Cloud auditing method with lightweight user dynamic revocation and data dynamic update
A dynamic update and lightweight technology, applied in key distribution, can solve the problems that cloud storage data cannot be updated dynamically in real time, users and their public and private keys remain unchanged, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
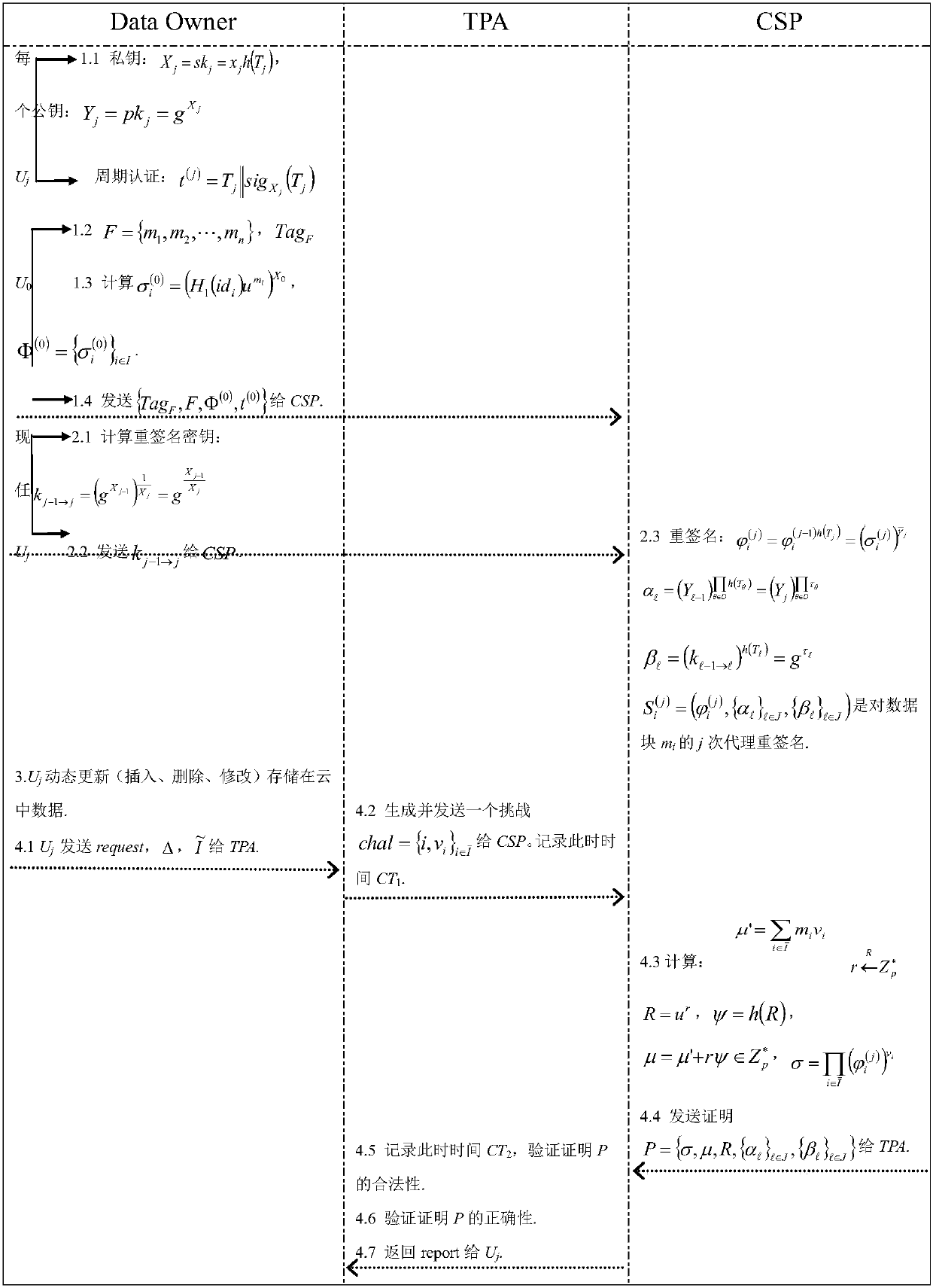
[0085] Example 1: In a certain period of time, only one user manages the data. When the user's term of office ends, a new user is replaced to continue to manage the data (the dynamic revocation of an individual user can be regarded as the same user changing the public and private keys in different periods right). Record different users as U in chronological order 0 ,U 1 ,...,U s , and the corresponding term is denoted as T 0 , T 1 ,...,T s . Initially, the initial user U 0 Block the file F and use its own private key to calculate the authentication label of all data blocks (It represents the initial user U 0 For data block m i certification label). When U 0 After the term ends, U 1 will replace U 0 Continue to manage data, and so on, when U j-1 By U j After replacing, U j will compute the re-signature key k j-1→j , and send it to the CSP, which replaces the newly appointed user U j Implement proxy re-signature. During each user's tenure, he can perform real...
