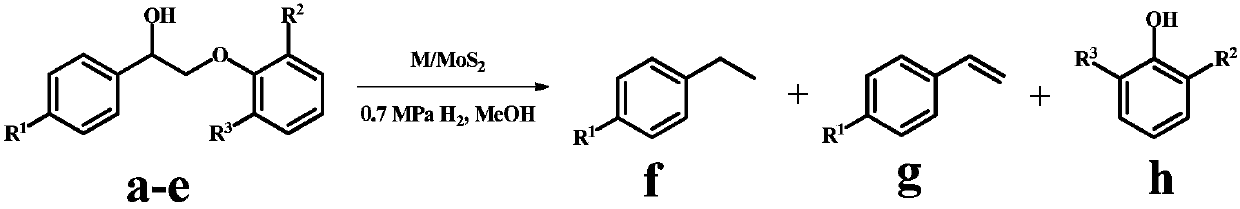
Application of monatomic catalyst in catalytic hydrogenation of lignin to aromatic compounds
A technology for catalytic hydrogenation of aromatic compounds, applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, preparation of organic compounds, catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as harsh reaction conditions, poor atom economy, and difficulty in control, and achieve low cost, reduce pollution, and avoid Effects of Environmental Pollution Problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] monatomic M 1 / MoS 2 The specific preparation method of the catalyst (M=Fe, Ni, Ru, Rh, Pd, Pt, Ir) is as follows:
[0022] Monatomic Ni 1 / MoS 2 Preparation: Add 0.32g of ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and 0.12g of sulfur powder into 57mL of oleylamine and stir at room temperature for 10min, then add 0.0145g of NiCl 3 ·6H 2 A solution of O fully dissolved in 3 mL of water was added to the above solution, stirred at room temperature for 1 h, then transferred to a 100 mL stainless steel reactor, and heated to 220 °C for 48 h. Then centrifuged and filtered, washed several times with ethanol and cyclohexane until the ligand oleylamine on the surface of the catalyst was washed off to obtain a black solid, and the collected black solid was vacuum-dried for 10 hours.
[0023] Fe 1 , Ru 1 , Rh 1 ,Pd 1 ,Pt 1 ,Ir 1 / MoS 2 Preparation: similar to Ni 1 / MoS 2 The preparation process, respectively, with 0.014gFeCl 3 ·6H 2 O, 0.0065g RuCl 3 ·H 2 O,0.0048g PdCl 2 ...
Embodiment 2-22
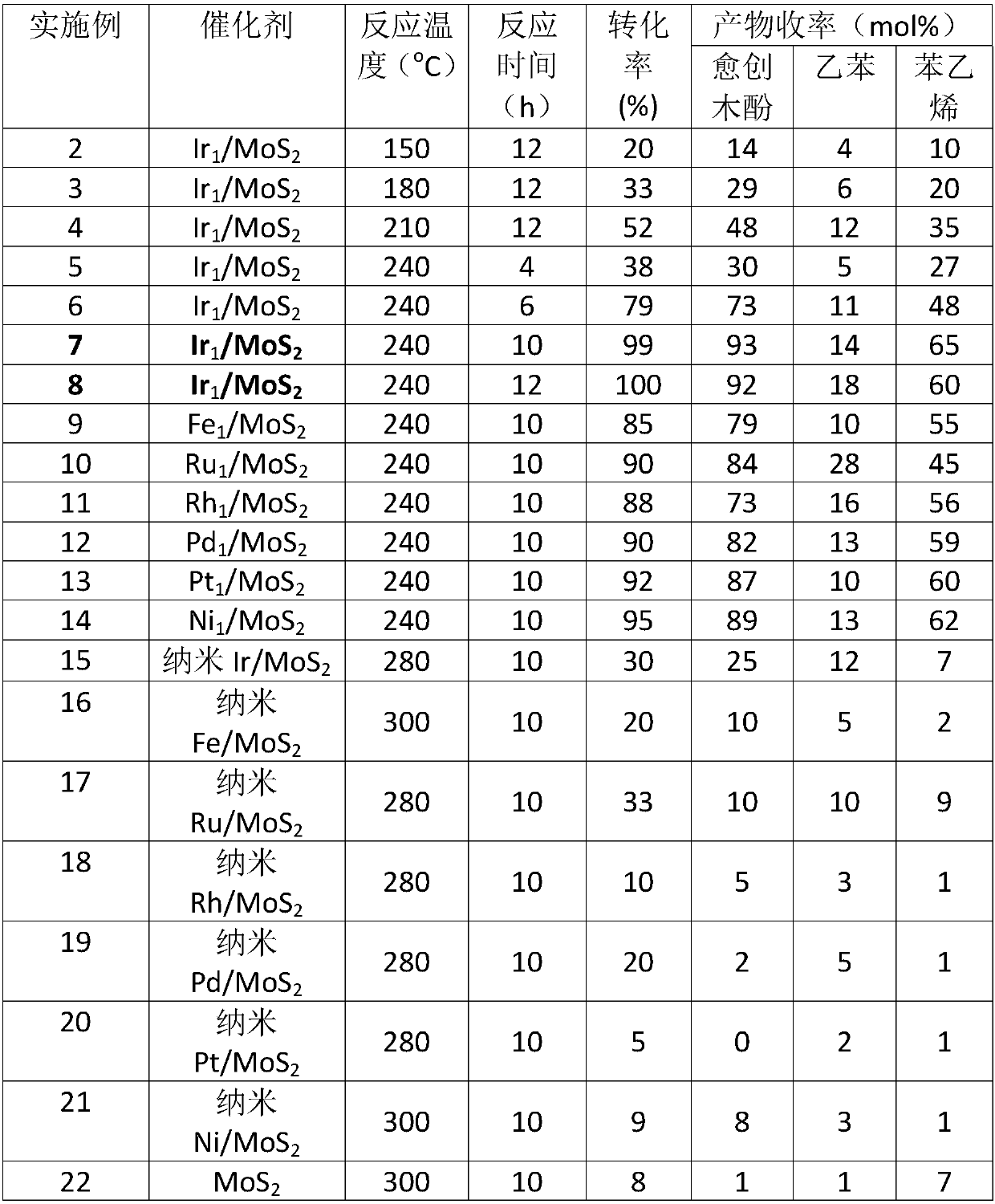
