Glycosylated oxalate decarboxylase as well as preparation and application of glycosylated oxalate decarboxylase
A technology of oxalate decarboxylase and glycosylation, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, applications, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of inactivity and instability, and achieve the effects of excellent stability, high activity, and high degradation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] In this example, the fermentation production process of glycosylated oxalate decarboxylase is described by taking Agrocybe abacus as an example. The conclusions of the experiments carried out by the inventors with Agrocybe arvenifera, Agrocybe sp. , except for some comparison results, the present application will not repeat the description.
Embodiment 2
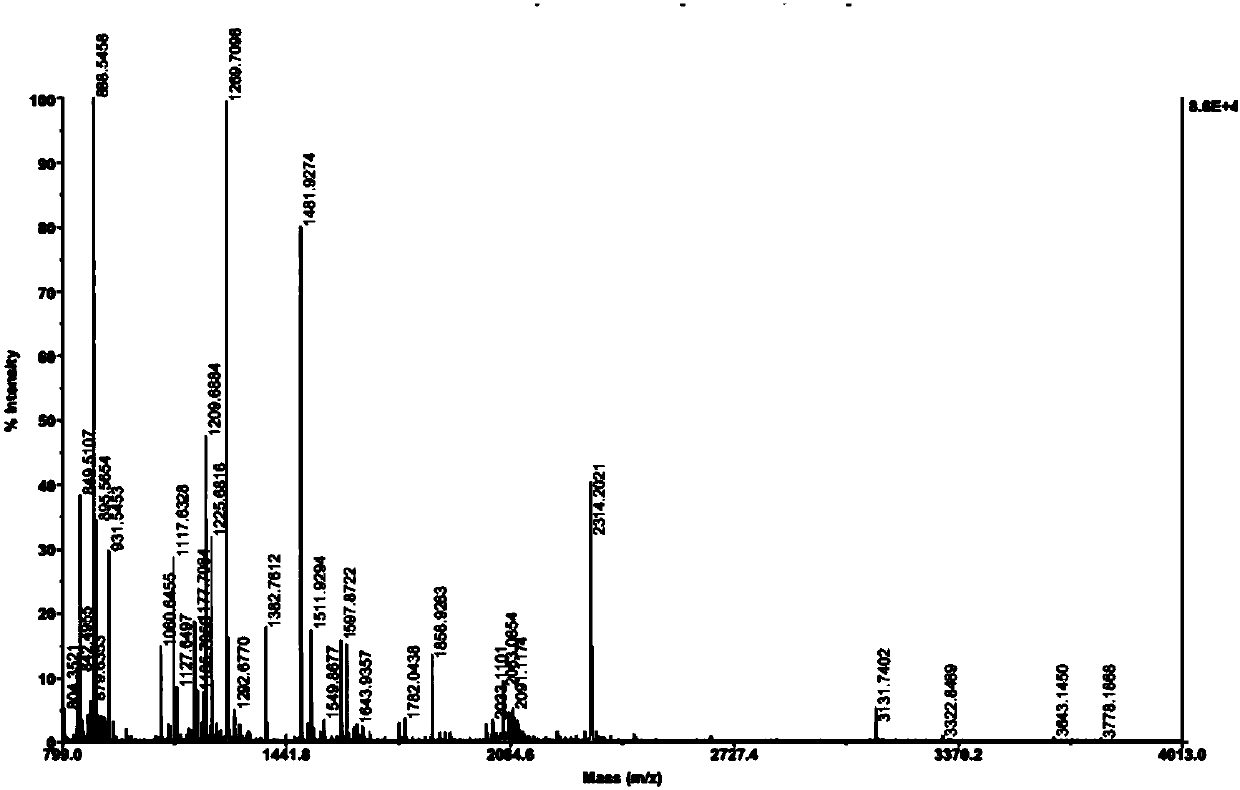
[0037] Embodiment 2: Purification and identification of oxalate decarboxylase
[0038] The supernatant containing oxalate decarboxylase obtained by the method in Example 1 was purified by Q sepharose chromatographic column to obtain purified oxalate decarboxylase. The specific operation process is as follows: adjust the pH value of the supernatant containing oxalate decarboxylase to 6.0 with 0.5M NaOH, then remove the precipitated impurities by high-speed centrifugation at 15000g, and concentrate the supernatant through a 50KDa ultrafiltration membrane; NaH 2 PO 4 Buffer (pH 6.0) equilibrates 5 column volumes (CV), loads the concentrated oxalate decarboxylase solution onto a well-balanced Q sepharose column, and then equilibrates with 2CV of equilibration buffer (25mM NaH 2 PO 4 , pH value 6.0) to wash away the impurity protein not hanging on the column, and then through the elution buffer (elution buffer A: 25mM NaH 2 PO 4 , pH 6.0; Elution buffer B: 25mMNaH 2 PO 4 , 1...
