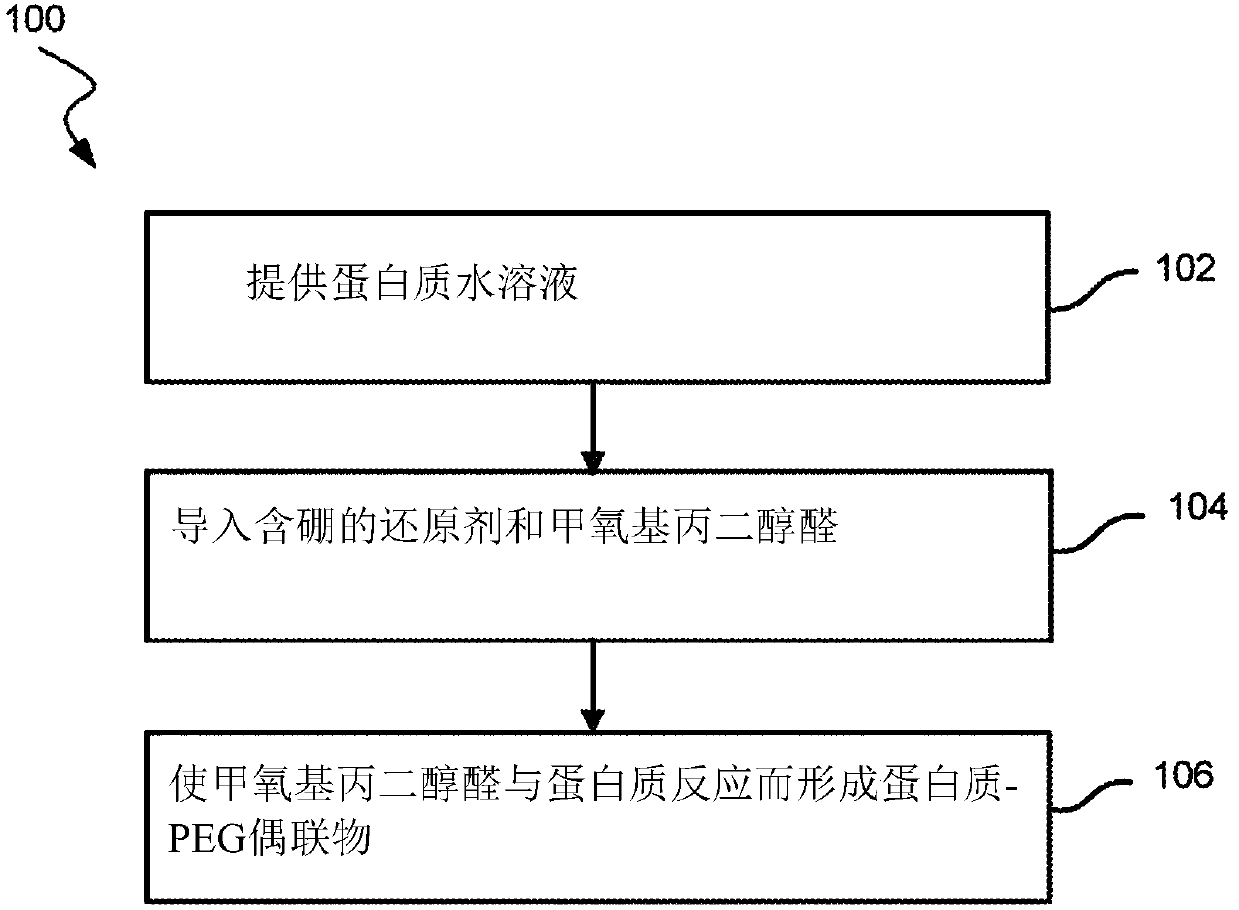
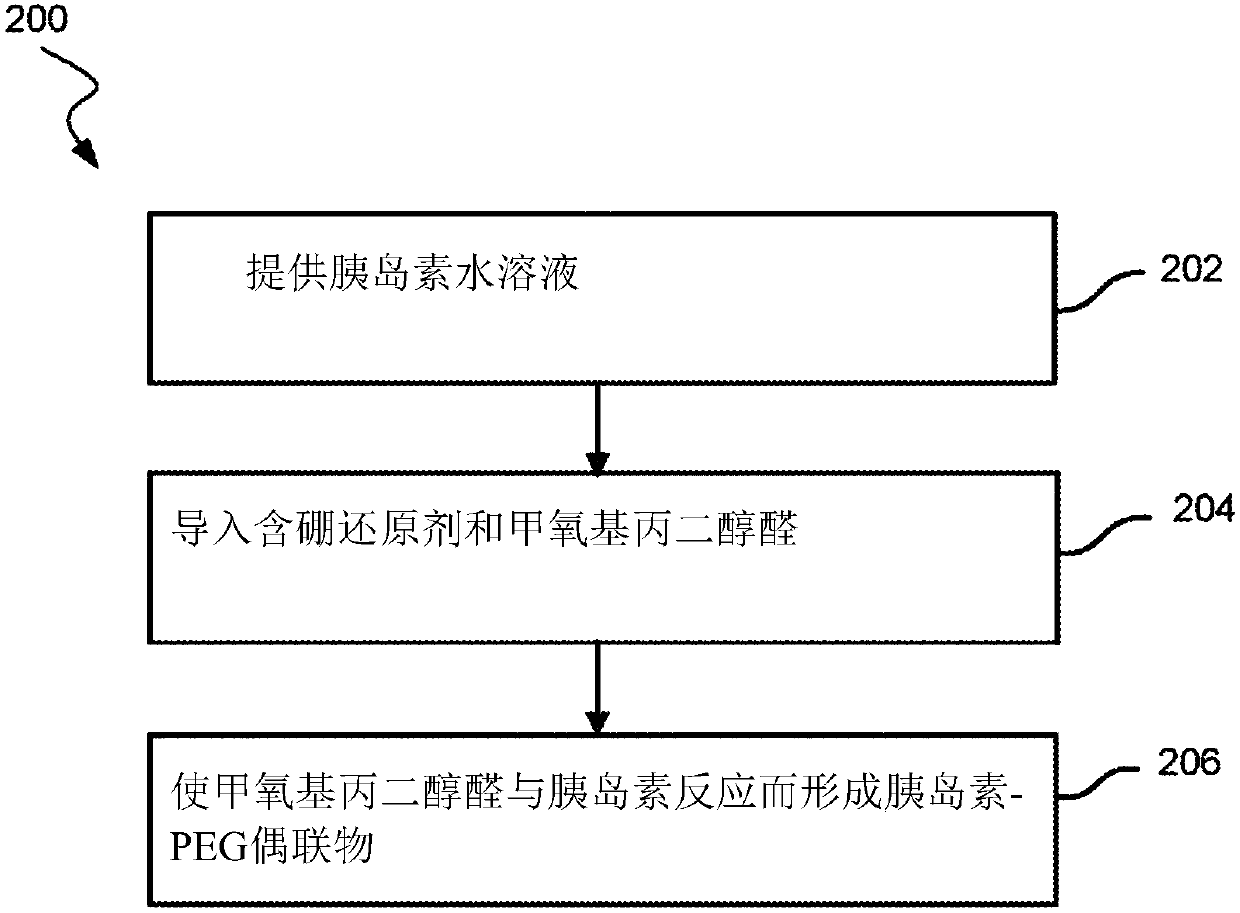
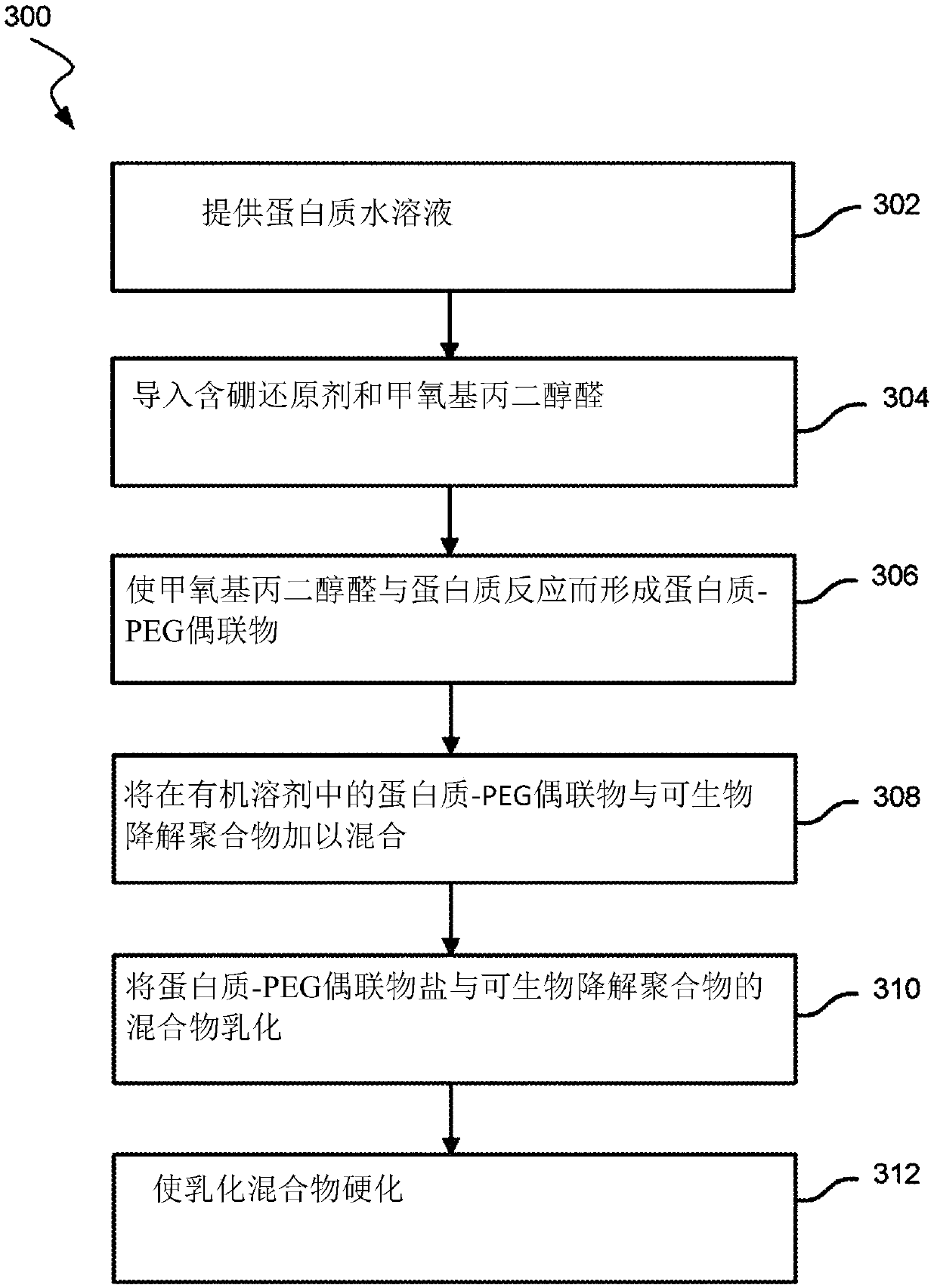
Amine pegylation methods for the preparation of site-specific protein conjugates
A polyethylene glycol aldehyde and protein technology, applied in the fields of peptide/protein components, chemical instruments and methods, animal/human proteins, etc., can solve the problem of reducing patient compliance rate, increasing patient inconvenience, and unsatisfactory patient treatment outcomes And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] At a range of sodium cyanoborohydride concentrations ([NaBH 3 CN]) to determine operating conditions and sodium cyanoborohydride limits for achieving consistent yields of monoPEGylated insulin-PEG conjugates ("mPEGIns"). The following parameters (values in parentheses) were kept constant over a series of experiments: [rhI] 0(0.86mM), [mPEGpropald] 0 / [rhI] 0 (1.04), [EDTA] / [rhI] 0 (0.17-0.18), temperature (28°C), buffer strength (30 mM), and pH (4.0). [rhI] 0 is the initial concentration of recombinant human insulin; [mPEGpropald] 0 is the initial concentration of methoxypropanediol aldehyde; [EDTA] is the concentration