A label and application for in vivo tracking and artificial removal of CAR-T cells
A tracer and cell technology, applied in the field of medical biology, to achieve the effect of reliable guarantee
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] Example 1 Construction of CAR-T cells
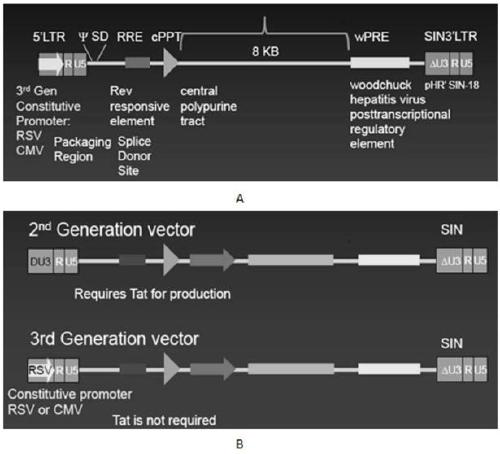
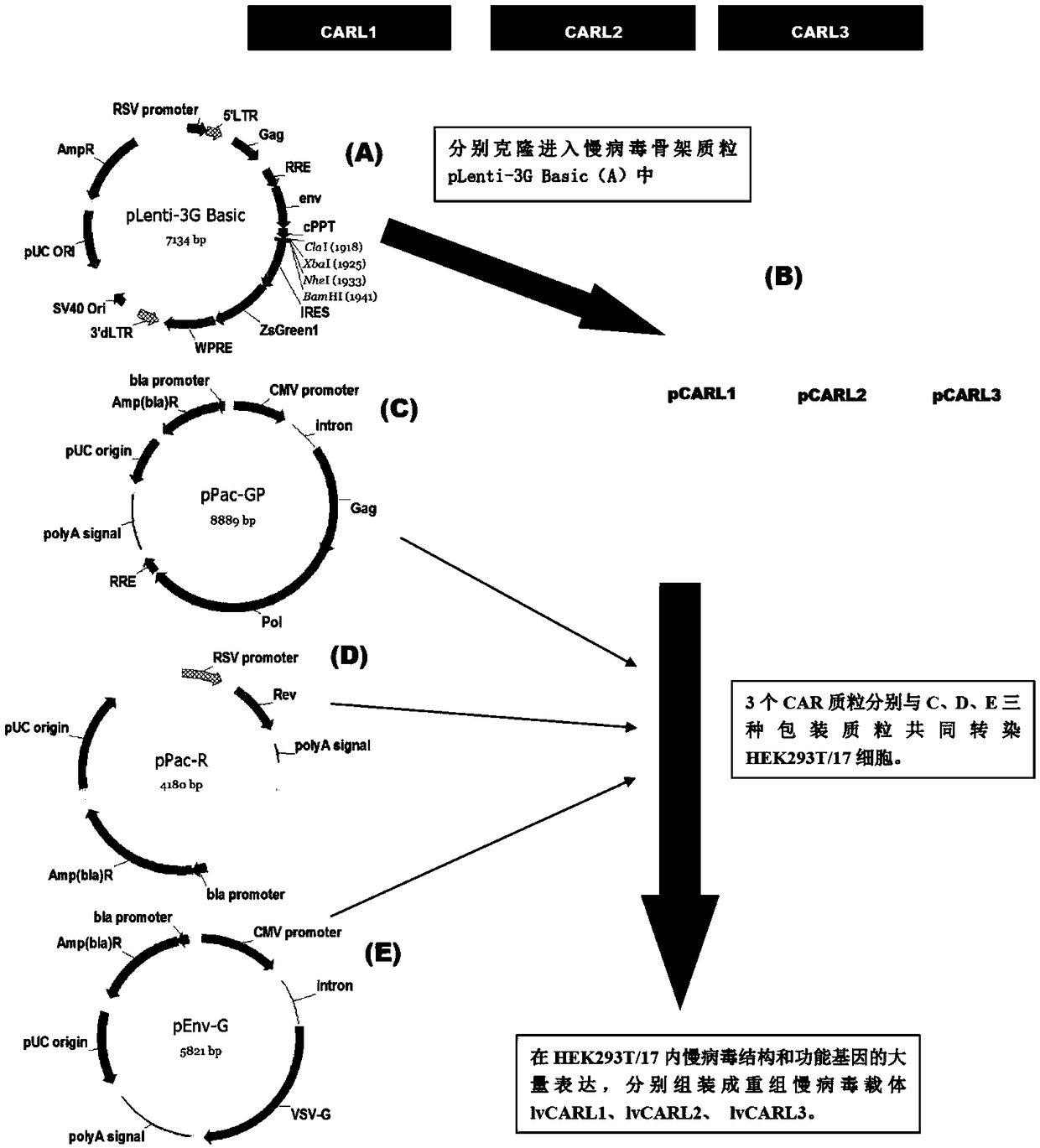
[0093] 1. Construction, purification and detection methods of recombinant lentiviral vectors lvCARL1-lvCARL3.
