Animal models for in vivo screening biological macromolecules having influences on tumor cell biology
A biological macromolecule and cell biology technology, applied in the field of animal model preparation, can solve the problems that are not easy to master, and sponges are easy to cause inflammatory reactions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1 Primary culture, isolation, purification and identification of salivary gland MEC cells
[0050] Cultivation, separation and purification: The direct culture method of tissue blocks is used for primary culture of sterile tissue samples. Under aseptic conditions, the tumor tissues treated with double antibodies were taken out, and gently rinsed with sterile RPMI-1640 complete medium (containing 10% fetal bovine serum) for 3 times; the tumor tissues of each group were cut into pieces with sterile ophthalmic scissors to about 2mm 3 Disperse the chopped tumor tissue into the culture bottle, slowly turn the culture bottle over, first add 2ml of complete medium, and then in 5% CO 2 , 37 ℃ incubator for tissue block culture; after 4 hours, turn over to normal state and add a small amount of culture medium to continue the culture. The culture medium was changed routinely until the cells reached 70%-80% confluence, the cells were digested with 0.25% trypsin and reatt...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The selection of embodiment 2 tumor cells
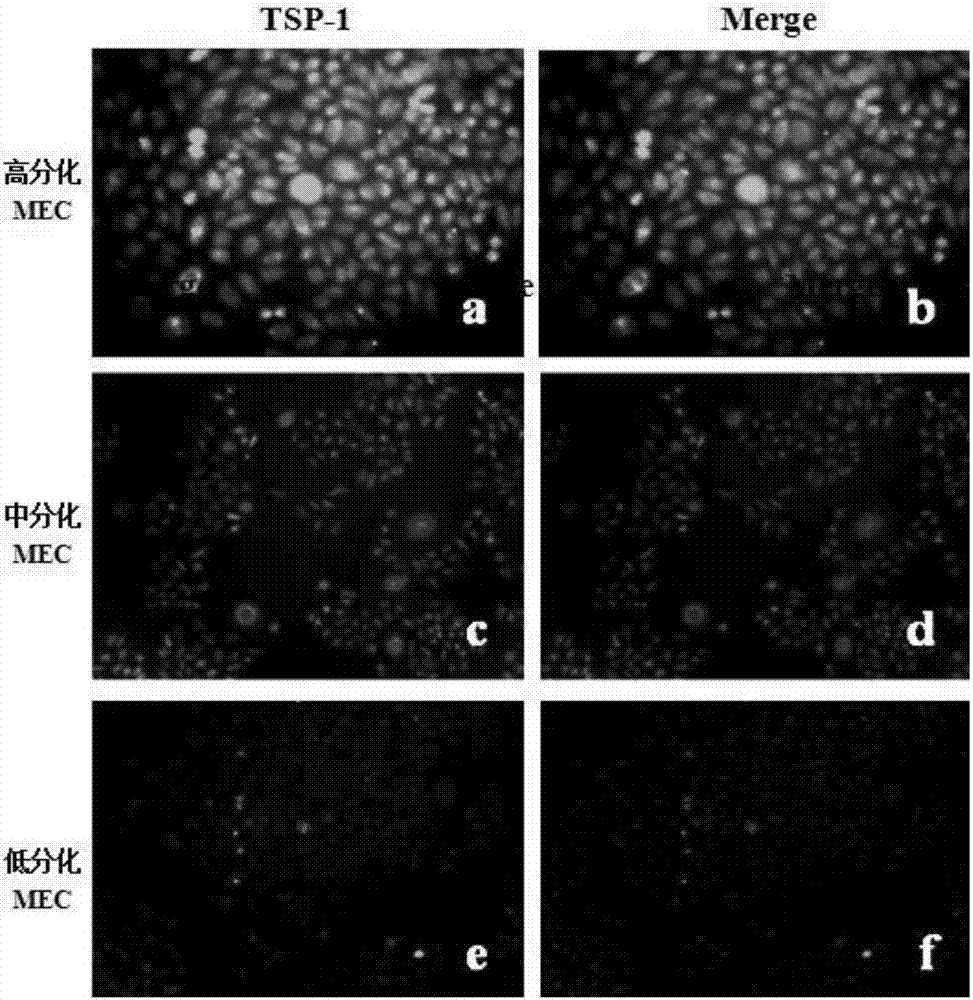
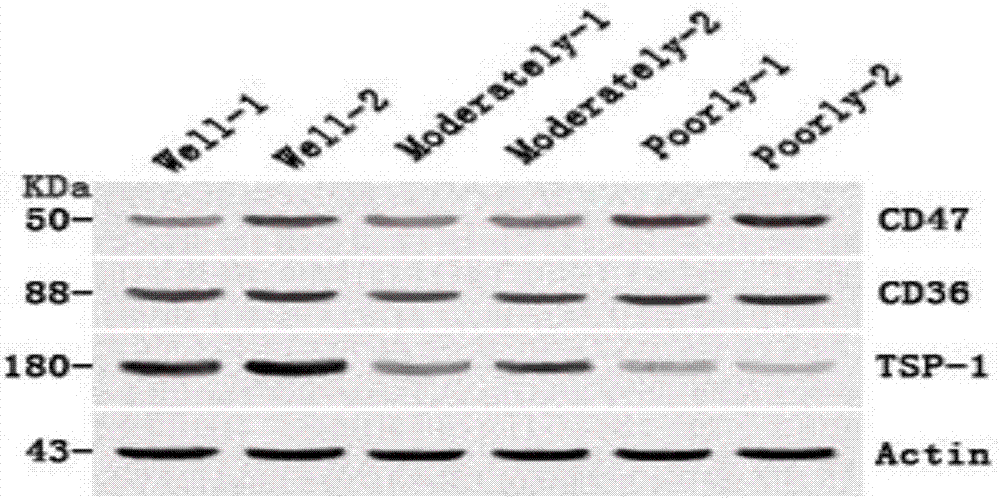
[0054] The expressions of TSP-1, CD36 and CD47 were detected in highly, medium and poorly differentiated salivary gland MECs by immunofluorescence and Western Blot. Immunofluorescence also adopts the method of cell crawling, 2ml per well at a concentration of 2×104 / ml is inoculated into a 6-well plate previously placed on a cover glass, and incubated with 1:100 mouse anti-human TSP-1 monoclonal antibody at 4°C Overnight, in the dark, add FITC fluorescently labeled rabbit anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody (1:200), biotin-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody (1:200), and DAPI for fluorescent staining of the nucleus for 2-3min, and seal The slices were protected from light and observed under a fluorescence microscope. The specific method of immunofluorescence double staining of CD36 and CD47 is roughly the same as that of TSP-1. Among them, the primary antibodies of CD36 and CD47 are both (1:50), human biotinylated-a...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3 selects suitable inoculum concentration and TSP-1 experimental action concentration and detection time point
[0058] The selected tumor cells were divided into 5×10 3 / ml, 1×10 4 / ml, 2×10 4 / ml, 5×10 4 / ml initial concentration, inoculate 96-well plate. Cells of each concentration were divided into 7 groups, each group was inoculated into 6 multiple wells, 200 μl of single cell suspension was added dropwise to each well, and placed in 5% CO 2 Incubate at 37°C. After 24 hours, use the MTT method to detect the MTT value in each well of the first group in each concentration group, and measure continuously for 7 days, and record the results with the horizontal axis as time and the vertical axis as MTT value to draw the cell growth of each concentration inoculation group curve. Select the appropriate cell inoculation concentration according to the results of each group, the results are shown in Figure 4 .
[0059] Inoculate the selected tumor cells i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Micropore | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Micropore | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com