Zr-based biomedical alloy and preparation method thereof
A biomedical and alloy technology, which is applied in the field of Zr-based biomedical alloys and its preparation, can solve the problems of unfavorable bone healing, stress shielding effect, and affecting the quality of nuclear magnetic resonance images, so as to facilitate healing, alleviate the influence of stress shielding, The effect of reducing the artifact area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
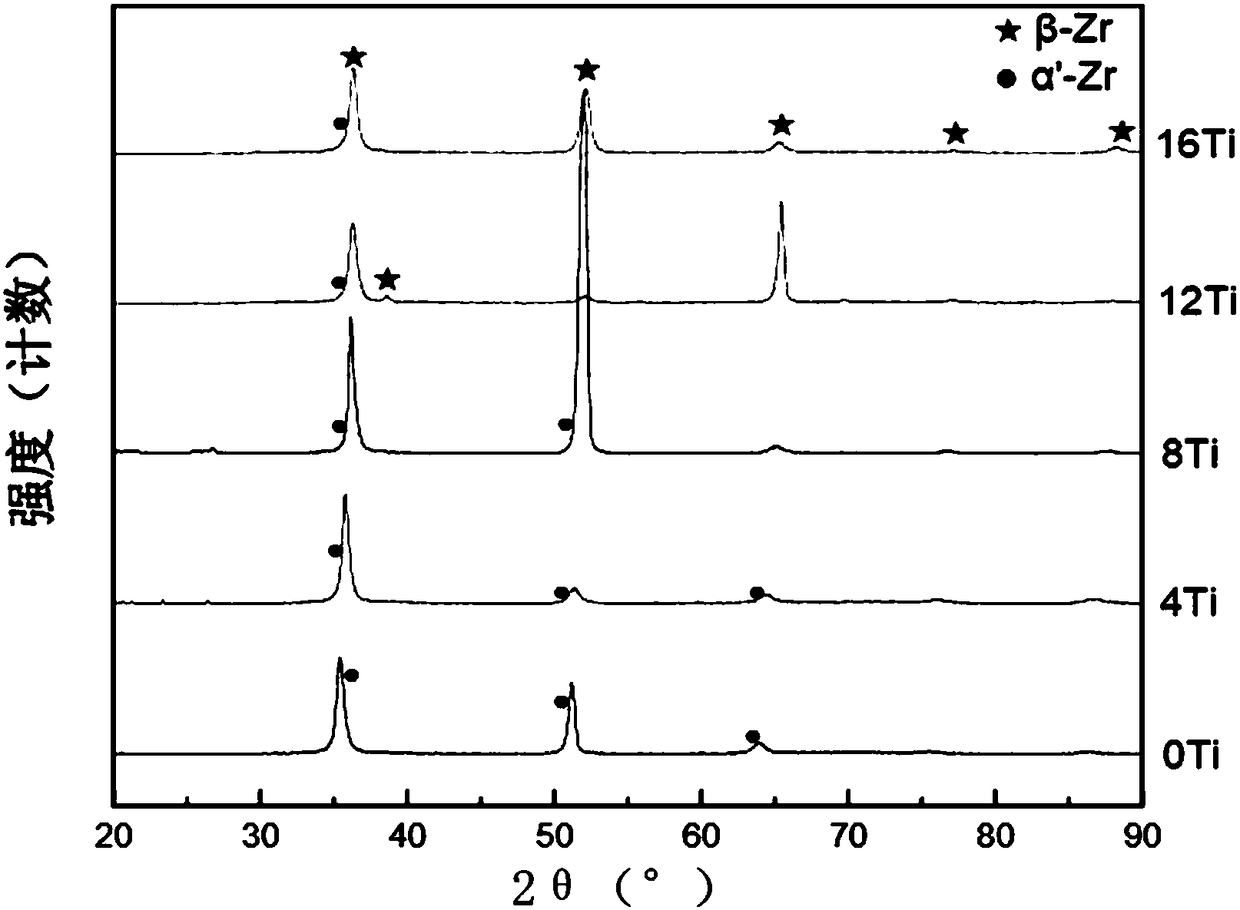
[0037] A Zr-based biomedical alloy with low modulus and low magnetic susceptibility of the present invention is composed of Nb: 16% by weight, and the balance is zirconium and unavoidable impurity elements.
[0038] The Zr-based biomedical alloy of the present embodiment is prepared by the following method:
[0039] (1) Weigh the raw materials, and weigh the corresponding Zr grains and Nb grains according to the weight percentages of the designed raw material components. The purity of Zr grains and Nb grains are all above 99.99wt%, and the particle size should be kept as consistent as possible.
[0040] (2) Mix the weighed raw materials evenly.
[0041](3) Smelting raw materials: Wipe the inside of the non-consumable vacuum smelting furnace clean to keep the furnace clean, then put the raw materials in step (2) into the copper crucible of the non-consumable vacuum smelting furnace, start vacuuming, and the vacuum degree controlled at 3×10 -3 Pa, argon gas was introduced to r...
Embodiment 2
[0046] A Zr-based biomedical alloy with low modulus and low magnetic susceptibility of the present invention is composed of: Nb: 16%, Ti: 4%, and the balance is zirconium and unavoidable impurity elements.
[0047] The Zr-based biomedical alloy of the present embodiment is prepared by the following method:
[0048] (1) Weigh the raw materials, weigh the corresponding Zr grains, Nb grains, and Ti grains respectively according to the weight percentage of each raw material component designed, and the purity of Zr grains, Nb grains, and Ti grains are all above 99.99wt%, and keep the The particle size is consistent.
[0049] (2) Mix the weighed raw materials evenly.
[0050] (3) Smelting raw materials: Wipe the inside of the non-consumable vacuum smelting furnace clean to keep the furnace clean, then put the raw materials in step (2) into the copper crucible of the non-consumable vacuum smelting furnace, start vacuuming, and the vacuum degree controlled at 3×10 -3 Pa, argon gas ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] A Zr-based biomedical alloy with low modulus and low magnetic susceptibility of the present invention is composed of Nb: 16%, Ti: 8%, and the balance is zirconium and unavoidable impurity elements.
[0056] The Zr-based biomedical alloy of the present embodiment is prepared by the following method:
[0057] (1) Weigh the raw materials, weigh the corresponding Zr grains, Nb grains, and Ti grains respectively according to the weight percentage of each raw material component designed, and the purity of Zr grains, Nb grains, and Ti grains are all above 99.99wt%, and keep the The particle size is consistent.
[0058] (2) Mix the weighed raw materials evenly.
[0059] (3) Smelting raw materials: Wipe the inside of the non-consumable vacuum smelting furnace clean to keep the furnace clean, then put the raw materials in step (2) into the copper crucible of the non-consumable vacuum smelting furnace, start vacuuming, and the vacuum degree controlled at 3×10 -3 Pa, argon gas w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| magnetic susceptibility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| magnetic susceptibility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com