A method for the determination of inorganic cations in tobacco gene editing materials
A technology of gene editing and determination method, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problem that conventional methods cannot meet the needs, and achieve the effects of improving sample analysis efficiency, good compatibility, and shortening analysis time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Take 4 kinds of finished tobacco leaves as investigation samples, and measure cationic content wherein, comprise the steps:
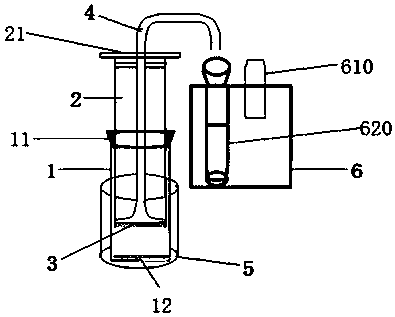
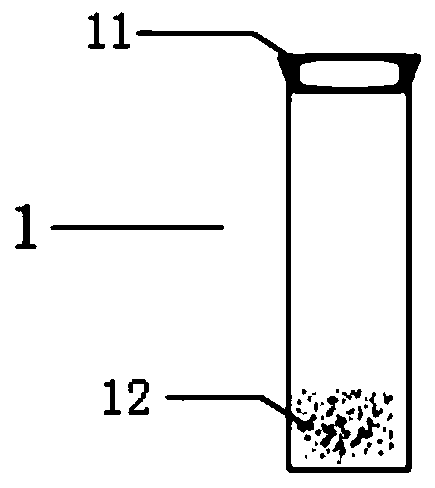
[0040] ①Sample pretreatment: Select 28 finished tobacco leaves currently in use as the investigation objects, dry them in an oven at 40°C, then crush them and pass them through a 40-mesh sieve; accurately weigh 0.2g of the sample powder into the outer tube, add 50mL of 5wt % hydrochloric acid aqueous solution as the extraction agent, and then, fix the inner casing of the extraction bottle on the mouth of the outer casing with a sealing ring. At this time, the extraction solution enters the catheter through the filter sieve and flows out from the catheter to achieve the effect of filtering the sample. Collect 1-1.5mL of the extract from the bend of the catheter to the outlet, and perform on-line purified ion chromatography analysis.
[0041] ②Ion chromatography analysis: Add an online solid phase extraction purification column before the ion chro...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Tobacco seedlings from 5 material samples from gene editing and breeding factories were selected as the research objects, and the samples were freeze-dried at -80°C. Sample processing and ion chromatographic analysis are the same as in Example 1. The measurement results show that: (a) the potassium content of one material is 0.285wt%, which is far lower than the average value of 1.64wt% of normal tobacco seedlings. Potassium absorption disorder. After continuous cultivation, the leaf margins turn yellow, and then turn brown, scorched like burning; brown spots or plaques appear on the leaves. (b) The potassium content of the two materials is 0.126wt%, which is far lower than the average value of 0.537wt% of normal tobacco seedlings. Magnesium absorption disorder, after continued cultivation, leaf chlorosis appeared, and the chlorosis spread from the leaf tip and leaf edge to the leaf base and middle, and the leaves formed reticular veins. (c) Absorption of inorganic ca...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Taking 5 kinds of finished tobacco leaves of Baijia tobacco as investigation samples, the content of 5 kinds of inorganic cations was determined. The measurement steps were the same as in Example 1. The content of inorganic cations in the samples was consistent with the range of inorganic cations in high-quality Baijia tobacco.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com