Building method for abrasive bricks at end part of unloading chute of rotary hearth furnace
A technology of wear-resistant bricks and rotary hearth furnaces, which is applied in the direction of furnaces, furnace components, lighting and heating equipment, etc., and can solve the problem of reducing the service life of the feeding chute of the rotary hearth furnace, easily producing cracks at the end of the feeding chute, and affecting the rotation of the bottom. Furnace production and operation and other issues to achieve the effect of improving overall stability, ensuring production and operation, and extending service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
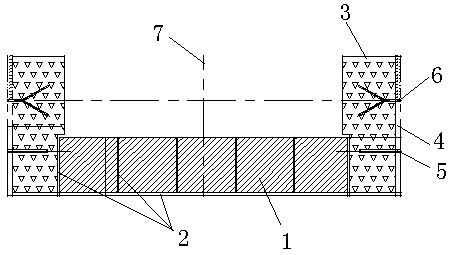
[0016] Example figure 1 As shown, the method for building wear-resistant bricks at the end of the discharge chute of the rotary hearth furnace of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0017] Step 1. Measure the size of the steel structure shell at the end of the discharge chute, calculate and plan the masonry position of the wear-resistant brick 1 and the placement position of the wear-resistant block 2, and reserve on both sides of the steel structure shell at the end of the discharge chute The pouring zone 3, the masonry position of the wear-resistant brick 1 is located between the reserved pouring zone 3;
[0018] Step 2. Make the wear-resistant steel plate 4 and fully weld it on both sides of the steel structure shell at the end of the discharge chute. The inner side of the wear-resistant steel plate 4 is welded with the tie bars 5 to connect with the steel plate at the bottom of the shell. The V-shaped anchor nail 6, the tie bar 5 and the V-shaped anchor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com