Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and applications
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and a production method, which is applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as high cost and complicated process of glucoamylase, and achieve the effects of reducing production cost, simplifying fermentation process, and good fermentation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Mutagenesis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0045] 1. Dilute the fermentation liquid of Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermented by COFCO Biochemical Energy (Zhaodong) Co., Ltd. 7 , take 100 μ l coating YPD (2% glucose, 2% peptone, 1% yeast powder, 2% agar powder, pH7.0) solid plate, after a single colony grows, pick a single colony and inoculate it into YPD (2% glucose , 2% peptone, 1% yeast powder, pH 7.0) liquid culture medium, 30 ℃, 250rpm carry out shaking flask culture, cultivate to OD600 is about 1.0~1.5, take a certain amount of culture medium and wash the bacteria with sterile physiological saline and use Prepare bacterial suspension with sterile saline.
[0046] 2. Set up a multifunction plasma mutagenesis system (multifunction plasma mutagenesis system, MPMS), using nitrogen as the working gas of the plasma, with a power supply of 300W, a platform height of 14mm, a plasma temperature of 10%. Flow rate 12slpm, under the condition of mutagenesis mode A, dr...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2: Continuous domestication and breeding of ethanol fermentation industrial materials
[0049] Selection Example 1 Screening of Saccharomyces cerevisiae exhibiting glucoamylase activity, continuous domestication of ethanol fermentation industrial materials to ensure the selection of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with better fermentation performance. Continuous domestication was carried out in a 2L fully automatic fermenter; the liquefied mash and distiller's mash from the Phase III (or Phase II) production plant of COFCO Biochemical Energy (Zhaodong) Co., Ltd. were taken to the automated fermenter, and the above-mentioned Saccharomyces cerevisiae was inoculated according to the inoculation ratio of 20%. After the initial fermentation to 36 hours, a certain proportion of fermented mash is taken out, and fresh liquefied mash is added to continue the fermentation, and the operation is repeated for several rounds. After each round of acclimatization, take part of the fer...
