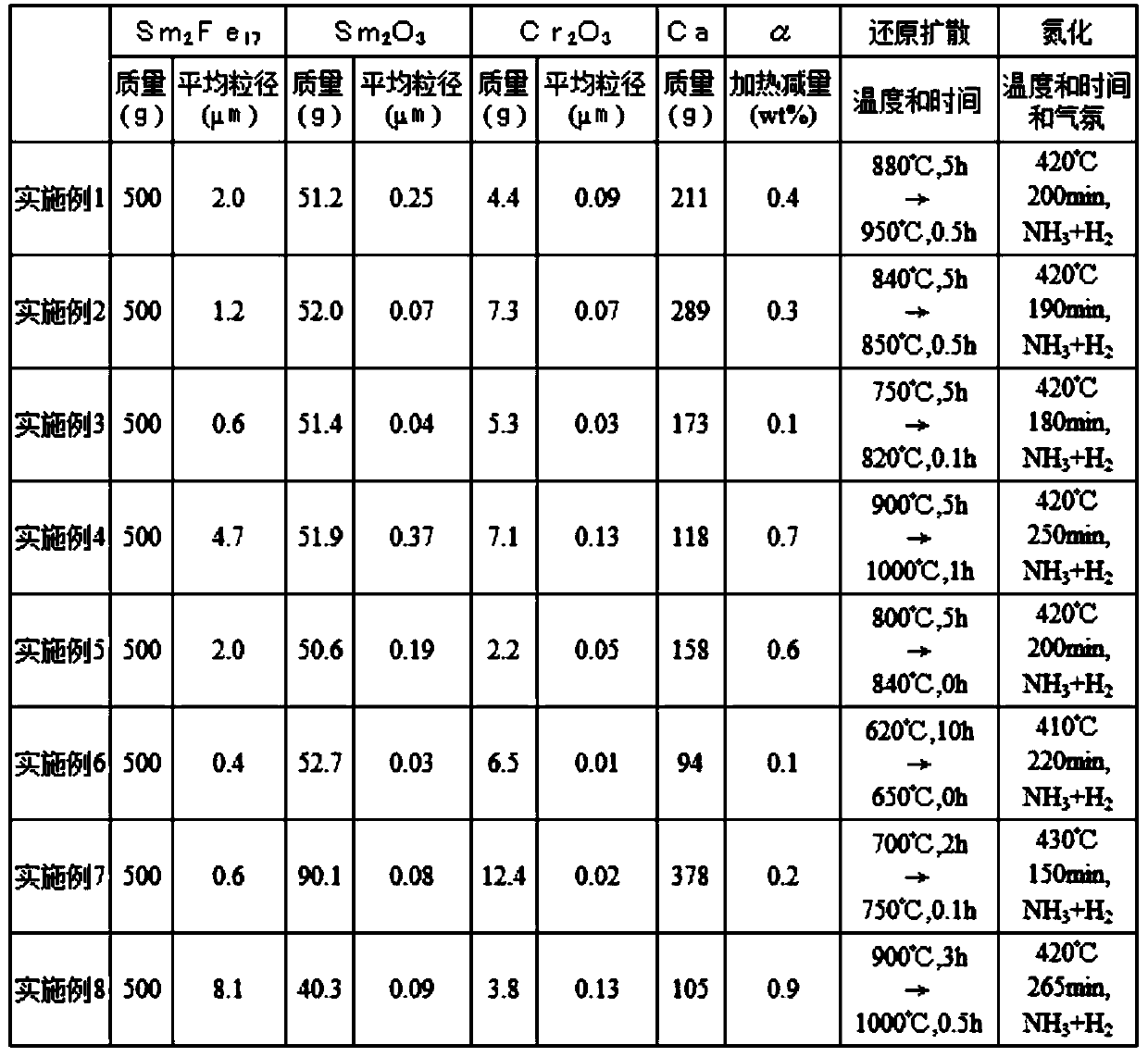
[0153] For 500 g of Sm prepared by the above method 2 Fe 17 Alloy powder, premixed 51.2g of samarium oxide with an average particle size (D50) of 2.3 μm, 4.4 g of Cr with an average particle size (D50) of 1.7 μm by a rocking mixer 2 o 3 The powder was pulverized by a media agitation mill with 1 kg of isopropanol as a solvent. The average particle size of the pulverized product observed by SEM, Sm 2 Fe 17 Alloy powder is 2.0μm, samarium oxide is 0.25μm, Cr 2 o 3 The powder is 0.09 μm.
[0154] After drying the obtained slurry under reduced pressure, the loss α after heating 50 g of the extracted mixed powder at 400° C. for 5 hours in a vacuum was measured, and it was 0.4% by mass. For all of the above mixtures, 211 g of granular calcium metal was added and mixed in an argon atmosphere, and as a reduction diffusion heat treatment, it was added in an iron crucible and heated under an argon atmosphere, kept at 880°C for 5 hours, and then kept at 950°C 0.5 hours and allowed...
