Method for evaluating toxicity effects of low-dose combined exposure of organic pollutants based on metabonomics technology
A technology for organic pollutants and toxic effects, applied in the field of molecular biology-based evaluation, it can solve the problems of limited information, data stability, poor repeatability, and incomparable analytical throughput, and achieves reduced variance and high sensitivity. , selective effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] HepG2 cells were cultured at 37°C in a cell incubator containing 5% CO2, and the medium was DMEM cell culture medium containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. Inoculate the cells grown in the logarithmic phase into a 6-well plate at a seeding density of 3×105 cells / well. After about 80% of the area of the orifice plate was covered by the culture solution, the individual and combined exposure tests of PAHs and SCCPs were carried out, and the cell samples were collected after 24 hours of exposure. PAHs and SCCPs were introduced into the cell culture medium by dissolving in DMSO, and the exposure concentration was set as follows: SCCP mixed standard sample (the total concentration ΣSCCPs was 100 μg / L), PAH mixed standard sample (each PAH concentration was 10 μg / L, and the total concentration ΣPAHs was 160μg / L), a mixture of PAHs and SCCPs (the concentrations of PAHs and SCCPs in the mixed standard sample are: ΣPAHs: 160μg / L and ΣSCCPs: 100μg / L). The exposure do...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Intracellular small molecule metabolites were analyzed using a pseudo-targeted metabolomics approach. First, Agilent UHPLC / Q-TOF MS was used for non-targeted analysis of cell samples, which were divided into positive and negative ion scanning modes, and the chromatographic conditions were as follows. Positive ion mode: ACQUITY UPLC BEH C8 (1.7μm, 2.1×100mm) is used for chromatographic column, mobile phase A is superstored water containing 0.1% (v / v) formic acid, phase B is containing 0.1% formic acid (v / v) of acetonitrile. The mobile phase gradient elution program is: start at 90% A, drop to 60% at 3 minutes, drop to 0% at 15 minutes and maintain for 5 minutes, return to 90% A at 20.1 minutes, and balance for 3 minutes; the flow rate is 0.35mL / min , the column temperature was 50°C, and the injection volume was 10 μL. Negative ion mode: ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 (1.8μm, 2.1×100mm) for chromatographic column, mobile phase A contains NH 4 HCO 3 5mmol / L ultrapure water, phas...
Embodiment 3
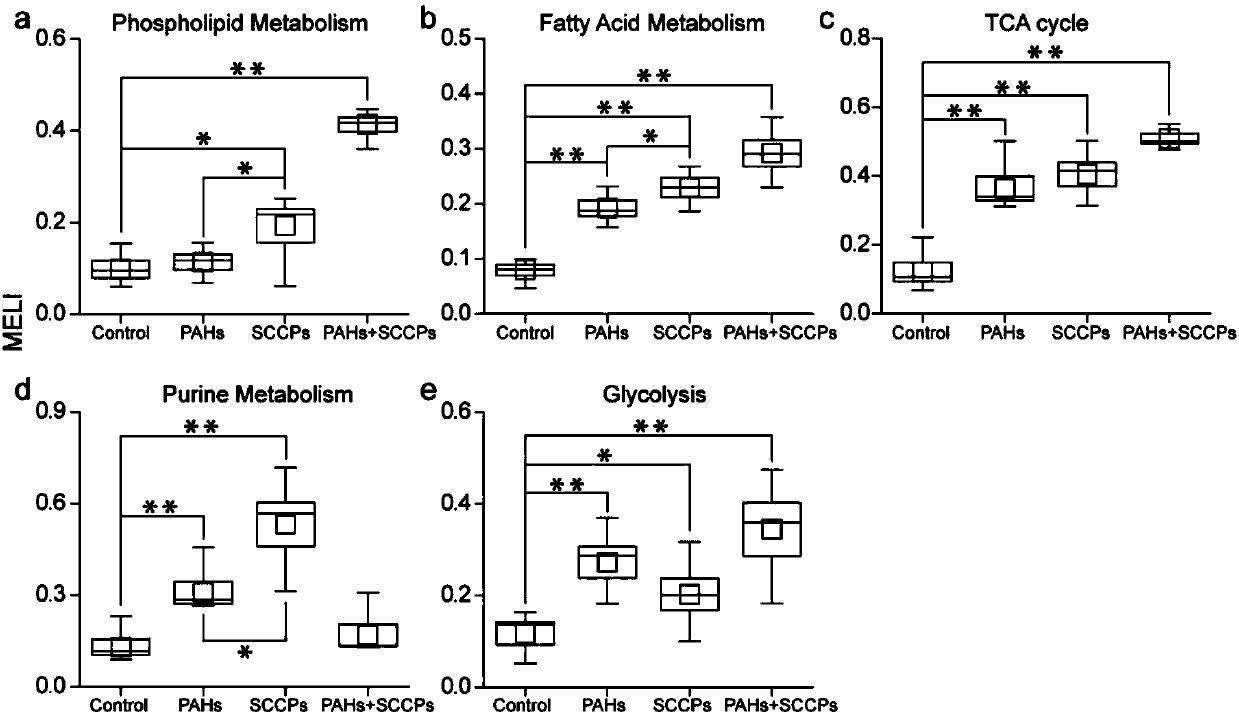
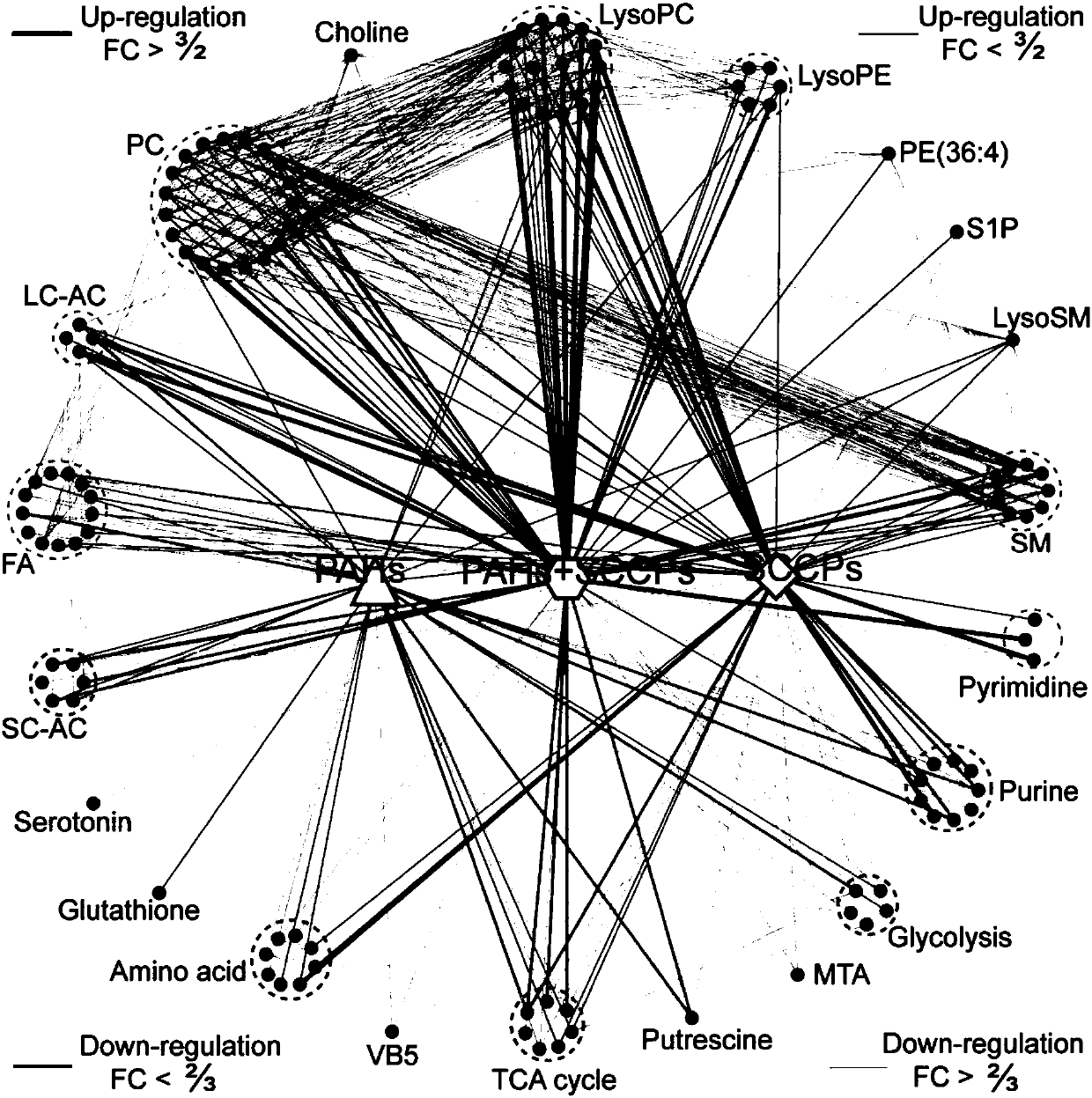
[0042] Statistical analysis was performed on the mass spectrometry data of intracellular metabolites obtained from UHPLC / Q-Trap MS analysis. The analysis was processed based on the online http: / / www.metaboanalyst.ca. / , and PLS-DA and ANOVA analysis were performed on intracellular metabolites , a total of 246 differential metabolites were found (P1). Among them, the molecular structures of 115 metabolites were characterized by MS / MS analysis and further confirmed with standards. In order to further explore the potential links between differential metabolites, the metabolic pathways involved in 115 differential metabolites were first identified through the metabolic pathway online database (KEGG, http: / / www.genome.jp / kegg / ). Then, through the calculation of the Pearson correlation coefficient (Pearson correlation coefficient) between the differential metabolites, the metabolites that participate in the same metabolic pathway and are significantly correlated (correlation coeffici...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com