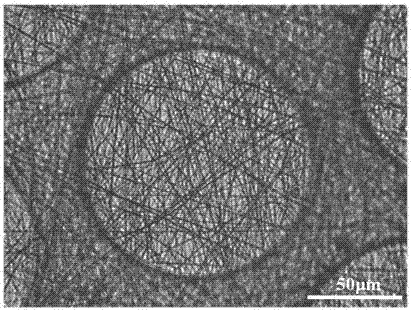
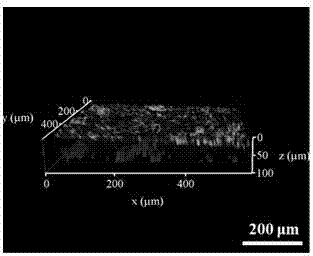
3D pseudo-skin construction method based on organs-on-chips and directional differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells
A technology of pluripotent stem cells and organ chips, which is applied in the field of 3D pseudo-epidermal construction, can solve the problems of insufficient skin source materials, unsatisfactory, and inability to realize multi-cell co-cultivation and drug screening, etc., to achieve a good microenvironment and promote cell adhesion. attached effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: Inoculation of iPSCs
[0049] When iPSC reaches the passage state, it can be used for inoculation. The specific steps are as follows:
[0050] Take out the PSCeasy human pluripotent stem cell (ES / iPS) medium (iPSC medium for short) and put it at room temperature, take out the culture dish coated with Matrigel Matrix (Matrigel, Matrigel for short, from Corning Company in the United States), and suck Remove the coating solution and add an appropriate amount of iPSC medium, place in 5% CO 2 In a 37°C constant temperature cell incubator, 37°C water bath preheated PBS solution (phosphate buffered solution, referred to as PBS, from Gibco in the United States) and 0.5mM EDTA passaging working solution (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, referred to as EDTA, from Thermo Fisher Corporation of the United States).
[0051] The old iPSC medium was aspirated, and apoptotic iPSCs were removed by rinsing the bottom of the dish by adding calcium and magnesium-free PBS soluti...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2: Differentiation of iPSCs into keratinocytes
[0059] On Day0, on the second day after the iPSCs with a seeding density of about 30% adhered to the wall, 2 ml of Defined keratinocyte serum-free medium (Keratinocyte serum-free medium, referred to as DKSFM, derived from Gibco in the United States) medium (1um all -trans RA (retinoic acid, referred to as RA, derived from Sigma Company of the United States), 10ng / ml RecombinantHuman BMP-4 Protein (bone morphogenic protein, referred to as BMP-4, derived from R&D Systems Company of the United States) and 1.5mmCaCl 2 ), change the medium every two days, 37℃, 5%CO 2 Incubator cultivation.
[0060] On Day 6, the old medium was aspirated, and 2 ml of Defined keratinocyte serum-free medium (DKSFM) medium was added. The DKSFM medium did not contain RA, BMP4 and CaCl2, and was changed every two days until keratinocytes were initially differentiated.
[0061] On Day 16, the old medium was aspirated, and an appropriate amo...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3: Differentiation of iPSCs into fibroblasts
[0063] Preparation of embryoid bodies (EBs): first to Aggrewell TM 400 (microwell Petri dish, referred to as Aggrewell TM 400, from Canada's STEMCELL company), add DMEM medium, rinse and suck out. Join Aggrewell TM medium, centrifuge at 1000rmp for 5min, remove air bubbles, digest iPSCs with a density of 80-90% adherent with 0.5mM EDTA, pipette the cells with PBS and centrifuge, and aspirate the supernatant.
[0064] After that, remove the spare Aggrewell from the incubator TM 400, remove the Aggrewell TM medium, refill 1ml containing 10 7 The suspension of iPSCs in cell / ml was centrifuged and cultured in an incubator for 24 hours. The next day, in a biosafety cabinet, the EBs were aspirated out and stained with Aggrewell in a low-adhesion six-well plate. TM medium (containing 0.3mM Ascorbic acid (ascorbic acid, referred to as AA, from the American company Sigma), 10ng / ml Recombinant Human TGF-beta 2 Protein...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com