Data authentication method based on HMAC-SM3 algorithm and quantum key distribution system
A technology of quantum key distribution and data authentication, which is applied in the field of quantum key distribution, can solve the problems of not being able to satisfy QKD terminal data authentication, not being able to verify data integrity, and having a high probability of CRC check value collision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
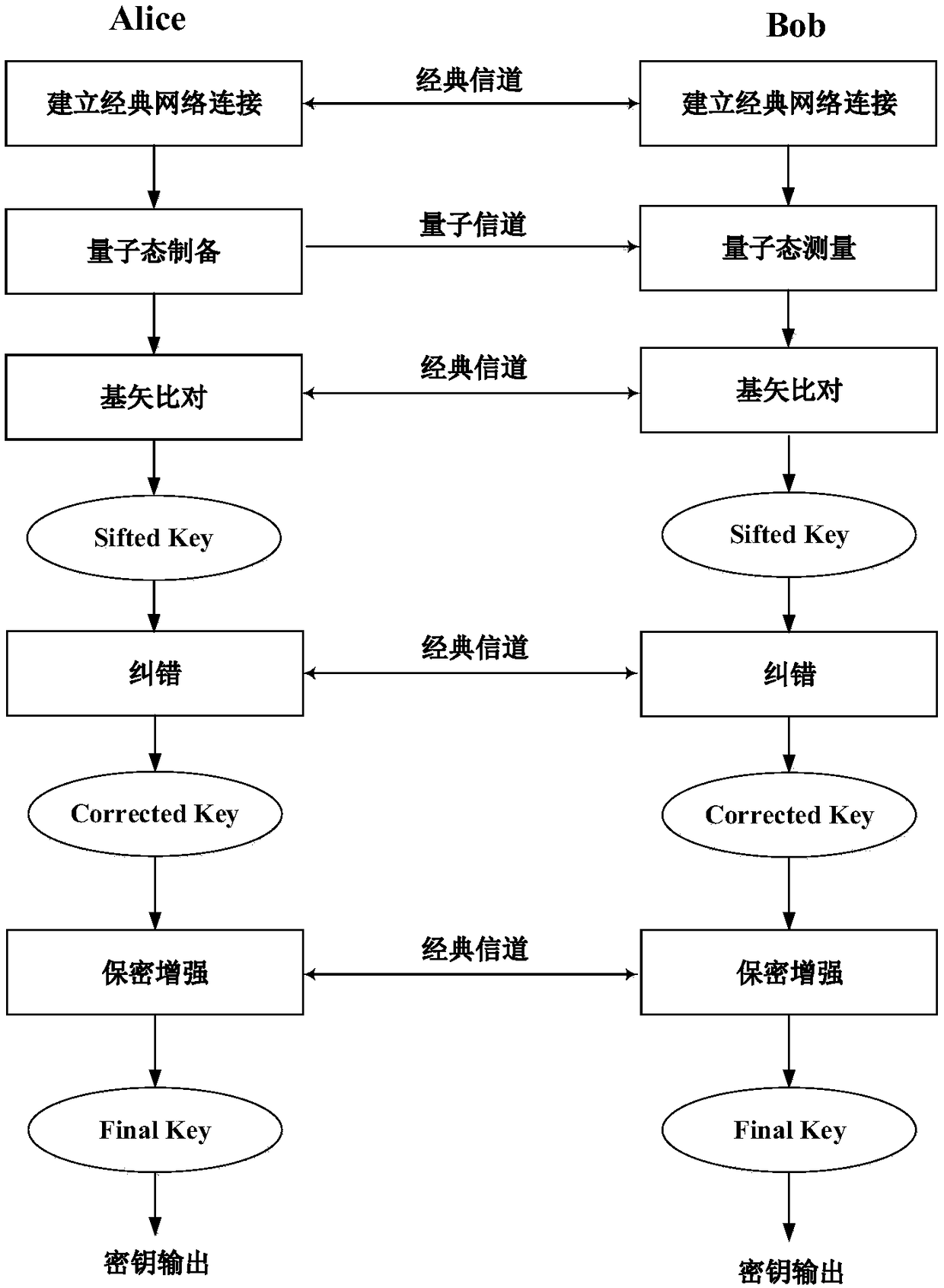
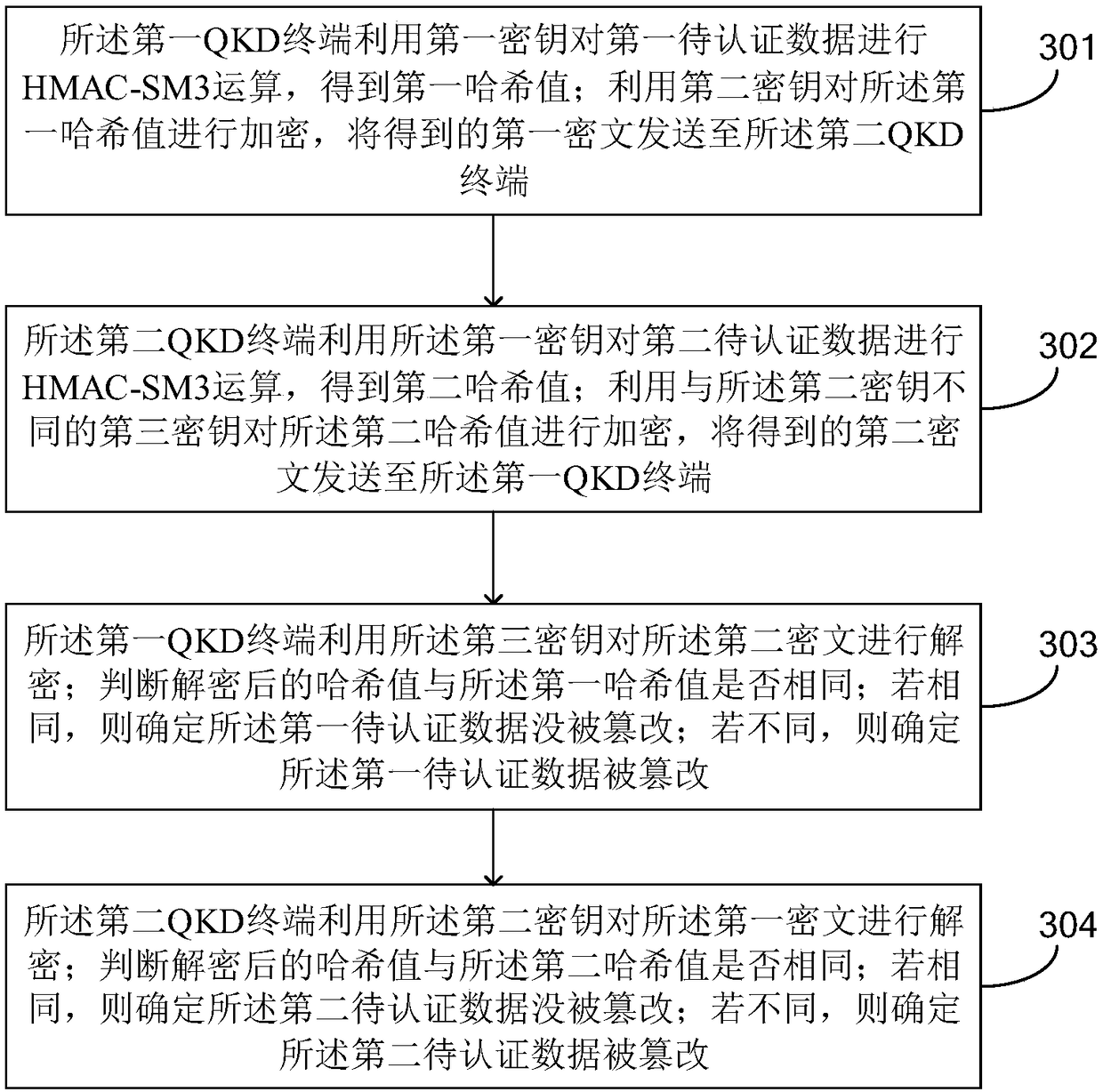
[0058] see image 3 , is a schematic flowchart of a data authentication method based on the HMAC-SM3 algorithm provided in the embodiment of the present application. The data authentication method is applied to a QKD system, and the QKD system includes a first QKD terminal and a second QKD terminal communicating through a classical network. Two QKD terminals, wherein the first QKD terminal is figure 1 Alice shown, the second QKD terminal is figure 1 Shown by Bob.
[0059] Since the first QKD terminal and the second QKD terminal respectively correspond to a quantum key management terminal, they can pre-allocate three different key data for the corresponding QKD terminal, which are the first key, the second key and the third secret key respectively. key.
[0060] The data authentication method includes the following steps:
[0061] S301: The first QKD terminal uses the first key to perform HMAC-SM3 operation on the first data to be authenticated to obtain a first hash value;...
Embodiment 2
[0078] see Figure 4 , is a schematic flowchart of another data authentication method based on the HMAC-SM3 algorithm provided by the embodiment of the present application. The data authentication method is applied to a QKD system, and the QKD system includes a first QKD terminal communicating through a classical network and The second QKD terminal, wherein the first QKD terminal is figure 1 Alice shown, the second QKD terminal is figure 1 Shown by Bob.
[0079] Since the first QKD terminal and the second QKD terminal respectively correspond to a quantum key management terminal, they can pre-allocate two different key data for the corresponding QKD terminal, namely the fourth key and the fifth key.
[0080] The data authentication method includes the following steps:
[0081] S401: The first QKD terminal uses the fourth key to perform HMAC-SM3 operation on the first data to be authenticated to obtain a third hash value; uses the fifth key to perform HMAC-SM3 operation on th...
Embodiment approach
[0134] In a possible implementation manner, specifically, within the same clock cycle, the FPGA may be used to perform parallel processing on the intermediate variable assignment operation or the word register assignment operation.
[0135] Specifically, in each round of iterative compression operation, after the intermediate variable assignment operation is completed, the operation result needs to be put into the register, so as to realize the word register assignment operation based on the operation result in the register, however, the data into the register A certain amount of time will be spent in the process, resulting in that the intermediate variable assignment operation and the word register assignment operation of the same round of iterative compression operation cannot be completed within the same clock cycle. Therefore, the intermediate variable assignment operation can be completed in parallel with one clock cycle of the FPGA, and the word register assignment operat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com