Method for reversely extracting iron by adopting solvent extraction
An extraction and solvent technology, applied in the field of hydrometallurgy, can solve the problems of difficult iron extraction, change of organic phase properties, and lower production efficiency, and achieve the effects of simplified iron recovery process, good filtration performance, and short process time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
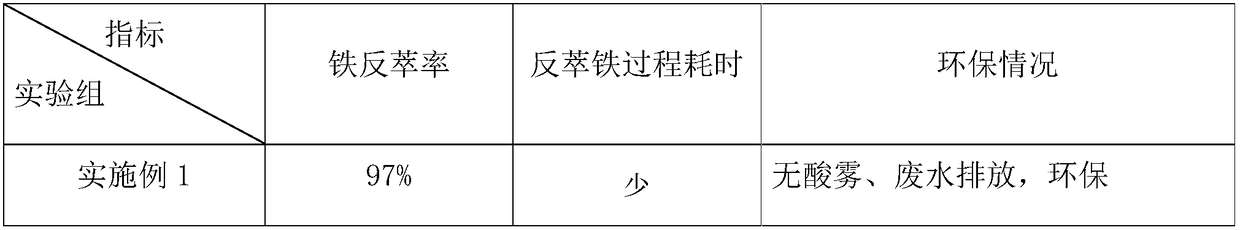
[0025] Acidic leachate from a factory, containing Fe 3+ 1.2g / L, Co 2+ 15.3g / L, Ni 2+ 5.1g / L, pH 2.0.
[0026] In this embodiment, the extractant in the organic phase is di-isooctyl phosphate, the diluent is kerosene, and the phase regulator and modifier can be conventional in the field (sequent examples are also the same). - The kerosene system extracts and removes iron, the volume concentration of diisooctyl phosphate in the organic phase is 5%, and the iron-loaded organic phase after iron extraction contains 1.0 g / L of iron.
[0027] In the antiferric solution used in this embodiment, the antiferrous agent is NaOH solution, and the nucleation accelerator is ferric hydroxide and polyacrylamide (PAM). The above-mentioned NaOH solution of 8g / L (0.2mol / L) is used for the iron-loaded organic phase to back-extract iron at room temperature, and ferric hydroxide and polyacrylamide (PAM) are added as nucleation accelerators, and the anti-iron solution is , NaOH accounts for 2%, n...
Embodiment 2
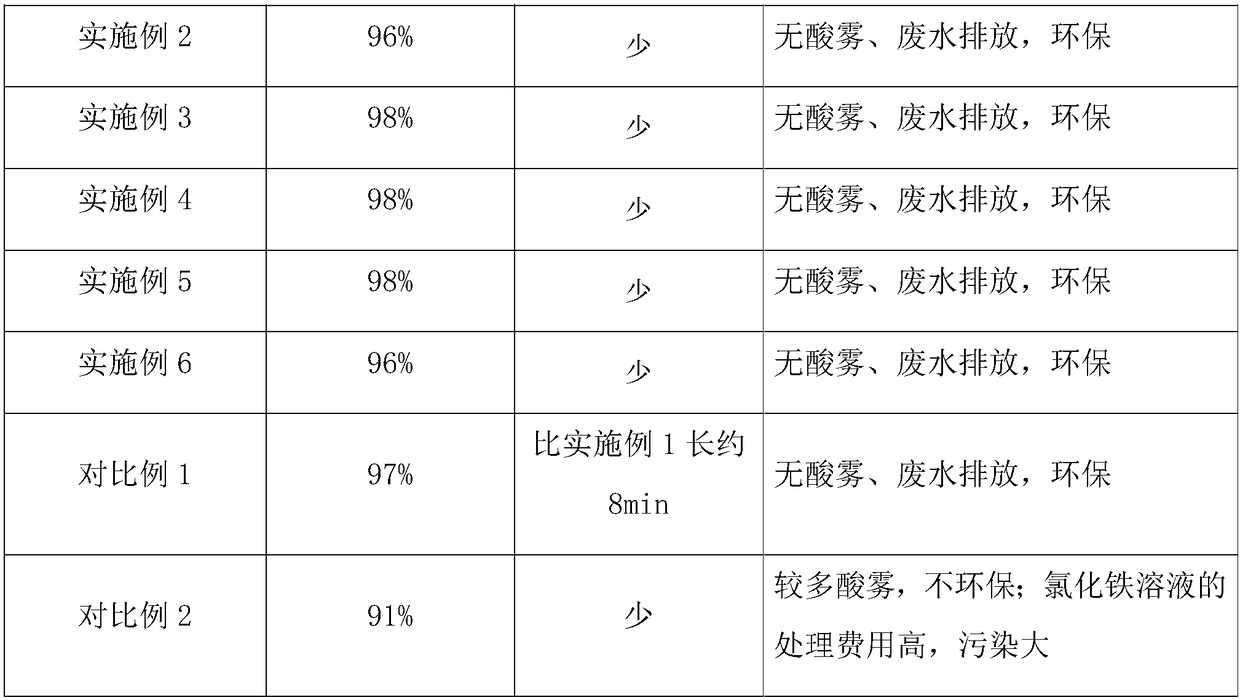
[0030] The vanadium-containing slag acid leaching solution of a certain factory contains Fe 3+ 1.0g / L, V 4+ 5.4g / L, pH 2.2.
[0031] In this embodiment, the extractant in the organic phase is diisooctyl phosphate, the diluent is kerosene, vanadium and iron are extracted with diisooctyl phosphate-kerosene system, and the volume concentration of diisooctyl phosphate in the organic phase is 15%. , the loaded organic phase after extraction contains 0.5g / L of iron and 3.3g / L of vanadium.
[0032] Load organic phase with 50g / L of H 2 SO 4 The vanadium is stripped from the solution so that the vanadium content of the organic phase after stripping the vanadium is less than 0.1g / L.
[0033]In the antiferric solution used in this embodiment, the antiferrous agent is NaOH solution, and the nucleation accelerator is PSF. The organic phase after stripping vanadium is separated half volume, strips iron with the NaOH solution of 120g / L (3mol / L) at normal temperature, and by mass ratio i...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The vanadium slag acid leaching solution of a certain factory contains Fe 3+ 3.5g / L, V 4+ 6.9g / L, pH 2.0.
[0037] In this embodiment, the extractant in the organic phase is diisooctyl phosphate, the diluent is kerosene, vanadium and iron are extracted with diisooctyl phosphate-kerosene system, and the volume concentration of diisooctyl phosphate in the organic phase is 20%. , the loaded organic phase after extraction contains 2.1g / L of iron and 4.1g / L of vanadium.
[0038] Load organic phase with 50g / L of H 2 SO 4 The vanadium is stripped from the solution, and the vanadium content of the organic phase after stripping the vanadium is less than 0.1g / L.
[0039] In the antiferric solution used in this embodiment, the antiferric agent is NaOH solution, and the nucleation accelerator is ferric sulfate. The organic phase after stripping vanadium uses 45g / L NaOH solution to strip iron at normal temperature, and carry out single-stage stripping according to O / A=1:1, in t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com