Preparation method of yttrium-doped antimony telluride phase changing material
A technology of phase change materials and yttrium doping, applied in the direction of electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of uneven distribution of elements in phase change materials, affecting device performance, and easy phase separation, etc., achieving low cost, uniform element distribution, and easy raw materials The effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
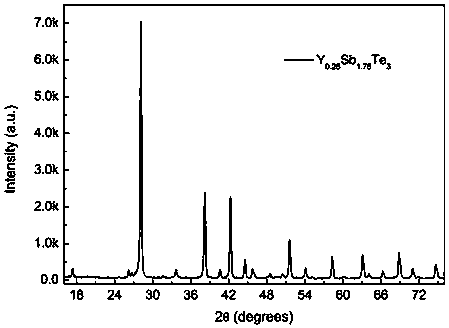
[0019] Preparation Y x Sb 2-x Te 3 , x=0.25, namely Y 0.25 Sb 1.75 Te 3
[0020] 1) Weigh 0.25mmol Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O, 1.75 mmol SbCl 3 and 3 mmol TeO 2 . Set Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O, SbCl 3 Dissolve in 5ml absolute ethanol to obtain solution A; TeO 2 Dissolve in 40ml dilute ammonia solution to obtain solution B;
[0021] 2) Mix solution A and solution B obtained in step 1), and stir magnetically at room temperature for 30 minutes to mix the raw materials evenly to obtain a precursor solution;
[0022] 3) Move the precursor solution obtained in step 2) into a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reactor, add 1.2g NaBH 4 , close the reaction kettle, and stop the reaction after insulated at 180°C for 20h;
[0023] 4) After the reaction temperature drops to room temperature, open the reaction kettle, pour off the upper liquid, and leave the lower precipitate and a part of viscous solution;
[0024] 5) The precipitate obtained in step 4) was washed alternately with deionize...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Preparation Y x Sb 2-x Te 3 , x=0.083, namely Y 0.083 Sb 1.917 Te 3
[0027] 1) Weigh 0.083mmol Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O, 1.917mmol SbCl 3 and 3 mmol TeO 2 . Set Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O, SbCl 3 Dissolve in 5ml absolute ethanol to obtain solution A; TeO 2 Dissolve in 40ml dilute ammonia solution to obtain solution B;
[0028] 2) Mix solution A and solution B obtained in step 1), and stir magnetically at room temperature for 30 minutes to mix the raw materials evenly to obtain a precursor solution;
[0029] 3) Move the precursor solution obtained in step 2) into a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reactor, add 1.2g NaBH 4 , close the reaction kettle, and stop the reaction after insulated at 180°C for 20h;
[0030] 4) After the reaction temperature drops to room temperature, open the reaction kettle, pour off the upper liquid, and leave the lower precipitate and a part of viscous solution;
[0031] 5) The precipitate obtained in step 4) was washed alternately with deio...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Preparation Y x Sb 2-x Te 3 , x=0.167, namely Y 0.167 Sb 1.833 Te 3
[0034] 1) Weigh 0.167mmol Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O, 1.833 mmol SbCl 3 and 3 mmol TeO 2 . Set Y(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O, SbCl 3 Dissolve in 5ml absolute ethanol to obtain solution A; TeO 2 Dissolve in 40ml dilute ammonia solution to obtain solution B;
[0035] 2) Mix solution A and solution B obtained in step 1), and stir magnetically at room temperature for 30 minutes to mix the raw materials evenly to obtain a precursor solution;
[0036] 3) Move the precursor solution obtained in step 2) into a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reactor, add 1.2g NaBH 4 , close the reaction kettle, and stop the reaction after insulated at 180°C for 20h;
[0037] 4) After the reaction temperature drops to room temperature, open the reaction kettle, pour off the upper liquid, and leave the lower precipitate and a part of viscous solution;
[0038] 5) The precipitate obtained in step 4) was washed alternately with dei...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com