Method for extracting valuable metals from fumes in steel plant
A technology of valuable metals and iron and steel plants, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve problems such as complex treatment process, complex leaching process, and undetermined scheme, and achieve the effect of simplifying the process flow, simple process and required equipment, and preventing explosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
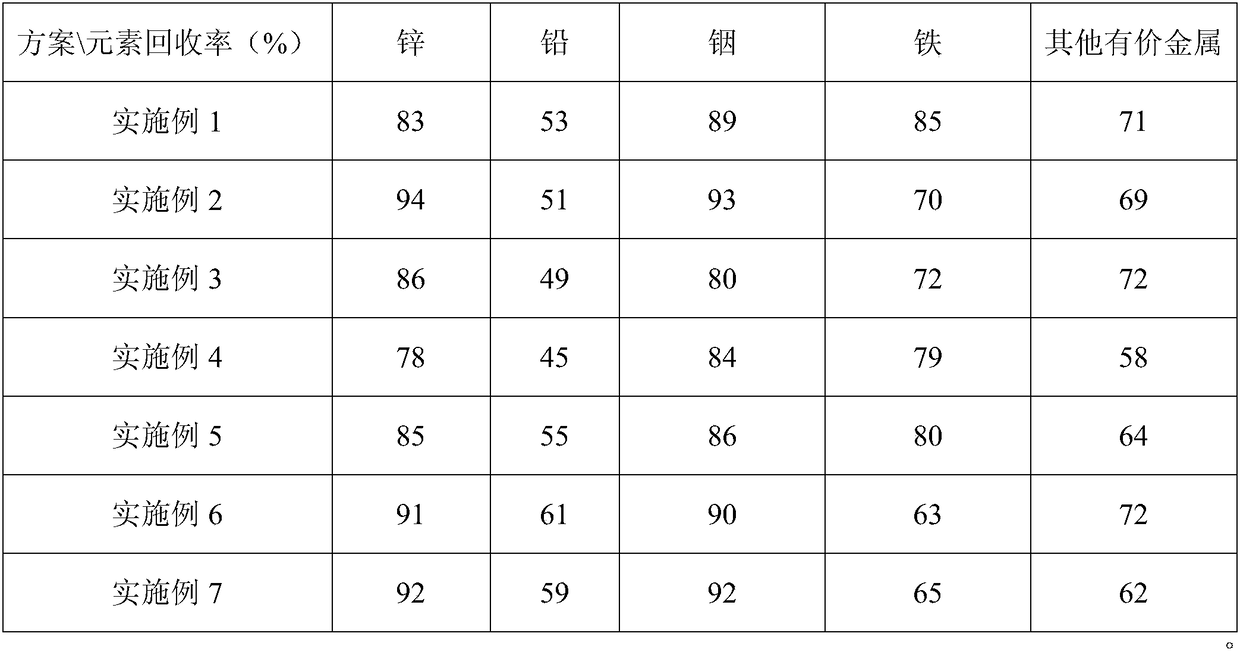
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] This embodiment is realized through the following steps:
[0039] 1) Blast furnace gas ash and steelmaking dust removal ash are pressed into balls with a diameter of 35 mm, wherein the total molar amount of metal oxides in the blast furnace gas ash and steelmaking dust removal ash is equal to the amount of coal powder in the blast furnace gas ash The molar ratio is 1:1; the mass content of fixed carbon in the added blast furnace gas ash is 20%; then the mixed spheres are put into the crucible, and then the whole is put into the vacuum reduction regenerative furnace, and the vacuum degree of 90Pa is placed in the Keep warm at 600°C for 4 hours. After the heat preservation is over, break the vacuum when the temperature in the furnace is lowered to 300°C, and take out the crucible;
[0040] 2) Perform magnetic separation on the reduced mixture to obtain iron concentrate, thereby separating valuable metals such as lead, zinc, indium and silver from the reduced mixture.
Embodiment 2
[0042] This embodiment is realized through the following steps:
[0043]1) Press the blast furnace gas ash and steelmaking dust removal mud into a mixing sphere with a diameter of 20mm, wherein the total molar amount of the added blast furnace gas ash and steelmaking dust removal mud and the molar amount of coal powder in the blast furnace gas ash The ratio of the amount is 6:1; the mass content of fixed carbon in the added blast furnace gas ash is 25%; then the mixed spheres are put into the crucible, and then the whole is put into the vacuum reduction regenerative furnace, with a vacuum degree of 50Pa at 1200 ℃ heat preservation for 0.5h, after the heat preservation is over, the vacuum is broken when the temperature in the furnace is lowered to 200 ℃, and the crucible is taken out;
[0044] 2) Perform magnetic separation on the reduced mixture to obtain iron concentrate, thereby separating valuable metals such as lead, zinc, indium and silver from the reduced mixture.
Embodiment 3
[0046] This embodiment is realized through the following steps:
[0047] 1) Press the blast furnace gas mud and steelmaking dust removal dust into a mixing sphere with a diameter of 25 mm, wherein the total molar amount of metal oxides of the added blast furnace gas mud and steelmaking dust removal dust is equal to the molar amount of pulverized coal in the blast furnace gas muddy The ratio of the amount is 12:1; the mass content of fixed carbon in the added blast furnace gas mud is 35%; then the mixed spheres are put into the corundum crucible, and then the whole is put into the vacuum reduction regenerative furnace, with a vacuum degree of 70Pa in the Keep warm at 1000°C for 2 hours. After the heat preservation is over, break the vacuum when the temperature in the furnace is lowered to 150°C, and take out the crucible;
[0048] 2) Perform magnetic separation on the reduced mixture to obtain iron concentrate, thereby separating valuable metals such as lead, zinc, indium and s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com