A fluorescent probe for detecting n-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase and its application
A technology of glucosamine and glucosamine, applied in the field of fluorescent probes for detecting N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase, which can solve the problems of low sensitivity and complicated operation, and achieve high specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1. In vitro determination of the selectivity of different hydrolases
[0026] (1) Prepare 99 µL in vitro metabolic reaction system in advance, including pH 7.4 phosphate buffer (100 mM), different kinds of hydrolytic enzymes (0.1 mg / mL), at 37 o Pre-incubation with shaking for 3 minutes under C condition;
[0027] (2) Add 1 µL of DDAG at a concentration of 1 mM (final concentration 10 μM) to the reaction system to initiate the reaction;
[0028] (3) After 30 minutes, add 50 µL of glacial acetonitrile and shake vigorously to terminate the reaction;
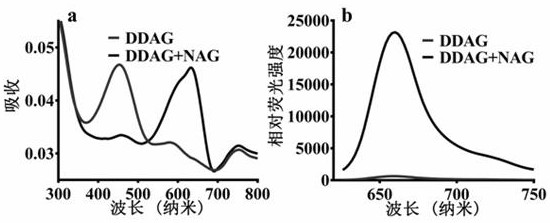
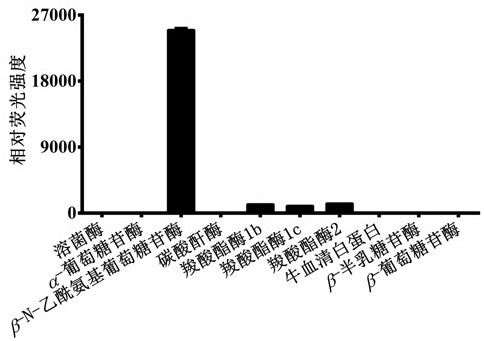
[0029] (4) Use a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge at 4 o C. 20,000 × g Under the condition of high-speed centrifugation for 20 minutes, the supernatant was taken for fluorescence detection (DDAG: Ex=608 nm, Em=660 nm). The results showed that only N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) catalyzed the reaction, and the reaction rate was much higher than that of other hydrolytic enzymes, indicating that N-acetyl-β-D-g...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2. In vitro determination of the selectivity of different hydrolases
[0031] (1) Prepare 99 µL in vitro metabolic reaction system in advance, including pH 7.4 phosphate buffer (100 mM), different kinds of hydrolytic enzymes (0.1 mg / mL), at 37 o Pre-incubation with shaking for 3 minutes under C condition;
[0032] (2) Add 1 µL of DDAG at a concentration of 1 mM (final concentration 10 μM) to the reaction system to initiate the reaction;
[0033] (3) After 30 minutes, add 50 µL of glacial acetonitrile and shake vigorously to terminate the reaction;
[0034] (4) Use a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge at 4 o C. 20,000 × g Under the condition of high-speed centrifugation for 20 minutes, the supernatant was taken for fluorescence detection (DDAG: Ex=608 nm, Em=660 nm). The results showed that only N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) catalyzed the reaction, and other ions and amino acids had no effect on the fluorescence intensity of the probe, indicating that N-...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3. Linearity study of N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase catalyzed DDAG probe reaction
[0036] (1) Prepare 99 µL in vitro metabolic reaction system in advance, including pH 7.4 phosphate buffer (100 mM), N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (0-3 μg / mL), at 37 o Pre-incubation with shaking for 3 minutes under C condition;
[0037] (2) Add 1 µL of NHPO with a concentration of 1 mM (final concentration 10 μM) to the reaction system to initiate the reaction;
[0038] (3) After 30 minutes, add 50 µL of glacial acetonitrile and shake vigorously to terminate the reaction;
[0039] (4) Use a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge at 4 o C. 20,000 × g Under the condition of high-speed centrifugation for 20 minutes, the supernatant was taken for fluorescence detection (DDAG: Ex=608 nm, Em=660 nm). The results showed that the probe reaction of N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) catalyzed DDAG showed a good enzyme linear relationship in the range of 0-3 μg / mL, r 2Value is 0.9945, illus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com