Preparation method for high-density, large-size, ultra-fine-pore nuclear graphite materials for fused salt piles
A high-density, large-scale technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of high-density, large-scale, ultra-fine pore-sized nuclear graphite materials for molten salt reactors, can solve the problems of large specific surface area and surface energy of particles and inability to prepare large-scale nuclear graphite materials, etc. Achieve uniform internal temperature, eliminate intermittent, and avoid stress concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] 1. Raw materials: 80 parts by weight of pitch coke with an average particle size of 1 μm and 20 parts by weight of pitch;
[0103] 2. Preparation method:
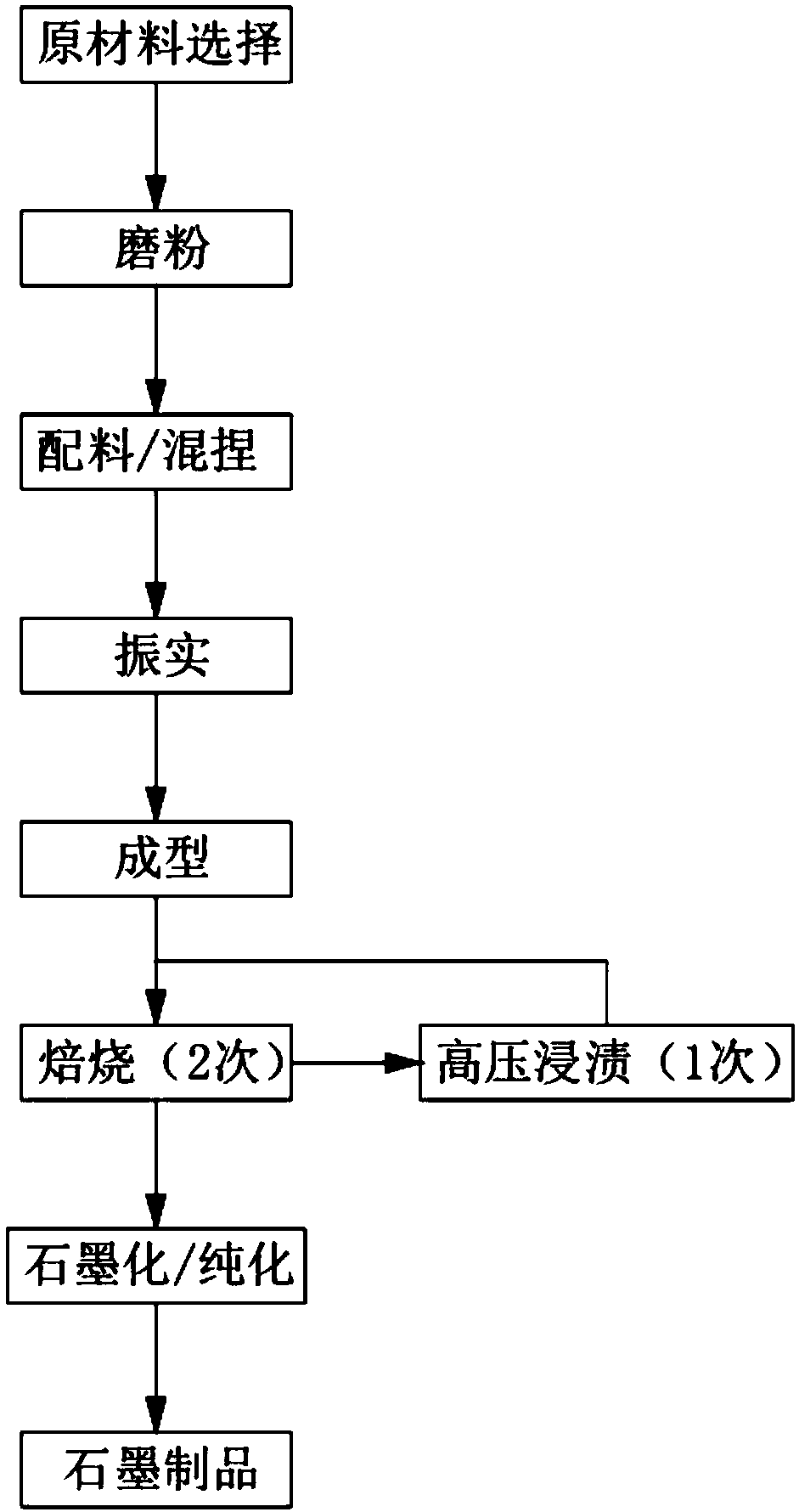
[0104] 1) Selection of raw materials: aggregate and binder, the fixed carbon content in the aggregate is ≥98.5%, the ash content is ≤0.5%, both boron (B) and gadolinium (Gd) are less than 0.1ppm, samarium (Sm), europium (Eu ), cadmium (Cd) and lithium (Li) are all less than 0.5ppm, moisture ≤0.5%, sulfur ≤0.1%;
[0105] The ash content in the binder is ≤0.5%, the volatile content is 35-60%, the coking value is 40-70%, the softening point is 80-200°C, the quinoline insoluble matter is 8-25%, and the toluene insoluble matter is 25- 55%;
[0106] 2) Raw material grinding: the aggregate is ground and pulverized so that the average particle size does not exceed 1 μm;
[0107] 3) Ingredients and kneading: Pour pitch coke and pitch into a kneader and knead at a temperature of 150°C for 80 minutes;
[0108] 4) Molding: P...
Embodiment 2
[0114] 1. Raw materials: 70 parts by weight of petroleum coke with an average particle size of 3 μm and 30 parts by weight of pitch;
[0115] 2. Preparation method:
[0116] 1) Selection of raw materials: aggregate and binder, the fixed carbon content in the aggregate is ≥98.5%, the ash content is ≤0.5%, both boron (B) and gadolinium (Gd) are less than 0.1ppm, samarium (Sm), europium (Eu ), cadmium (Cd) and lithium (Li) are all less than 0.5ppm, moisture ≤0.5%, sulfur ≤0.1%;
[0117] The ash content in the binder is ≤0.5%, the volatile content is 35-60%, the coking value is 40-70%, the softening point is 80-200°C, the quinoline insoluble matter is 8-25%, and the toluene insoluble matter is 25- 55%;
[0118] 2) Raw material grinding: the aggregate is ground and pulverized so that the average particle size does not exceed 3 μm;
[0119] 3) Batching and kneading: Pour pitch coke and pitch into a kneader and knead at a temperature of 300°C for 120 minutes;
[0120] 4) Molding:...
Embodiment 3
[0126] 1. Raw materials: 65 parts by weight of pitch coke with an average particle size of 5 μm and 35 parts by weight of pitch;
[0127] 2. Preparation method:
[0128] 1) Selection of raw materials: aggregate and binder, the fixed carbon content in the aggregate is ≥98.5%, the ash content is ≤0.5%, both boron (B) and gadolinium (Gd) are less than 0.1ppm, samarium (Sm), europium (Eu ), cadmium (Cd) and lithium (Li) are all less than 0.5ppm, moisture ≤0.5%, sulfur ≤0.1%;
[0129] The ash content in the binder is ≤0.5%, the volatile content is 35-60%, the coking value is 40-70%, the softening point is 80-200°C, the quinoline insoluble matter is 8-25%, and the toluene insoluble matter is 25- 55%;
[0130] 2) Raw material grinding: the aggregate is ground and pulverized so that the average particle size does not exceed 5 μm;
[0131] 3) Ingredients and kneading: Pour pitch coke and pitch into a kneader and knead at a temperature of 400°C for 150 minutes;
[0132] 4) Molding: Pu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com