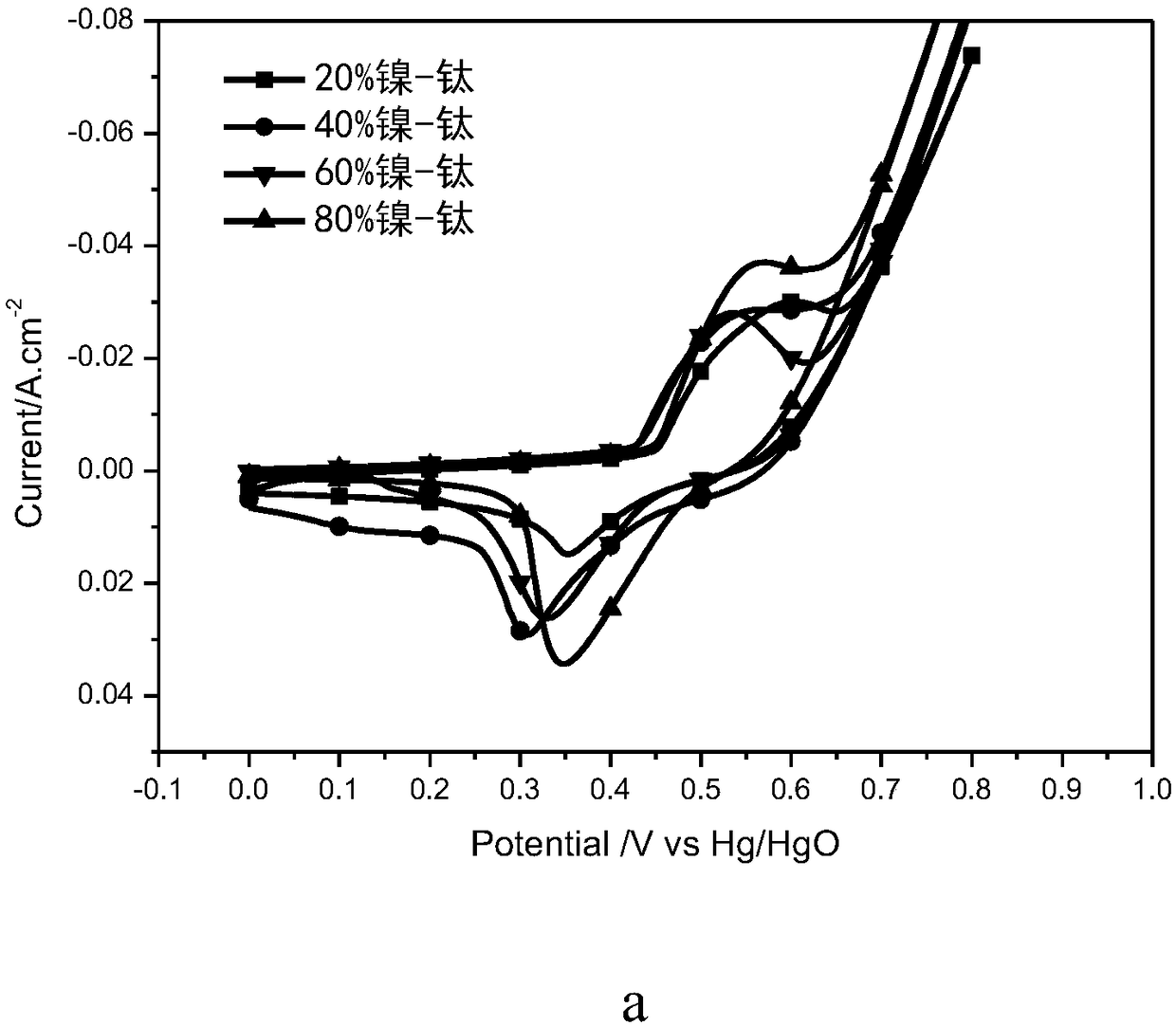
Preparation method of porous titanium-substrate-loaded nickel oxide (nickel hydroxide) electrode with electroconductive ceramic interface
A technology of conductive ceramics and nickel hydroxide, applied in the fields of electrochemical energy and nanomaterials, can solve the problems of different interfacial charge conduction capabilities and huge differences in the stability of electrochemically active electrodes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Use an electronic analytical balance to weigh 0.4g 5000 mesh titanium hydride powder, 0.1g 5000 mesh nickel powder, pour the powder into a 500 ml corundum ball mill jar in turn, use zirconia beads as ball mill beads, and mix for 30min at a speed of 350r / min, because The sample itself is relatively fine, so this step is only for mixing the sample evenly.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Just can obtain the metal powder of pure titanium, 80% titanium, 60% titanium, 40% titanium, 20% titanium, pure nickel by changing the ratio of titanium and nickel in Example 1, and the metal powder is taken out from the ball mill jar, because the ball mill jar High-speed ball milling will cause the sample to stick to the wall and cause powder agglomeration, so the sample powder taken out must be ground for 30 minutes in a mortar to make the powder compact formable. Weigh 5.0g of mixed sample powder and pour it into a steel mold with a size of 10mm*17mm. The pressure of the oil cylinder is 3.6T, that is, the pressure is 211.76 Mpa. After pressurization, the pressure is kept for 10s, and the titanium-nickel metal powder compact is obtained after demoulding. .
Embodiment 3
[0034] Put the titanium-nickel metal powder compact into a corundum porcelain boat and put it into a tube furnace. The first stage of burning: vacuumize. Then set the sintering parameters, raise the temperature from room temperature to 600°C, and the heating rate is 1°C / min, so that the titanium hydride is slowly decomposed from the green body, so that the void structure is complete and does not collapse, and the holding time is 60 minutes to completely dehydrogenate. The second stage of firing: first ventilate the mixed gas of argon and oxygen for 30 minutes to exhaust the air in the tube as much as possible, then raise the temperature from 600°C to 950°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min to sinter the metal powder and form ceramics on the surface Oxide layer, keep warm for 60min.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com