Multi-batch primary separation method of same-donor-derived human mesenchymal stem cells
A separation method and stem cell technology, applied in the field of multi-batch primary separation, can solve problems such as high price, limited cell viability, and decreased mesenchymal stem cell viability, and achieve the effect of avoiding risks and drawbacks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] Example 1 A method for the isolation of multiple batches of primary human mesenchymal stem cells from the same donor
[0103] The method is as above, wherein, step (5) uses different concentrations of fetal bovine serum (FBS) or human AB serum to soak the small pieces of umbilical cord tissue in the previous step for 15 minutes, and obtain primary cells after plating.
[0104] Primary cells refer to the earliest algebraic cells directly derived from in vitro cultured tissues. In the present invention, the mesenchymal stem cells obtained after culturing or incubating the small tissue pieces and the original culture supernatant without passage are collectively referred to as primary cells.
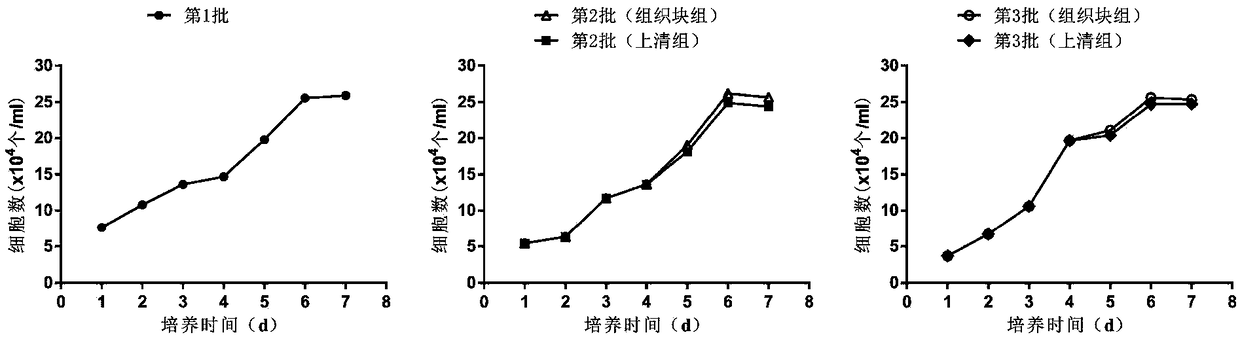
[0105] For each group, the earliest appearance time of primary cells, the time of the first passage, the success rate of tissue block culture (the number of tissue blocks that successfully freed cells / the total number of inoculated tissue blocks × 100%), the number of primary cells ( ...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Example 2 A method for the isolation of multiple batches of primary human mesenchymal stem cells from the same donor
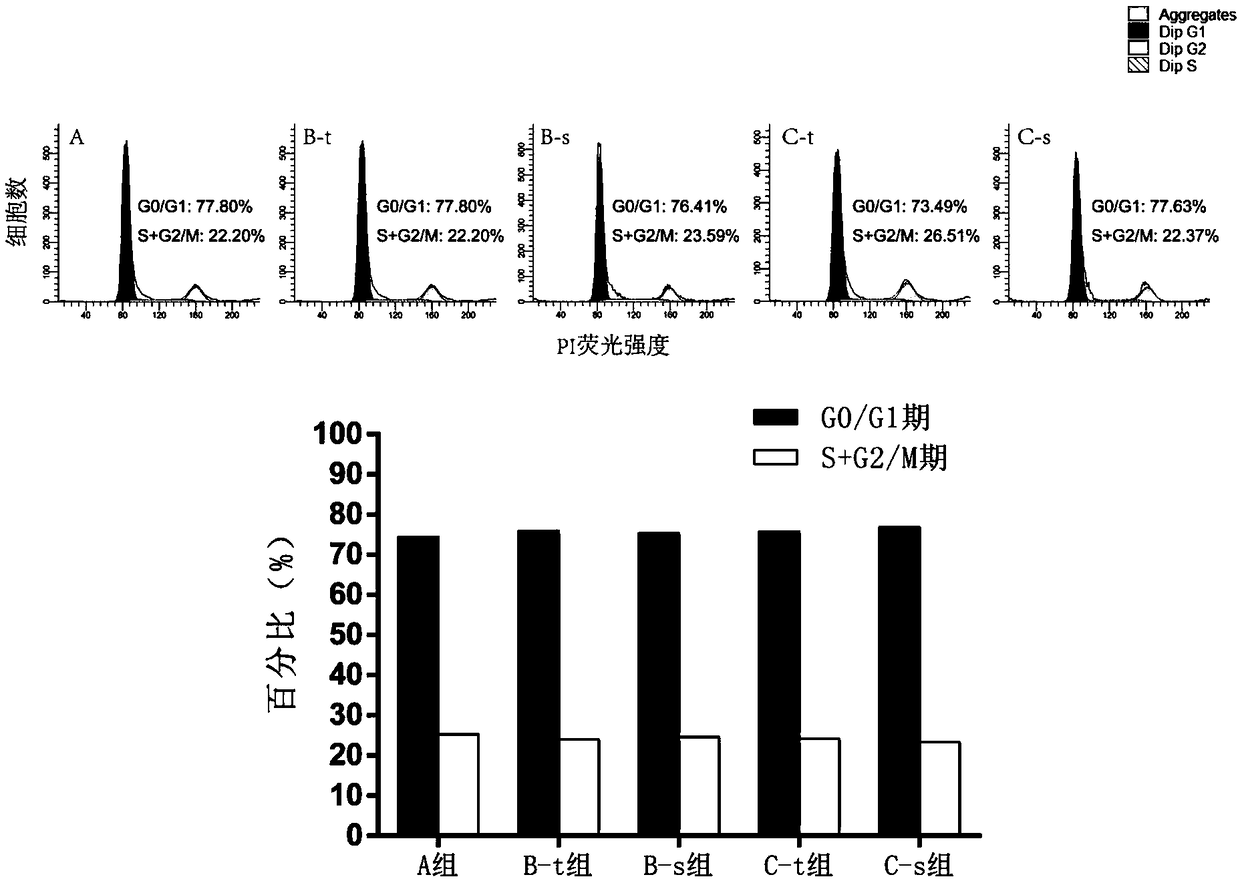
