Screening and identification of microorganism for degradation of deoxynivalenol (DON) in feeds
A technology for microbial screening and vomitoxin, which is applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, microorganisms, and separation of microorganisms, etc. It can solve the problems of low DON degradation efficiency, long degradation time, and difficult to popularize applications, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The screening of degrading DON microorganisms, the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0034] 1. DON standard curve and its standard high performance liquid chromatography
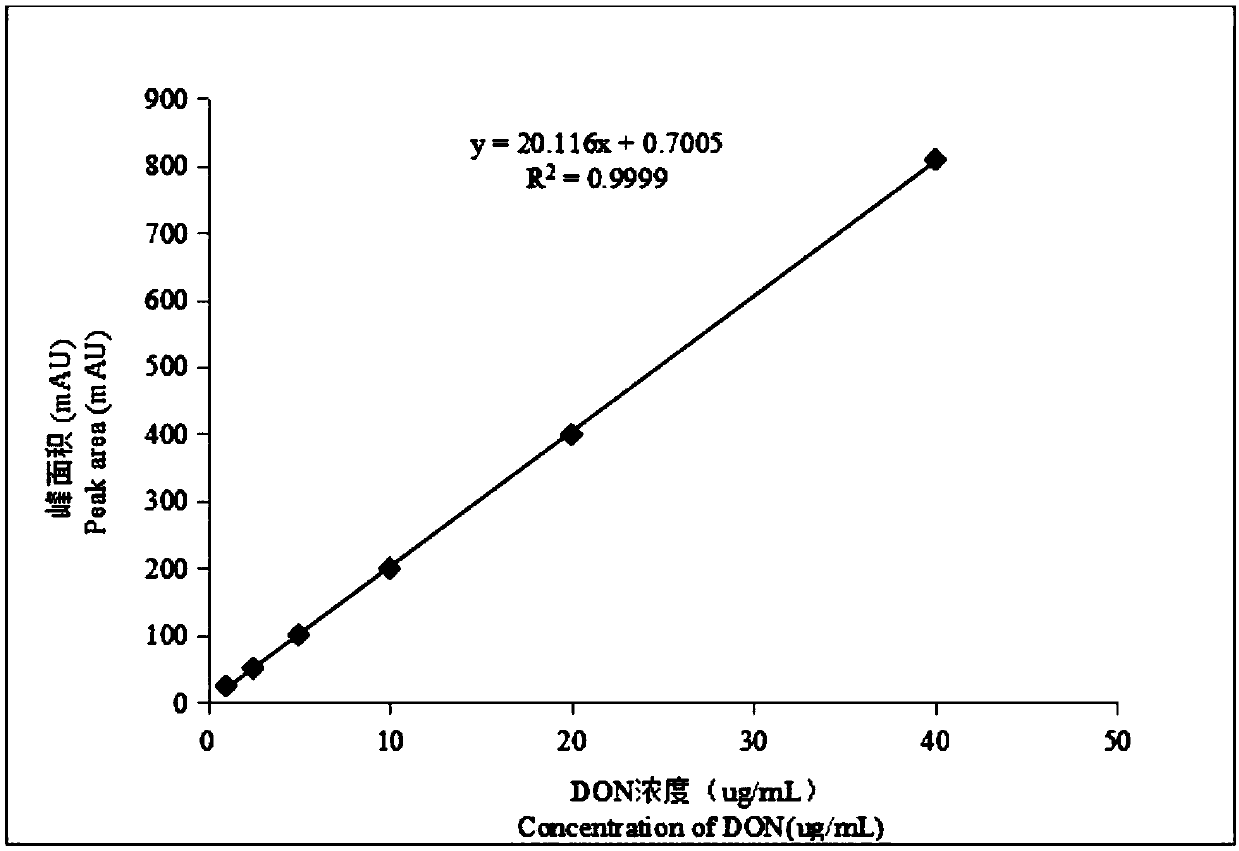
[0035] The HPLC detection conditions are: DAD detector, column temperature 35°C, injection volume 50 μL, mobile phase: 20% methanol; flow rate: 0.8mL / min; detection wavelength: 218nm. attached figure 1 As shown, the standard curve obtained by HPLC-DAD measuring different concentrations of DON standard products, the relationship between the peak area and the DON concentration obtained from this curve is: y=20.116x+0.7005, the linear relationship coefficient R2=0.9999, indicating that DON standard products The concentration was highly linear with the peak area detected by DAD.
[0036] attached figure 2 Shown is the chromatogram of DON standard substance with a concentration of 20 μg / mL. The peak time of DON standard product is 5.975 minutes. Therefore, when detecting the content of DON ...