Embodiment 2
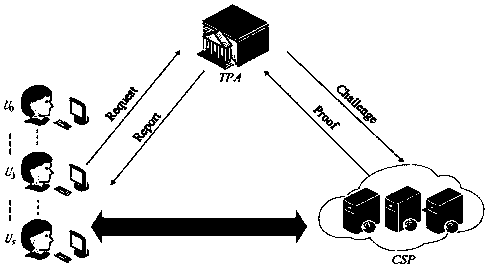
[0086] Embodiment 2: The present invention involves three parties: cloud service provider CSP, third-party audit TPA, user U (responsible for managing company data and uploading it to CSP), considering that the company's data manager U is unlikely to be in a certain position for a long time There may be personnel changes at any time due to reasons such as promotion or resignation, and the present invention uses U 0 ,U 1 ,...,U s to represent users who are dynamically replaced in chronological order, T 0 , T 1 ,...,T s Indicates the tenure of each user.
[0087] The open cloud auditing method provided by the present invention can be dynamically revoked by lightweight users and dynamically updated in several steps, and specifically includes the following steps:
[0088] 1) Initialization: Input the security parameter λ, assign a value to δ at the same time, and the system outputs the public parameter {G 1 ,G 2 ,p,g,e,h 1 ,H 2 ,h,u,ρ}, where G 1 , G 2 is the cyclic mul...
Embodiment 3
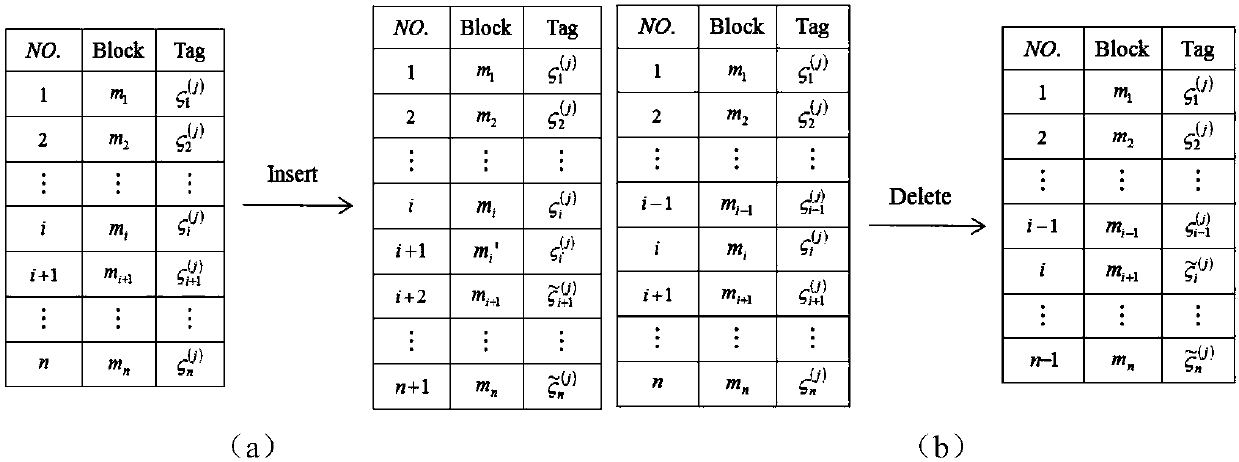
[0129] Embodiment 3: In the traditional method, the authentication tag of the data block contains the real index of the data block, and the dynamic update efficiency of cloud data is not high, such as image 3 As shown (the left (a) is inserting a data block, and the right (b) is deleting a data block), if a data block is inserted or deleted, the indexes of all data blocks after this data block will change, even if these data blocks The content has not changed, and users must still recompute their authentication tags for blocks whose index changes. In order to reduce the communication overhead, computing overhead and user burden of the system, the present invention introduces a virtual index, which can ensure that all data blocks are sorted in the correct order, for example: if η i j , then data block m j in data block m i behind. Define data block m i The initial virtual index is η i =i·ρ, ρ=2 δ (δ∈N + ), ρ represents the step size, and the selection of δ is related to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com