Embodiment 2~5
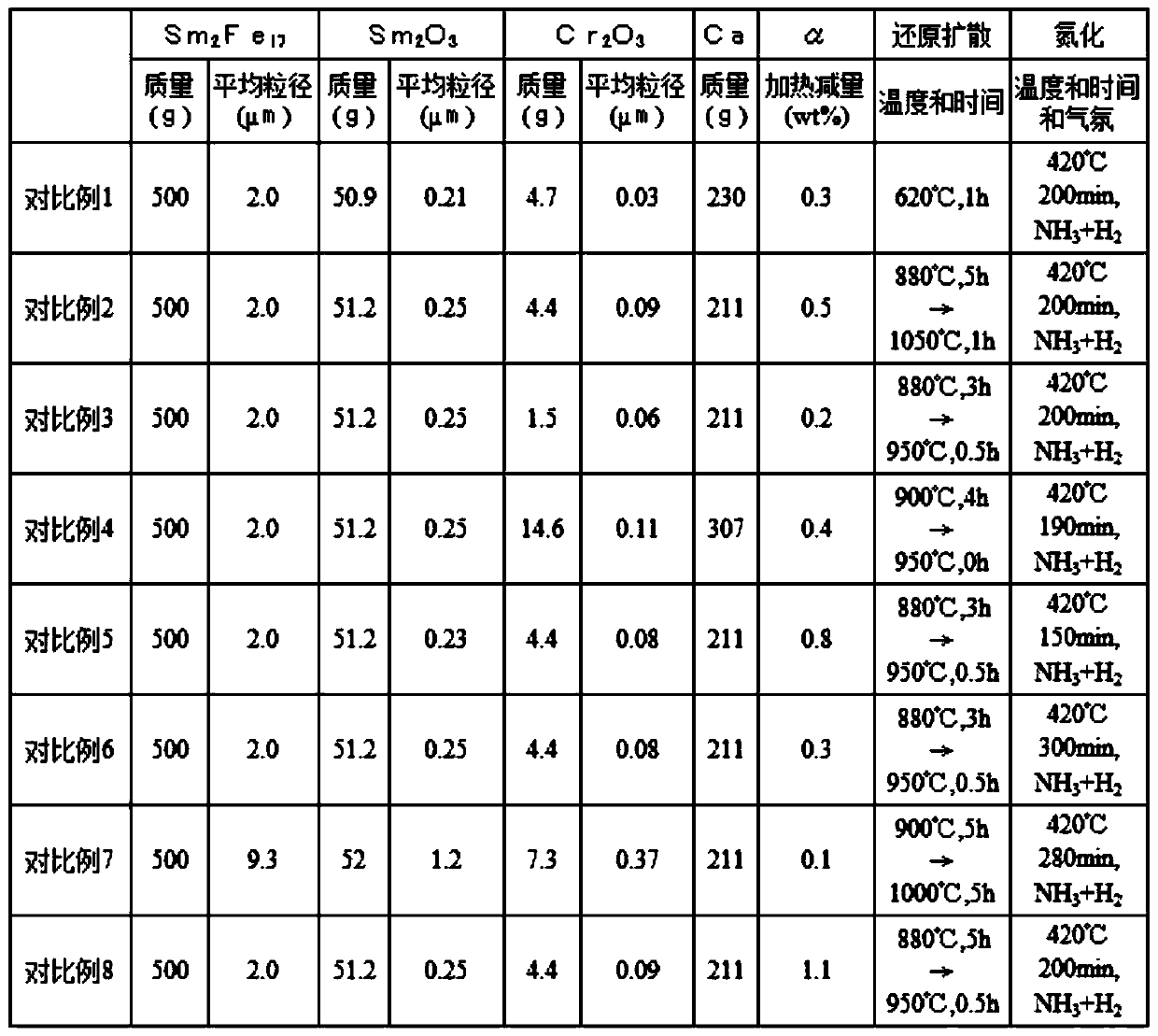
[0161] In Example 1, the Sm pulverized by the media stirring mill 2 Fe 17 Alloy powder, samarium oxide powder, Cr 2 o 3 The average particle size of the powder and its mixing amount, the input amount of granular metal calcium, the reduction-diffusion heat treatment conditions, and the nitriding heat treatment conditions were changed as shown in Table 1, respectively, and the rare earth was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1. Iron-nitrogen-like magnetic powder.
[0162] In addition, before adding the granular metallic calcium, 50 g of the mixed powder extracted from the dried product was measured for weight loss α after heating at 400° C. for 5 hours in a vacuum. In addition, in Example 5 of Table 1, the description of reduction diffusion "800°C, 5h→840°C, 0h" means that the heater was turned off immediately after holding at 800°C for 5 hours, then raising the temperature to 840°C.
