Small-molecule auxiliary electronic waste recycling method based on ester bond exchange reaction
A technology of electronic waste and exchange reaction, which is applied in the direction of protection devices against harmful chemicals, etc., can solve the problems of resin and glass fiber that cannot be recycled and reused, cumbersome process, and low efficiency, and achieve significant practical value, broad application space, The effect of high recovery efficiency
Inactive Publication Date: 2019-06-28
XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
View PDF1 Cites 2 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0005] 1. The mechanical recycling method is low in cost, has little negative impact on the environment, and is widely used. However, the method is not efficient and the process is cumbersome. The crushing and grinding will cause damage to the glass fiber and other materials in the plate, so that it can only be downgraded and reused. (such as filling particles), and there is also an inevitable material loss problem during the separation process
[0006] 2. In the heat treatment method, the equipment is expensive, and the reaction temperature of high-temperature pyrolysis of resin is far above 200°C. Resin and glass fiber cannot be recycled and reused. In addition, the toxic waste gas generated during the pyrolysis process will seriously pollute the air, and special treatment must be carried out. Purification and protection
[0007] 3. The chemical treatment method requires expensive equipment and requires harsh high temperature and high pressure conditions. The strong acid and strong alkali treatment solution will corrode the surface of resin and glass fiber, making it difficult to recycle and reuse. In addition, the waste liquid will seriously threaten environmental safety and human health.
[0008] To sum up, how to efficiently and environmentally friendly recycle e-waste is still a major challenge for the development of the recycling industry
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment
[0041] The present invention has verified the feasibility of the method for recycling electronic waste assisted by small molecules through recycling experiments of two types of circuit boards.
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
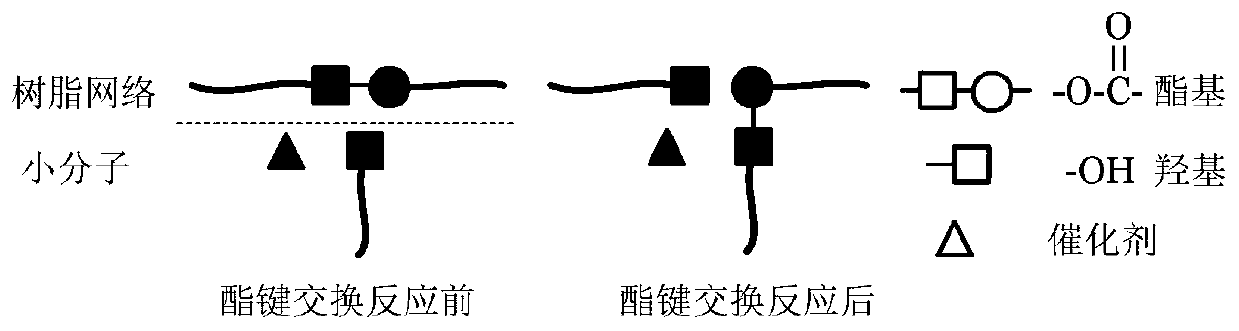
The invention discloses a small-molecule auxiliary electronic waste recycling method based on an ester bond exchange reaction. The small-molecule auxiliary electronic waste recycling method includes the following steps that waste electronic waste is immersed into small molecule treatment liquid, and the mixture is placed into a heatable vessel; the small molecule treatment liquid is slowly heatedto 120 DEG C to 200 DEG C, and heat preservation is conducted for 0.5 hours to 8 hours; then substrate resin containing ester bond functional groups is degraded, electronic components and substrates are separated, and full recovery and recycling of various materials in the electronic waste are achieved. According to the small-molecule auxiliary electronic waste recycling method, it is realized that the substrate resin containing the ester bond functional groups is degraded at a low temperature, the electronic components and the substrates are separated, and therefore complete recovery and recycling of various materials including the electronic components, the resin, glass fibers and the like can be achieved accordingly.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic waste treatment, and in particular relates to a method for recycling electronic waste assisted by small molecules based on transesterification reaction. Background technique [0002] With the rapid development of the electronics industry, there are various types and huge quantities of electronic waste generated around the world every year. Electronic waste represented by industrial circuit boards is rich in various organic substances (such as bromide, etc.) and high-purity metal elements (such as gold, silver, copper, platinum, etc.), which not only cause serious environmental pollution, but also It will cause a great waste of resources [1,2]. Therefore, e-waste recycling has become an important part of the development of a green circular economy. [0003] In the process of electronic waste recycling, removing organic matter and separating electronic components and substrates is a very critic...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): A62D3/30A62D101/28
Inventor 王铁军陈志强施前杨孟
Owner XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com