Embodiment 3
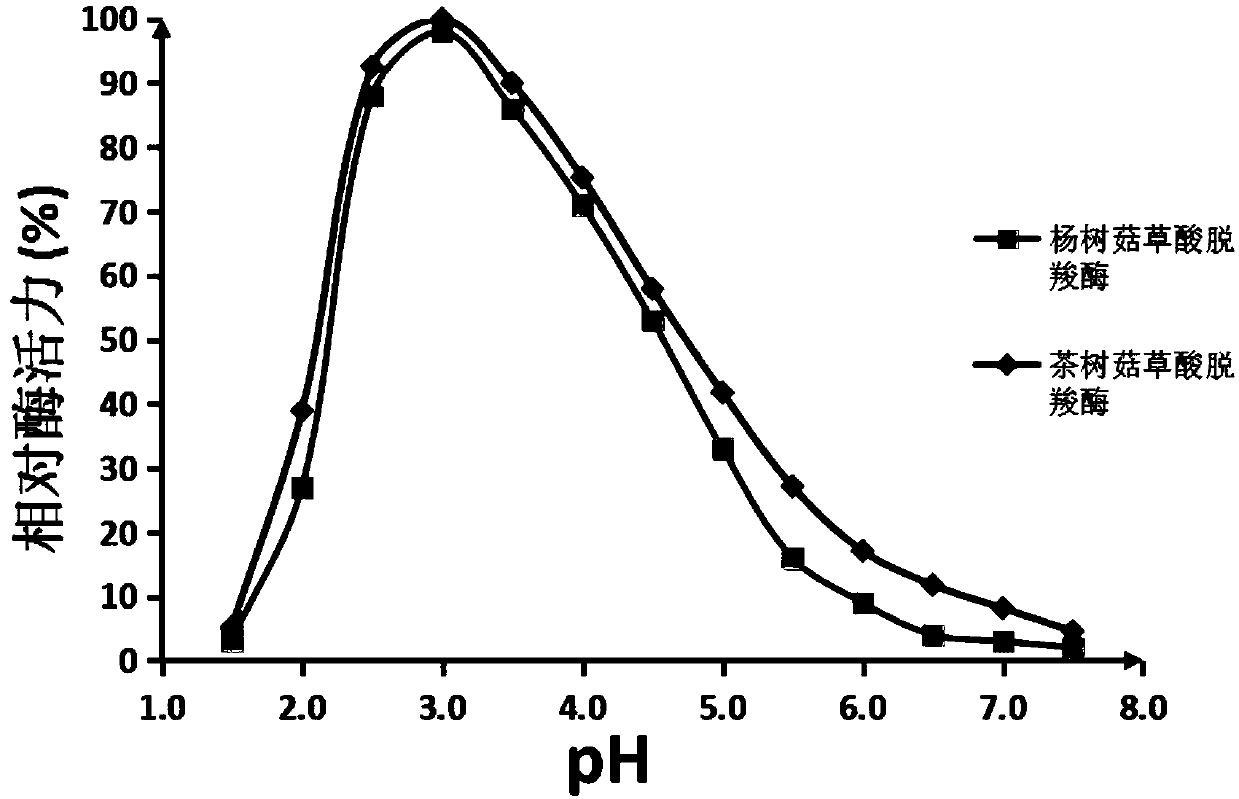
[0039] Embodiment 3 Oxalate decarboxylase activity and enzymatic property determination
[0040] In the present invention, an HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography, high performance liquid chromatography) method is used to measure the activity of oxalate decarboxylase. The specific operation process is as follows: 1.0mL 5mM (millimolar concentration) oxalate solution (containing 25mM citrate buffer, pH value 3.0), after preheating at 37°C for 10 minutes, add 0.01-0.1ml (according to enzyme The concentration is determined by adding the volume) to the solution or bacterial powder suspension containing oxalate decarboxylase to start the reaction. After reacting for 30 minutes, add 50 μL of 2.5M (molar concentration) sulfuric acid to inactivate the enzyme. Centrifuge rapidly and take the supernatant, and measure the residual oxalate concentration by HPLC. One enzyme activity unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme required to degrade 1 micromole of oxalate per minute ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com