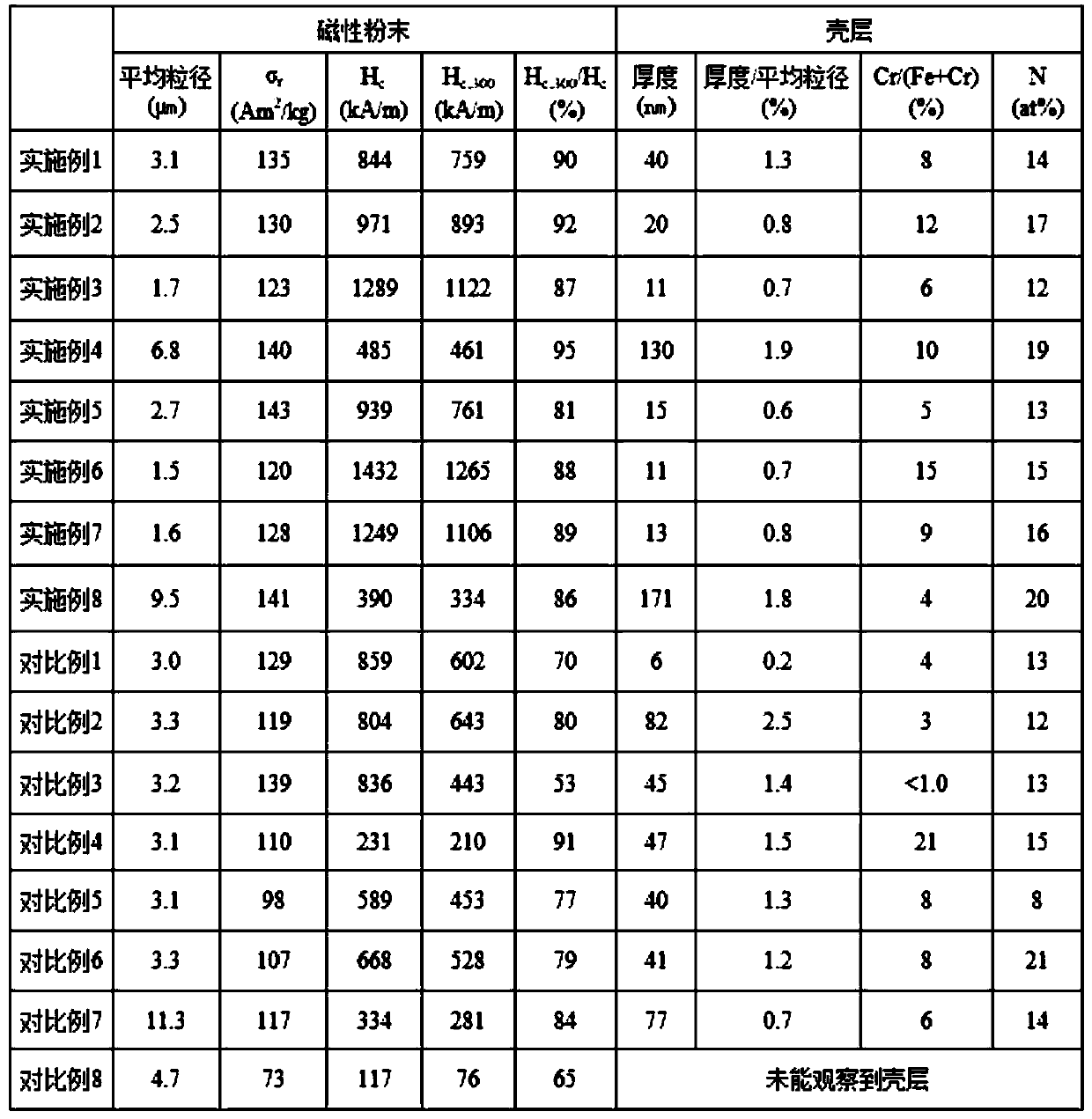
[0163] It has been confirmed that all the above powders are Th 2 Zn 17 Type crys...
Embodiment 6~8
[0165] In Example 1, the Sm after being pulverized by a media agitation mill was changed. 2 Fe 17 Alloy powder, samarium oxide powder, Cr 2 o 3 The average particle size of the powder and its mixing amount, the input amount of granular metal calcium, and the reduction-diffusion heat treatment conditions and nitriding heat treatment conditions were changed as shown in Table 1, respectively. Except for this, a rare earth iron-nitrogen magnetic powder was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1. In addition, before adding the granular metallic calcium, 50 g of the mixed powder extracted from the dried product was measured for the loss α after heating at 400° C. for 5 hours in a vacuum.
[0166] It has been confirmed that all the above powders are Th 2 Zn 17 Type crystal structure, observed by TEM, has Sm formed on the surface 2 (Fe 1-x Cr x ) 17 N y layered core-shell structure. Average particle size and residual magnetization σ of each magnetic powder r , coerciv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com