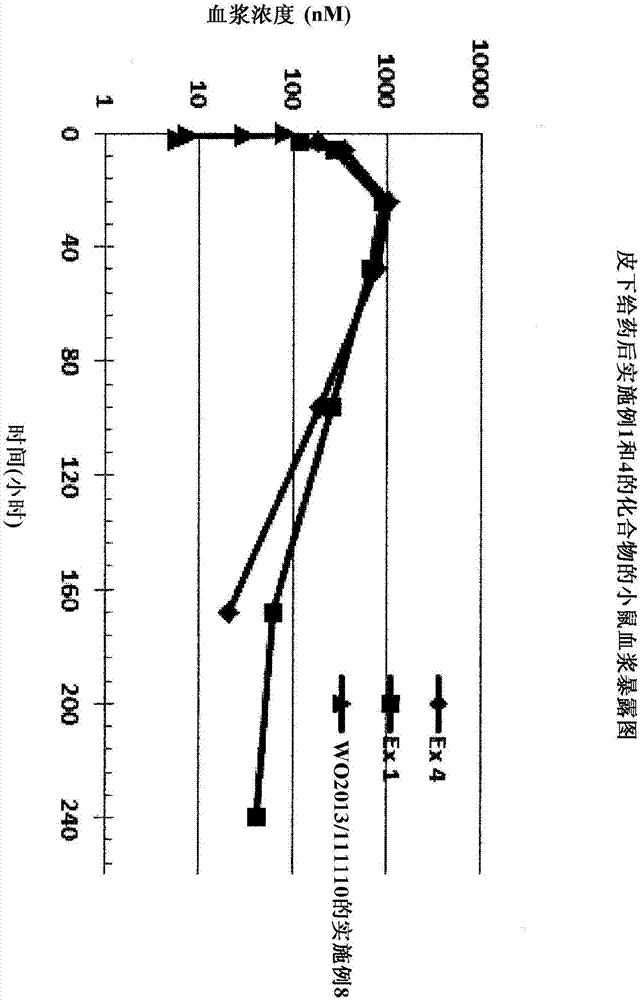
Synthetic apelin fatty acid conjugates with improved half-life
A technology of conjugates and fatty acids, which is applied in the preparation of the composition and in the field of treating cardiovascular diseases, and can solve problems such as sensitivity to protease activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0054] In embodiment 1, the invention thus provides a conjugate or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof comprising:
[0055] a. APJ agonist peptides having the following formula (I):
[0056] Q-R-P-R-L-C*-H-K-G-P-(Nle)-C*-F (I); or an amide or ester thereof, or a peptide substantially equivalent thereto; wherein the two cysteine amino acids marked with "*" are in their side chains Disulfide bonds are formed between the thiol functional groups of
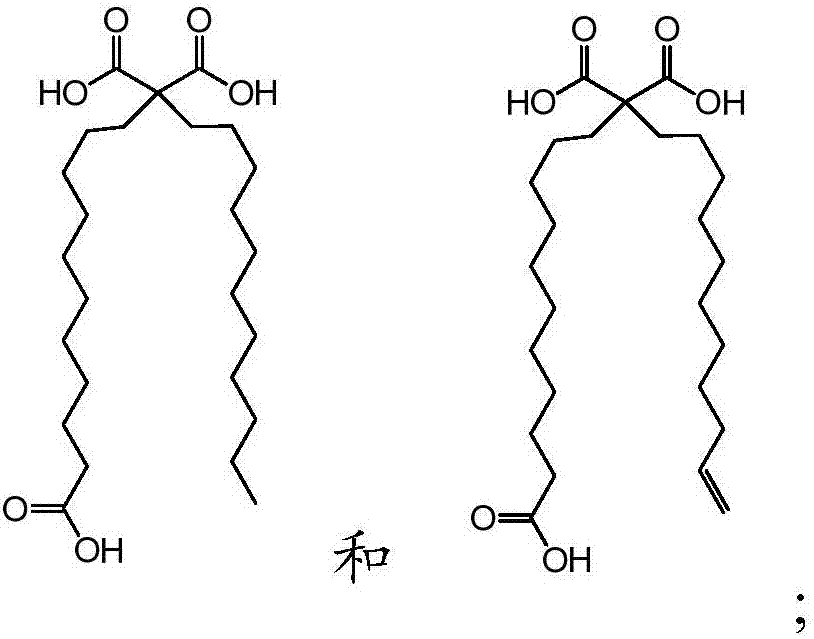
[0057] b. Fatty acids selected from:
[0058]
[0059] wherein the fatty acid is covalently linked to the N-terminus of the peptide via one of its carboxylic acid functional groups, optionally via a polyethylene glycol linker.