Embodiment 2
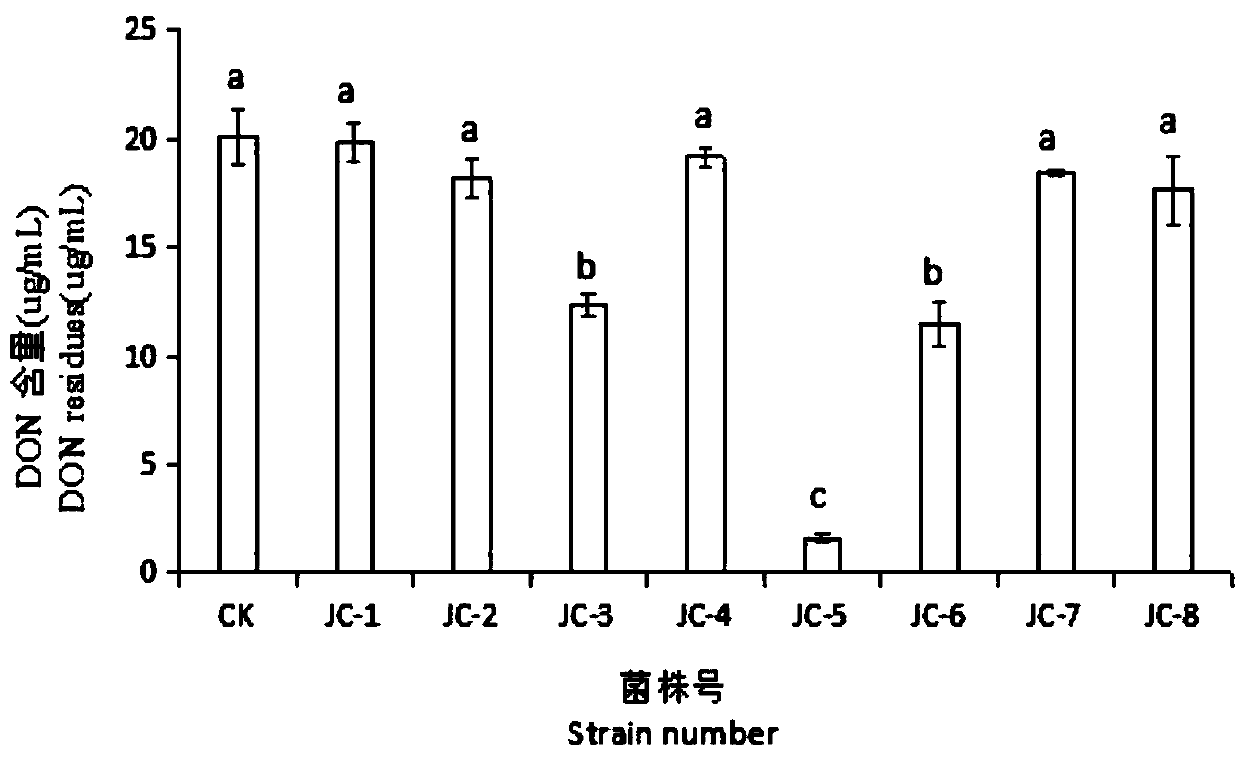
[0045] Select the strains with significant degradation effect on DON to carry out the degradation effect test, respectively take the bacteria suspension with the concentration of 1×107 CFU / mL that has the degradation effect after re-screening, and inoculate them with a final concentration of 20 μg / mL according to the 10% inoculum amount. Shake flask culture at 120r / min at 30°C in salt liquid medium, take samples at 6h, 12h, 24h, 36h, and 48h to measure the DON content, calculate the degradation rate, and compare the degradation effects of the target strains for re-screening. The strain with the best DON degradation effect was the final target strain.
[0046] The DON content was determined by HPLC, and the DON degradation rate was calculated, and the degradation rate was calculated according to formula 1. The chromatographic column is Agilent ZorbaxSB-C18 column, the specification is 4.6mm×150mm, 5μm; HPLC detection conditions: DAD detector, column temperature 35℃, injection v...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The identification of bacterial strain, specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0059] 1. Morphological identification: mark the target strain on the LB plate, culture at 30°C until a single colony grows, and observe its colony morphology on the surface of the LB medium.
[0060] attached Figure 8 The colony form of the DON-degrading strain JC-5 in LB medium is characterized by: the colony is milky white, with neat edges, round, opaque, round and smooth surface, uniform texture, and easy to pick.
[0061] attached Figure 9 It is the thalline morphology of the bacterium under the microscope after Gram staining. The bacterium is a Gram-negative bacterium with a short rod shape and no spores.
[0062] 2. 16SrDNA identification: Use the Omega Bacteria Genomic DNA Extraction Kit to extract the total DNA of the strain and use bacterial 16sr DNA amplification primers 27F: 5-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3 and 1492R: 5-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3 to amplify the 16s r DNA fragment,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com