of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. The starting materials were also the same for each reaction. exist Figure 4 Yields of mono-PEGylated insulin-PEG conjugates are graphed as a function of sodium cyanoborohydride. in [rhI] 0 At this value, mPEGIns yields are shown in [NaBH 3 CN] = 1.0 mM and [NaBH 3 CN] = optimal concentration between 1.5 ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Chelating Zn in rhI Raw Materials by EDTA 2+ ion, thus dissolving rhI. In order to comply with the United States Pharmacopoeia (USP), the Zn contained in the rhI raw material 2+ Must be less than or equal to 1.00% (w / w). Mimic Zn by substituting an appropriate amount of zinc acetate for a small portion of sodium acetate in the reaction buffer 2+ concentration.
[0051] For a narrow range of [EDTA] / [rhI] 0 experimenting. The following parameters (values in parentheses) were held constant for this series of reactions: [rhI] 0 (0.86-0.88mM), [mPEGpropald] 0 / [rhI] 0 (1.04), [NaBH 3 CN] (1.2 mM), temperature (28°C), buffer strength (30 mM), and pH (4.0). The yield of mPEGIns in each reaction was monitored by RPHPLC analysis, and in Figure 5A This result is shown graphically in [EDTA] / [rhI] 0 The function. Figure 5A The data shown in the [EDTA] / [rhI] of 0.25 0 There is a maximum yield of PEGIns at . [EDTA] / [rhI] greater than 0.175 0 In terms of the value o...
Embodiment 3
[0053] For a larger range of [EDTA] / [rhI] 0 Example 2 was repeated. For repeatability experiments the following parameters were held constant (values in square brackets): [rhI] 0 (0.86mM), [mPEGpropald] 0 / [rhI] 0 (1.07), [NaBH 3 CN] (2.0 mM), temperature (28°C), buffer strength (40 mM), and pH (4.0). exist Figure 5B This set of experiments is given in [EDTA] / [rhI] 0 mPEGIns yield as a function. exist Figure 5B In the range shown in, an increase in [EDTA] / [rhI] was observed 0 Reduced mPEGIns yield.
[0054] With 0.36% (w / w) Zn 2+ rhI to complete the experiments of Examples 2 and 3. Figure 5A Indicates [EDTA] / [rhI] in the range of 0.175 to 0.50 0 Should result in approximately the same yield of mPEGIns. Said Zn 2+ content, [EDTA] / [Zn 2+ ] The corresponding range is 0.55 to 1.56. For this case, [EDTA] / [Zn 2+ ] = 0.55 corresponds to [EDTA] / [rhI] 0 = 0.48. based on Figure 5B Data in [EDTA] / [Zn 2+ ] can have a range upper limit of 2.0. However, when cons...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com