Embodiment approach 1A
[0060] In Embodiment 1A, the invention relates to a conjugate, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, comprising:
[0061] a. APJ agonist peptides having the following formula (I):
[0062] Q-R-P-R-L-C*-H-K-G-P-(Nle)-C*-F (I); where the two cysteine amino acids marked with "*" form a disulfide bond between the thiol functional groups in their side chains; and
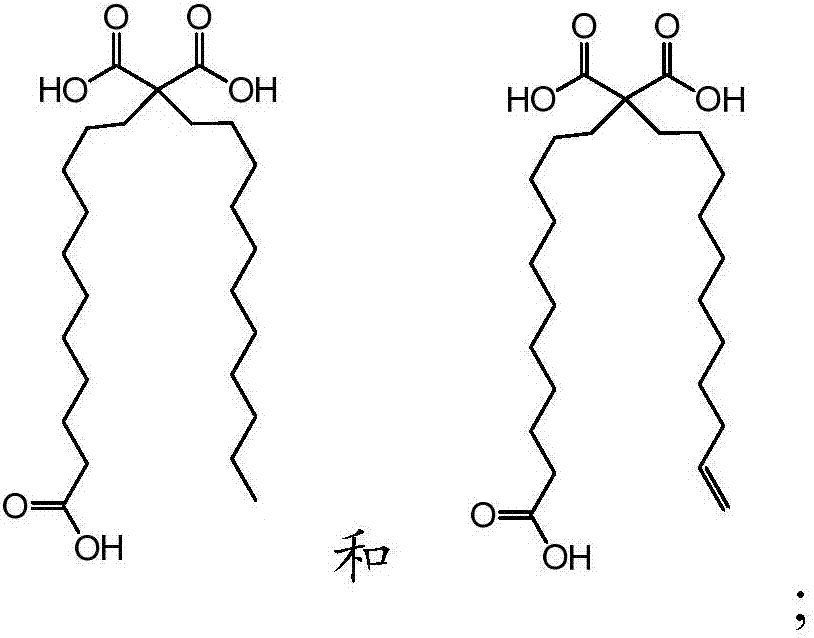
[0063] b. Fatty acids selected from:
[0064]
[0065] wherein the fatty acid is covalently linked to the N-terminus of the peptide via one of its carboxylic acid functional groups, optionally via a polyethylene glycol linker.
[0066] The fatty acids described in Embodiment 1 or 1A have been described in US Provisional Application No. 62 / 082327 (PAT056274-US-PSP2).
[0067] Any polyethylene glycol linker group is optional. The linker is polymeric in nature, being a polyethylene glycol moiety containing two reactive groups / functional groups, one of which is reactive with the polypeptide of formula I and ...
Embodiment 1
[0399] Example 1: Fatty Acid-Linker #1-Q-R-P-R-L-C*-H-K-G-P-(Nle)-C*-F(C 6 -C 12 disulfide bridge)
[0400]
[0401] step 1:
[0402] To a solution of Intermediate 1b (300 mg, 0.096 mmol) in THF (100 mL) was added fatty acid-linker construct #_1 (960 mg, 0.575 mmol) in THF (35 mL) and water (15 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature. When complete, the reaction was concentrated under partial vacuum and carried on to the next step as crude, assuming quantitative yield. (Product MW: 4681.870)
[0403]
[0404] Step 2: Deprotection:
[0405] To a solution of TFA (4.75 mL), TIPS (0.125 mL) and water (0.125 mL) was added DTT (296 mg, 1.920 mmol). Then, the premixed mixture was added to the compound of Step 1 (449 mg, 0.096 mmol), and stirred at room temperature. When complete, the reaction was concentrated under partial vacuum. The residue was treated with cold diethyl ether to give a cloudy reaction mixture which was allowed to stand at room...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com