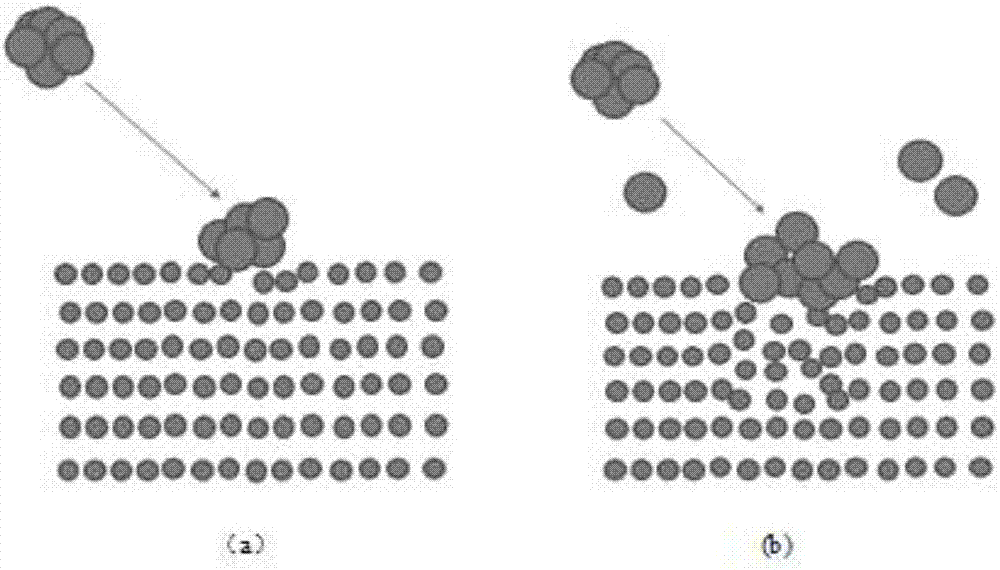
Method and system for assisting chemical vapor deposition to prepare DLC thin film through energy-loaded ionization atomic cluster
A technology of chemical vapor deposition and atomic clusters, which is applied in the field of diamond-like film preparation, can solve the problems of DLC film compactness enhancement technology, achieve broad industrialization prospects, reduce surface roughness and surface friction coefficient, and improve film /base binding effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] In this example, see figure 1 , an enhanced PECVD system, comprising a rear cavity device and a front cavity device, the rear cavity device is an energy-carrying ionization atomic cluster beam excitation system, the front cavity device is a PECVD system, and the energy-carrying ionization atomic cluster beam excitation system is The cavity of the ionized atomic cluster beam excitation system is connected with the inner cavity of the PECVD system to form a system integrated body cavity. A vacuum connection system is set between the two systems of the energy-carrying ionization atomic cluster beam excitation system and the PECVD system. The vacuum connection system can be used to integrate the system. The vacuum degree of the body cavity is adjusted and controlled. In the system complex body cavity, a baffle is set between the ionized atomic cluster beam excitation system cavity of the energy-carrying ionized atomic cluster beam excitation system and the inner cavity of th...
Embodiment 2
[0058] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
[0059] In this embodiment, the substrate temperature is set at 100° C., the accelerating voltage of the ionized radical beam is 3000 V, and the DLC film is prepared by composite PECVD.
[0060] In this embodiment, the same method as that in Embodiment 1 is used to place the substrate on the workpiece holder and bombard and clean the substrate with the energy-carrying ionized atomic cluster beam. Set the substrate temperature to 100 °C. Set the accelerating voltage of the energy-carrying ionizing radical beam excitation system to 3000V, then turn on the PECVD deposition device, and coat the film for 2 hours, with a DLC film thickness of 1 μm.
[0061] Experimental test analysis:
[0062] Example 2 The nanoindentation hardness of the DLC film was tested using the same method and parameters as in Example 1. The test results show that the DLC film prepared in Example 2 has a hardness of 15GPa an...
Embodiment 3
[0064] This embodiment is basically the same as the previous embodiment, and the special features are:
[0065] In this embodiment, the substrate temperature is set at 100° C., the accelerating voltage of the ionized radical beam is 9000 V, and the DLC film is prepared by composite PECVD.
[0066] In this embodiment, the same process steps as in the first embodiment are used to pretreat the surface of the substrate and prepare the DLC film, the temperature of the substrate is set to 100° C., but the accelerating voltage is adjusted to 9000 V, and the thickness of the DLC film is 1 μm.
[0067] Experimental test analysis:
[0068] Example 3 The nanoindentation hardness of the DLC film was tested using the same method and parameters as in Example 1. The test results show that the DLC film prepared in Example 3 has a hardness of 35GPa and an elastic modulus of 140GPa.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com