[0112] The method is as above, step (5) soak the umbilical cord tissue pieces in the previous step with 100% fetal bovine serum for 15 minutes. The primary isolation time and yield of each batch of hUC-MSCs were compared. Among them, group A is the first culture group of umbilical cord tissue blocks; group B-t is the mesenchymal stem cells (primary cells) obtained from the recovered umbilical cord tissue blocks after the first culture through the second culture; group B-s is the supernatant of the first culture of tissue blocks The mesenchymal stem cells (primary cells) obtained after incubation with B-t solution alone; the C-t group is the mesenchymal stem cells (primary cells) obtained from the umbilical cord tissue block (recovered from the B-t group) through the third culture; the C-s group is the tissue block Mesenchymal stem cells (primary cells)...
Embodiment 3
[0137] Example 3 A method for the isolation of multiple batches of primary human mesenchymal stem cells from the same donor
[0138] The method is as described above, in step (5), 100% human AB serum is used to soak the small pieces of umbilical cord tissue in the previous step for 15 minutes. The primary isolation time and yield of each batch of hUC-MSCs were compared. Among them, group A is the first culture group of umbilical cord tissue blocks; group B-t is the mesenchymal stem cells (primary cells) obtained from the recovered umbilical cord tissue blocks after the first culture through the second culture; group B-s is the supernatant of the first culture of tissue blocks The mesenchymal stem cells (primary cells) obtained after incubation with B-t solution alone; the C-t group is the mesenchymal stem cells (primary cells) obtained from the umbilical cord tissue block (recovered from the B-t group) through the third culture; the C-s group is the tissue block Mesenchymal s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| percent by volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com