[0094] see image 3 , the construction method of the recombinant lentiviral vector of the present invention is as follows:
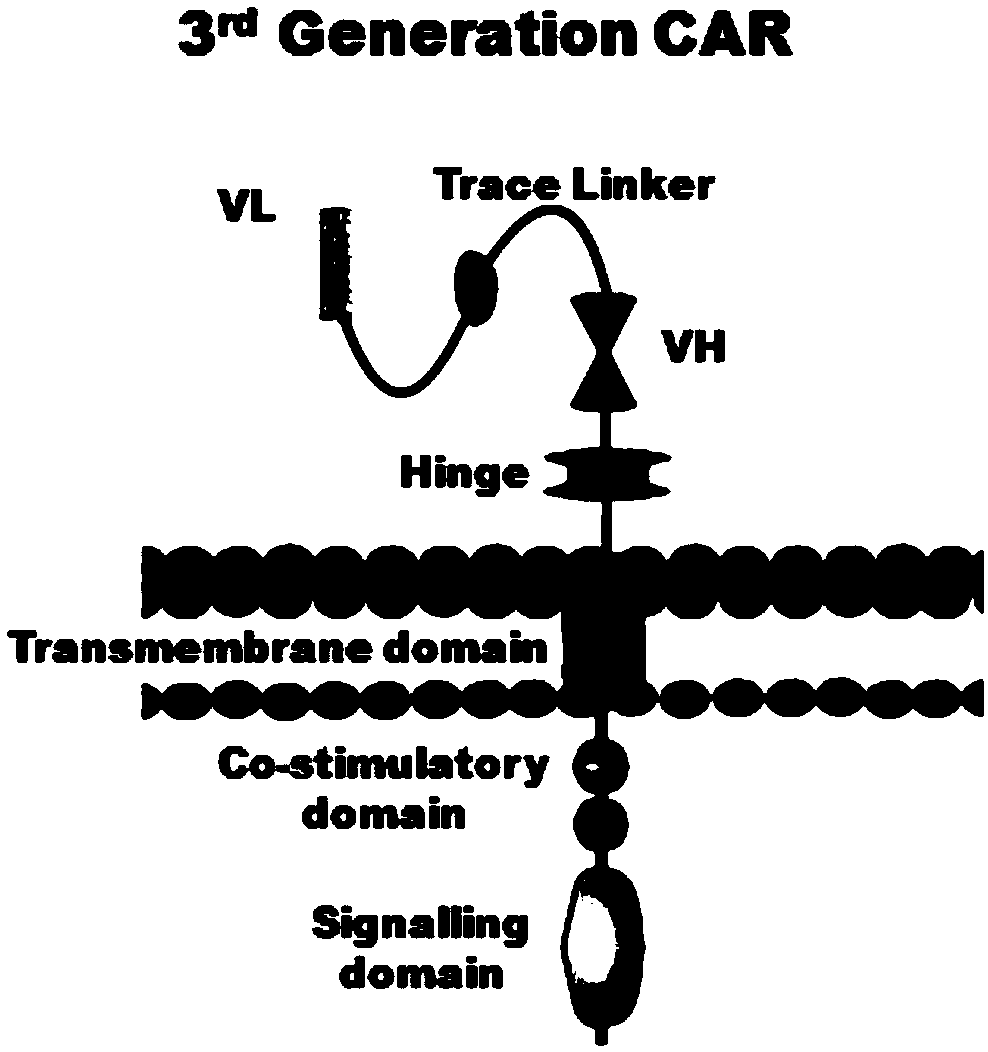
[0095] 1. Human EF1α promoter, CAR structure [CARL1, CARL2, CARL3] (CARL1, CARL2, CARL3 are the tracer hinge Trace-Linker1 containing the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.18 respectively, as shown in SEQ ID NO.19 The traced hinge Trace-Linker2 of sequence shown, the CAR sequence of traced hinge Trace-Linker3 of sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.20, such as Figure 4 shown), cloned into lentiviral backbone plasmid pLenti-3G basic, and obtained recombinant lentiviral plasmids pCARL1-pCARL3 respectively.
[0096] (1) The lentiviral backbone plasmid pLenti-3G basic was double-digested with Cla I and EcoR I restriction endonucleases, and the product was subjected to 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis to confi...
Embodiment 2
[0202] Pathogen detection and expression detection of CARL1-T~CARL3-T cells.
[0203] 1. Endotoxin detection;
[0204] (1), endotoxin working standard is 15EU / branch;
[0205] (2), Limulus reagent sensitivity λ=0.25EU / ml, 0.5ml / tube
[0206] (3) Dilution of endotoxin standard substance: Take one endotoxin standard substance, dilute it with BET water in proportion to dissolve into 4λ and 2λ respectively, seal with parafilm, shake and dissolve for 15min; each step of dilution should be mixed in the vortex Mix on the mixer for 30s;
[0207] (4) Adding samples: Take several LAL reagents, add 0.5 ml of BET water to each tube to dissolve, and distribute to several endotoxin-free test tubes, each tube has 0.1 ml. Two of them are negative control tubes, add 0.1ml of BET water;
[0208] Two are positive control tubes, add 0.1ml of endotoxin working standard solution with 2λ concentration;
[0209] 2 tubes are sample positive control tubes, add 0.1ml sample solution containing 2λ e...
Embodiment 3
[0239] Example 3 Functional detection of CARL1-T~CARL3-T cells.
[0240] 1. Evaluation of target cell killing effect.
[0241] (1) Culture target cells separately [CD117 + K562, K562 cells] and effector cells [CARL1-T~CARL3-T cells];
[0242] (2) Collect target cells 4x10 5 cells and CARL1-T~CARL3-T cells 2.8x10 6 cells, 800g, centrifuge for 6min, discard the supernatant;
[0243] (3) Resuspend the target cells and effector cells in 1ml D-PBS(-) solution, centrifuge at 800g for 6min, discard the supernatant;
[0244] (4) Repeat step 3 once;
[0245] (5) Resuspend effector cells with 700ul medium (AIM-V medium + 1-10% FBS), and resuspend target cells with 2ml medium (AIM-V medium + 1-10% FBS);
[0246] (6) Set up experimental wells with effect-to-target ratios of 1:1, 5:1, and 10:1, and set up a control group (K562 cells), with 3 replicate wells in each group;
[0247] (7) 250g, 5min plate centrifugation;
[0248] (8) Cultivate for 4 hours in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37°C;...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com