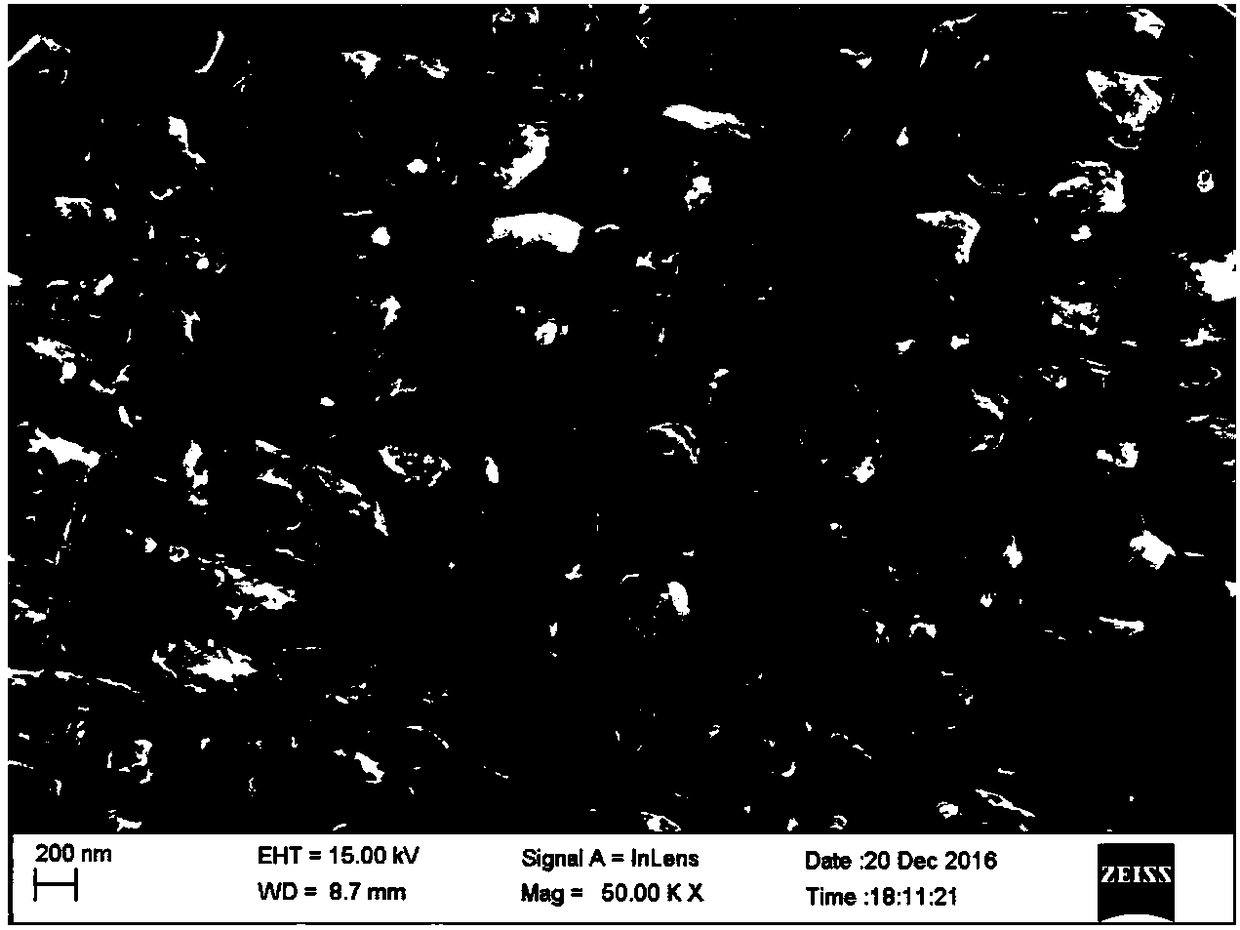
High-strength gamma'-phase-strengthened cobalt-based high-temperature alloy
A high-temperature alloy, high-strength technology, applied in mechanical equipment, engine components, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the oxidation resistance of alloys, and achieve excellent high-temperature oxidation resistance and thermal corrosion performance, high-temperature strength, and high-temperature The effect of excellent corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
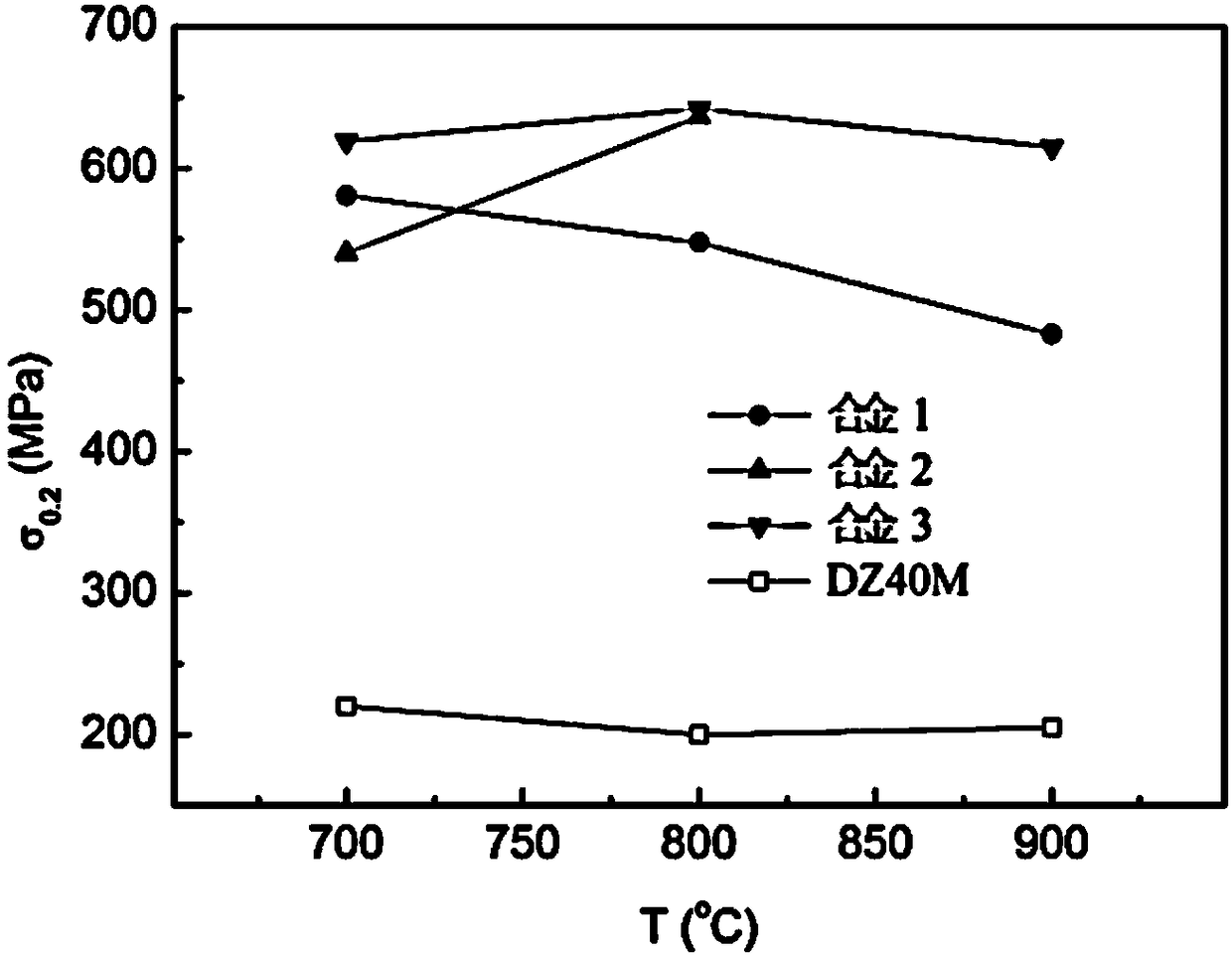
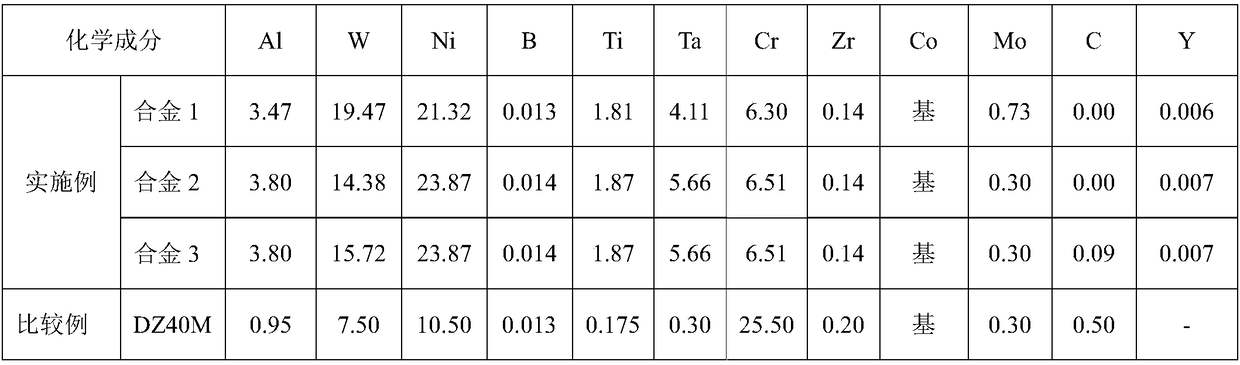
[0034] In Table 1, the yield strength of alloy 1 is higher, which is determined by figure 2 It can be seen that the yield strength of alloy 1 is about 2.5 times that of the traditional cobalt-based directionally solidified superalloy DZ40M. Not only that, Alloy 1 has good high temperature oxidation resistance and hot corrosion resistance. Table 2 shows the average oxidation rate of alloys 1-3 and DZ40M at 900°C and according to the standard name "Test Method for Determination of Oxidation Resistance of Steel and Superalloys" (standard number HB5258-2000, implementation date January 1, 2001) Evaluation of the oxidation resistance of alloys; Table 3 shows the average hot corrosion weight gain of alloys 1-3 at 800 and 900 °C. It can be seen from Table 2 and Table 3 that compared with DZ40M, the average oxidation weight gain and average hot corrosion weight gain of Example alloy 1 are significantly smaller than those of the comparative alloy, showing excellent oxidation resistan...
Embodiment 2
[0041] In Table 1, the yield strength of alloy 2 is higher, which is determined by figure 2 It can be seen that the high temperature yield strength of alloy 2 is about 2.5-3 times that of the traditional cobalt-based directionally solidified superalloy DZ40M. Not only that, but it can be seen from Table 2 and Table 3 that compared with DZ40M, the average oxidation weight gain and average hot corrosion weight gain of Example alloy 2 are significantly smaller than those of the comparative alloy, showing excellent oxidation resistance and hot corrosion resistance.
Embodiment 3
[0043] In Table 1, the yield strength of alloy 3 is higher, which is determined by figure 2 It can be seen that the high temperature yield strength of alloy 3 is about 2.5-3 times that of the traditional cobalt-based directionally solidified superalloy DZ40M. Moreover, it can be seen from Table 2 and Table 3 that compared with DZ40M, the average oxidation weight gain and average hot corrosion weight gain of Example alloy 3 are significantly smaller than those of the comparative example alloy, showing excellent oxidation resistance and hot corrosion resistance. In addition, Example Alloy 3 has good durability properties. Under the condition of temperature of 900°C and test stress of 160MPa, the durability life of Example alloy 3 is as high as 184.117h, while that of DZ40M is 85h. The alloys of the present invention exhibit excellent high temperature durability properties. (DZ40M data comes from "China Superalloy Handbook")
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com