[0027] Example 2-22 Single atom M 1 / MoS 2 The catalyst catalyzes the depolymerization reaction of the lignin model molecule 2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1-phenylethanol: 100mg lignin model molecule is mixed with single-atom M / MoS 2Dissolve 20 mg of the catalyst in 30 mL of methanol, replace with hydrogen six times, seal the reaction vessel at 0.7 MPa and raise the temperature to 150°C-240°C, and carry out stirring reaction at 750 rpm for 4h-12h. After the reaction was completed, the temperature was lowered to room temperature, and the supernatant was filtered and then sampled for analysis. Qualitative analysis of the product was carried out by GC-MS technology and standard sample control, and quantitative analysis was realized by gas chromatography internal standard method. The reaction results are shown in Table 1.
[0028] Table 1 Single atom M under different conditions 1 / MoS 2 Catalysts and Nanocatalysts M / MoS 2 Catalytic depolymerization of lignin model molecule 2-(2-meth...
Embodiment 23-29
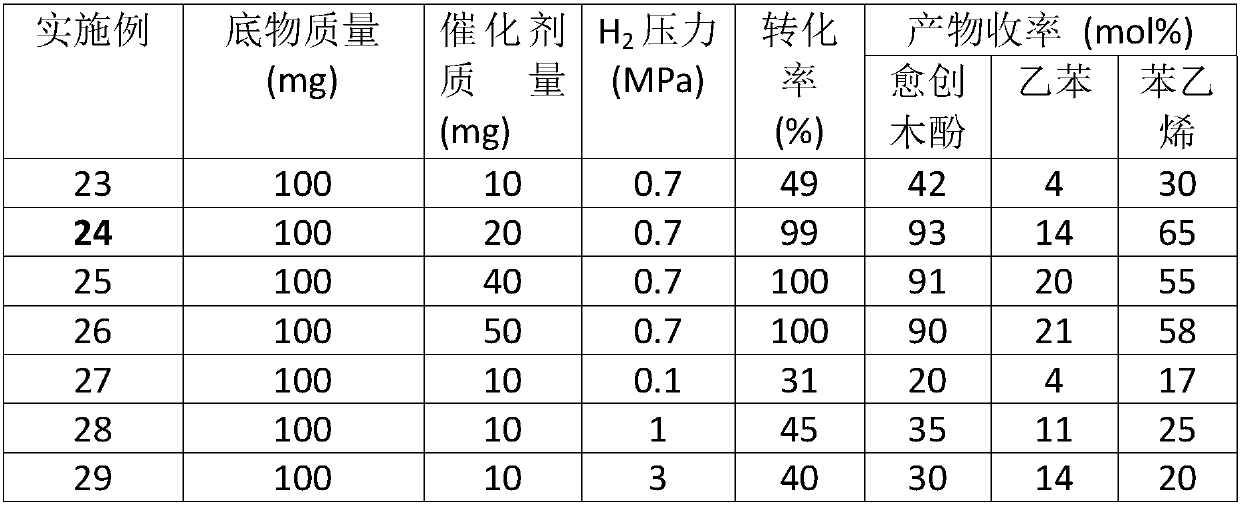
[0032] Ir 1 / MoS 2 Catalytic depolymerization of lignin model molecule 2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1-phenylethanol under different conditions: a certain mass of lignin model molecule was mixed with single-atom catalyst Ir in a reactor 1 / MoS 2 Dissolve in 30mL of different solvents respectively, replace with hydrogen for five times, fill with hydrogen to set pressure, raise the temperature of the reactor to 240°C, and carry out stirring reaction at 750 rpm for 10h. After the reaction was completed, the temperature was lowered to room temperature, and the supernatant was filtered and then sampled for analysis. Qualitative analysis of the product was achieved by GC-MS coupled technology and standard sample control, and quantitative analysis was realized by gas chromatography internal standard method. The reaction results are shown in Table 2.
[0033] Table 2 Single atom catalyst Ir under different conditions 1 / MoS 2 Catalytic depolymerization of lignin model molecule 2-(2-metho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com