Embodiment 3
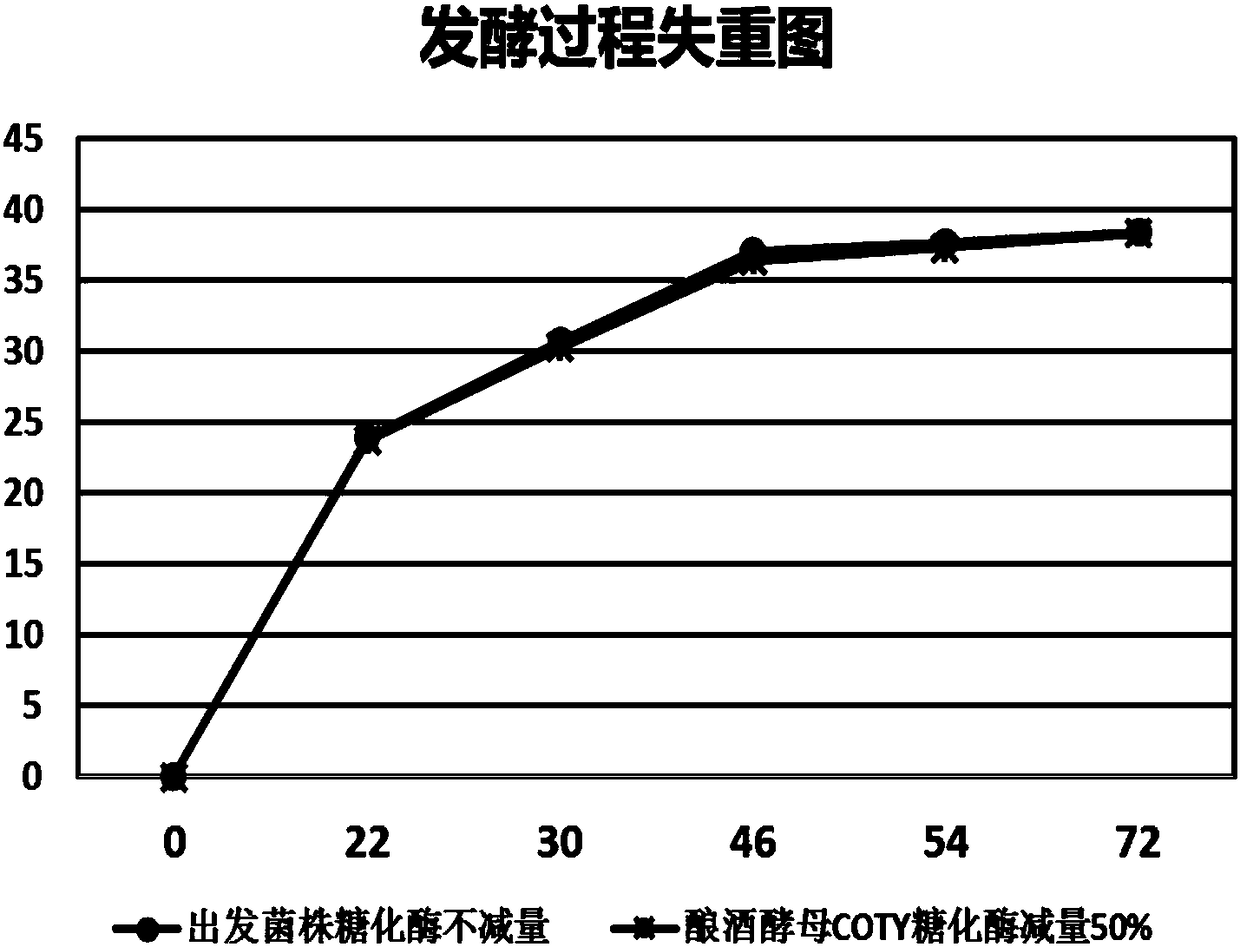
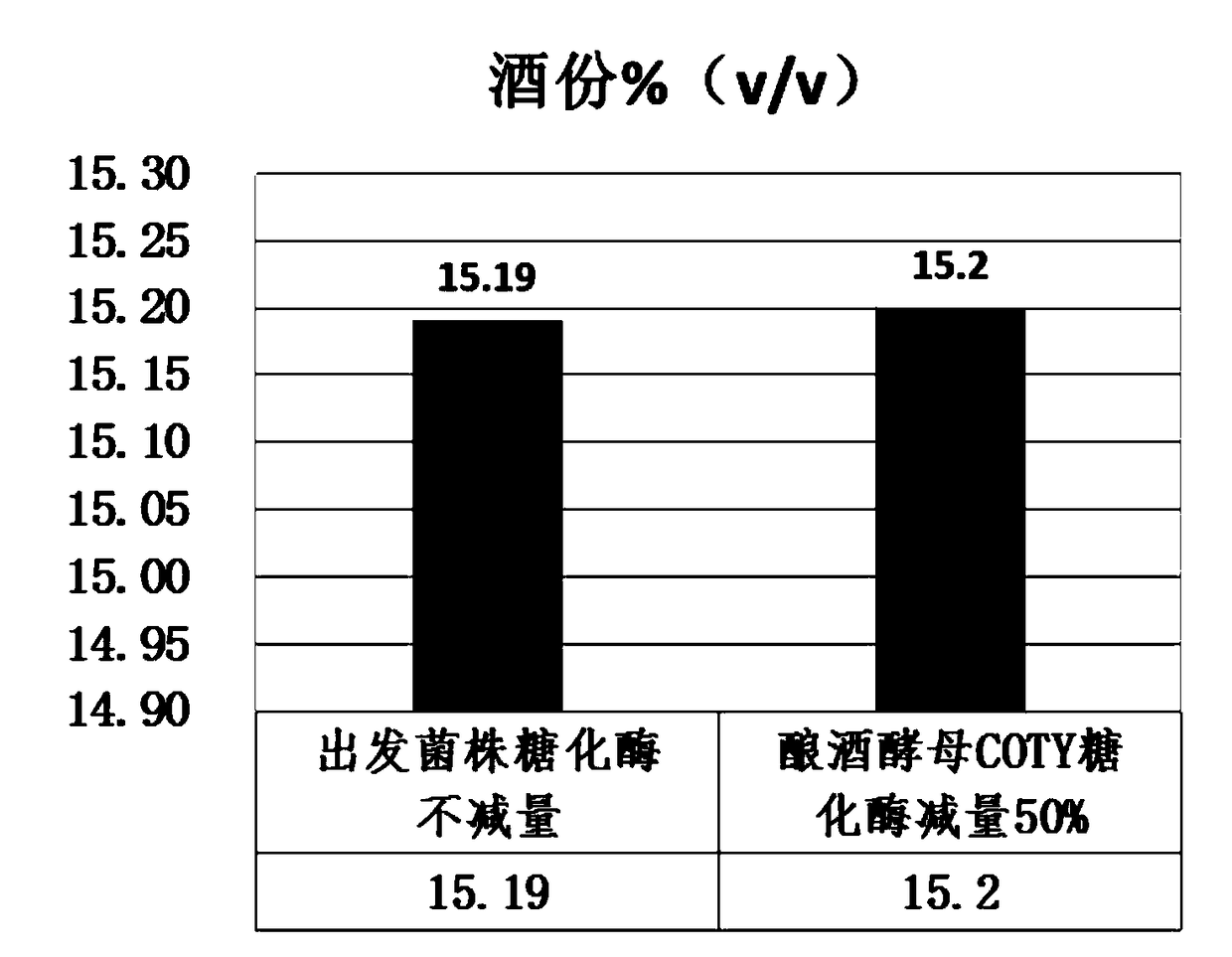
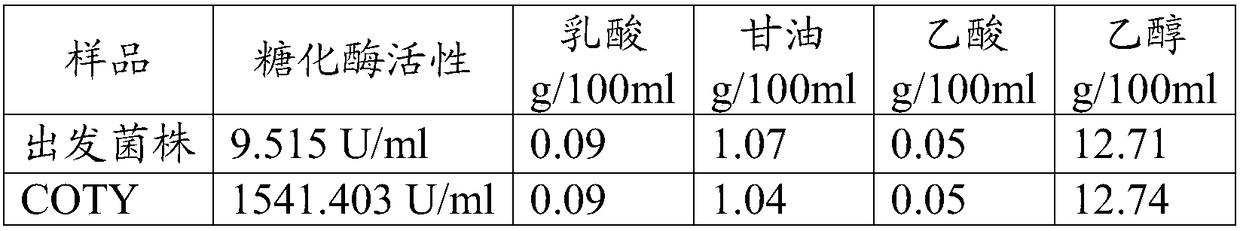
[0054] Example 3: Saccharomyces cerevisiae COTY real bioethanol fermentation material and pilot test inspection of fermentation process
[0055] The Saccharomyces cerevisiae COTY and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains that were domesticated and screened in Example 2 were used for the verification of reducing the use of exogenous glucoamylase in the fermentation process. The two strains were passed through YPD (2% glucose, 2% peptone, 1% Yeast powder, pH 7.0) liquid culture medium to the same cell density, centrifuged to collect bacteria, washed and inoculated to reduce 0%, 15%, 30%, 50%, 75% of exogenous glucoamylase In 200ml of liquefied mash, vibrate at 30°C and 250rpm for 96 hours. After the fermentation, HPLC was used to detect the content of ethanol, residual glucose and glycerin. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0056] Table 2 Detection of ethanol content, residual glucose and glycerin content
[0057]
[0058]
[0059] Note: A: The glucoamylase of the starti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com